Purpose
The basic Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control system used on all vehicles is the charcoal canister storage method. This method transfers fuel vapor from the fuel tank to an activated carbon (charcoal) storage device (canister) to hold the vapors when the vehicle is not operating. When the engine is running, the fuel vapor is purged from the carbon element by intake air flow and consumed in the normal combustion process.
Operation
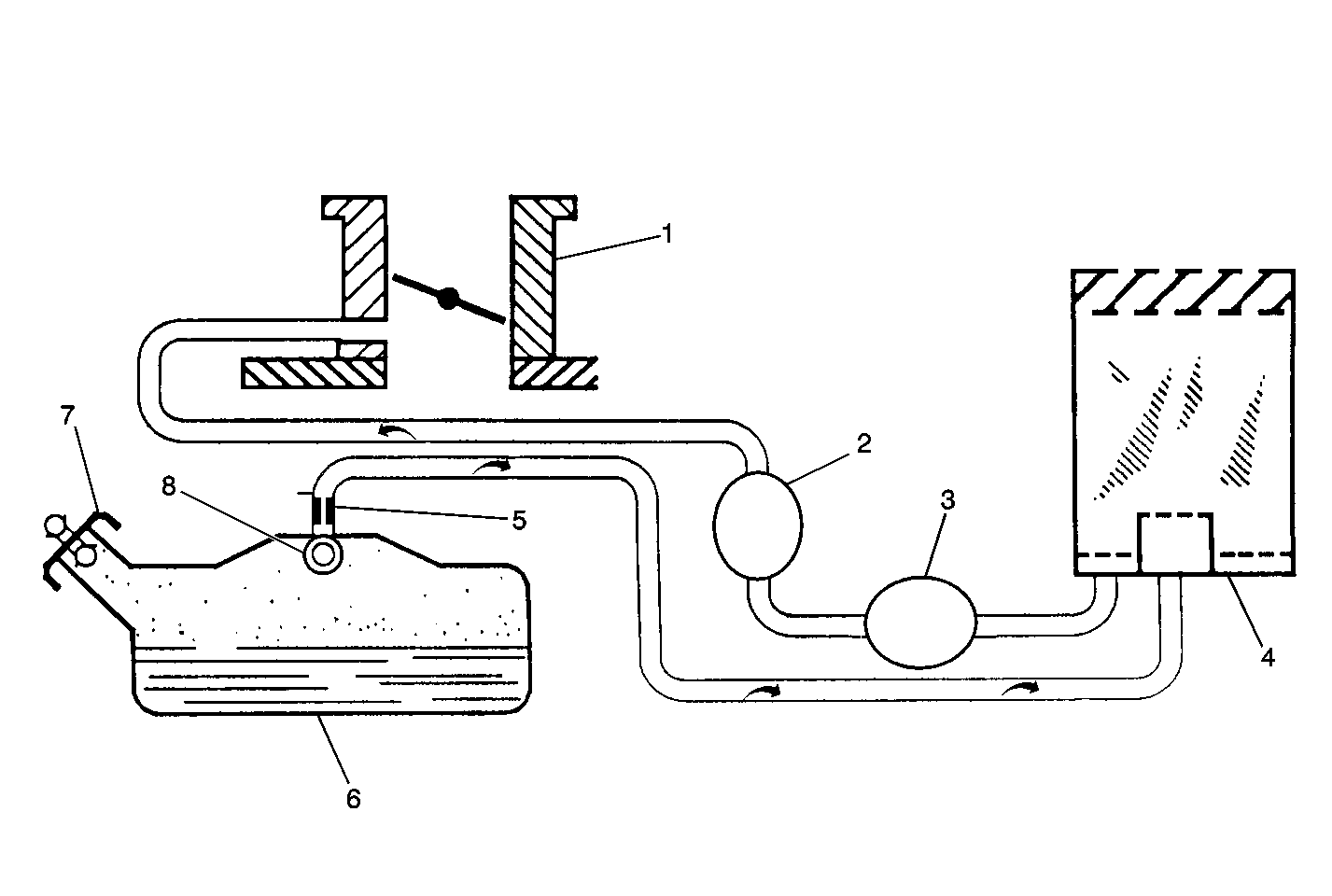
The EVAP purge solenoid valve allows manifold vacuum to purge the canister. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) supplies a ground to energize the EVAP purge solenoid valve (purge ON). The EVAP purge solenoid control is Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) or turned ON and OFF several times a second. The PCM controlled PWM output is commanded when the appropriate conditions have been met:
| • | Engine coolant temperature above 69°C (156°F). |
| • | After the engine has been running about 65 seconds on a cold or warm start. |
| • | The vehicle is operating in closed loop fuel control. |
Canister purge PWM duty cycle varies according to operating conditions determined by mass air flow, fuel trim, and. intake air temperature. Canister purge will be disabled if TP angle increases to above 45%. Canister purge will be re-enabled when TP angle decreases below 43%.
The EVAP vacuum switch is a normally closed switch positioned in the purge line between the canister and the EVAP purge solenoid. The EVAP vacuum switch will open when vacuum increases to greater than 5 inches of water in the purge line. The EVAP vacuum switch is used by the PCM to monitor EVAP canister purge solenoid operation and purge system integrity. The EVAP vacuum switch should be closed to ground with no vacuum present (0% EVAP Purge PWM). With EVAP Purge PWM at 25% or greater, the EVAP vacuum switch should open.
Results of Incorrect Purge Operation
Poor idle, stalling and poor driveability can be caused by:
| • | Malfunctioning purge solenoid. |
| • | Damaged canister. |
| • | Hoses split, cracked and/or not connected properly. |
Visual Check of Evaporative Emission Canister
Inspect the Evaporative Emission Canister for the following condition(s):
| • | Cracked or damaged -- Replace the canister. |
| • | Fuel leaking from the canister -- Replace the canister and check routing and condition of emission hoses. |
Canister Purge Solenoid and EVAP Vacuum Switch
An incorrect EVAP purge system flow should set a DTC P0441.
A continuous purge condition with no purge commanded by the PCM should set a DTC P1441.
A fault in the EVAP vacuum switch circuit should set a DTC P1442. Refer to the DTC charts for further information.
