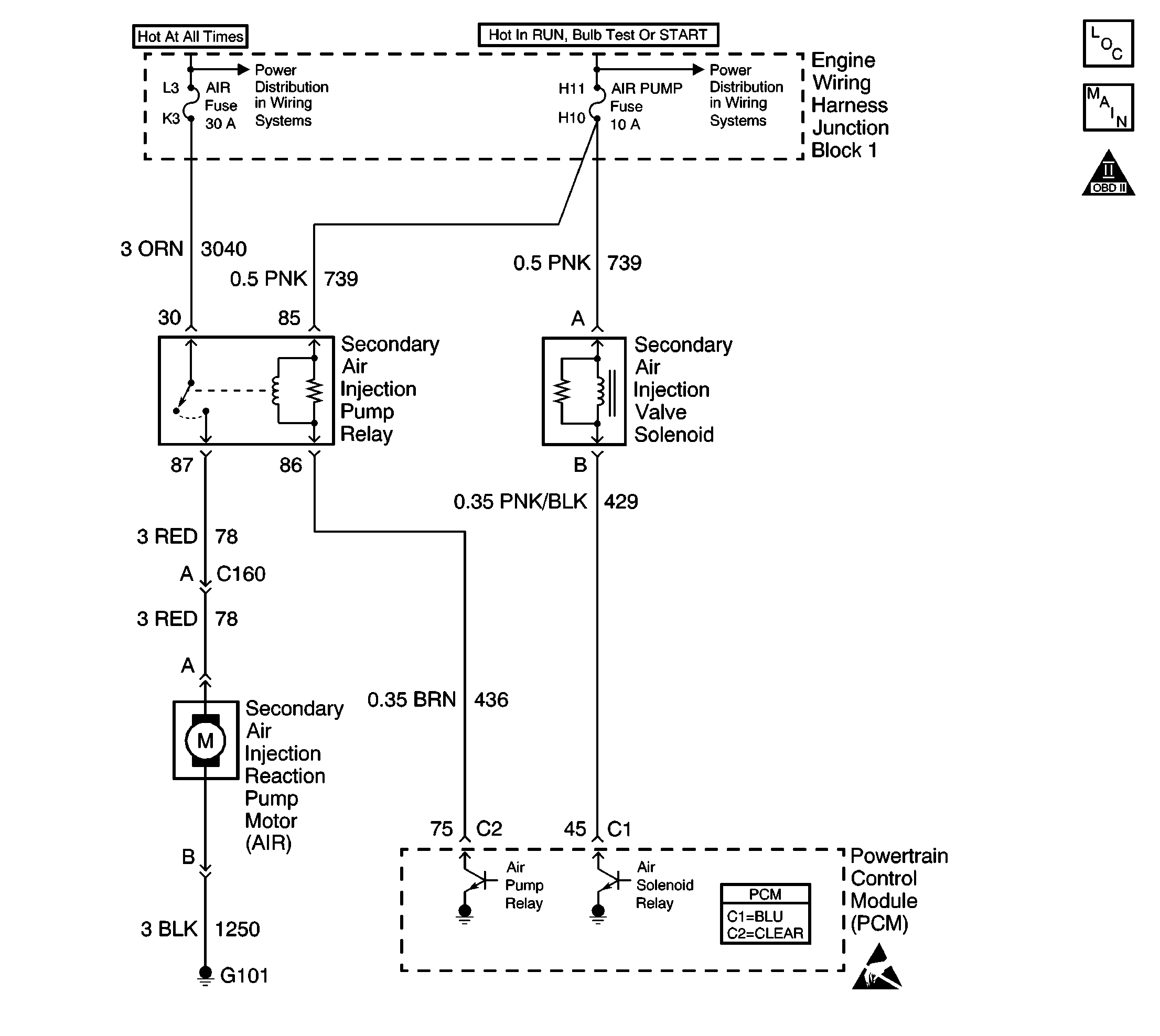
Circuit Description
An AIR pump is used on this vehicle to lower tail pipe emissions on start-up. The PCM grounds the AIR pump relay control circuit, which energizes the AIR pump. The PCM also grounds the AIR solenoid valve, which allows vacuum to AIR solenoid valves. The PCM enables both control circuits when AIR system operation is desired. When the AIR system is active, the AIR pump forces fresh air into the exhaust stream in order to accelerate catalyst operation. When the AIR system is inactive, the AIR solenoid valves prevent air flow in either direction. DTC P0412 applies to the AIR solenoid control circuit. DTC P0418 applies to the AIR pump relay control circuit. DTC P0410 sets if an air flow problem is detected.
DTC P0410 consists of Passive and Active Tests. The Passive test is executed after the engine is started, and consists of two parts (Passive Test 1 and Passive Test 2).
The passive test consists of the following:
Passive Test 1
When the AIR system is enabled, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltage. If the HO2S voltage goes below a threshold, the PCM interprets this as an indication that the AIR system is operational.
Passive Test 2
When the AIR system is disabled, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltage. The HO2S voltage should increase above a threshold and switch normally.
If both of these tests indicate a pass, no further action is taken. If one of the above tests failed or is inconclusive, the diagnostic will proceed to the Active Test.
The Active Test is performed specifically for diagnostic purposes, and consists of the following:
Active Test
During this test the PCM turns the AIR system on during closed loop operation. When the AIR system is activated, the PCM monitors the HO2S 1 voltage and ST Fuel Trim. If the AIR system is operating properly, the HO2S 1 voltage should go below a predetermined threshold. The Active Test may run up to 4 times before failing.
Conditions for AIR System Operation
| • | PCM must have accumulated at least 10 Miles. |
| • | ECT between 4.5°C (40.1°F) and 30°C (86°F) |
| • | IAT greater than 4.5°C (40.1°F) |
| • | IAT Less than 70°C (158°F) |
| • | BARO greater than 75 kPa |
| • | MAF less than 40 gm/s |
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs P0101, P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0300, P0412, P0418, P0442, P0443, P1441 and HO2S DTCs not set.
Passive Test
| • | Engine is running |
| • | TP sensor steady |
| • | Engine load is less than 80 percent |
| • | Engine air flow is less than 35 g/s |
| • | Ignition voltage is greater than 11.0 volts |
| • | Air fuel ratio is greater than 11.5:1 |
| • | Start up ECT is less than 30°C (86°F) |
| • | IAT is greater than 4.5°C (40.1°F) |
| • | The AIR system is enabled for up to 70 seconds |
| • | Passive Test fails if: |
| • | HO2S1 voltage does not fall below a voltage threshold for a calibrated amount of time. (Passive Test 1) |
| • | HO2S1 voltage does not rise above a voltage threshold for a calibrated amount of time after the pump is turned off. (Passive Test 2) |
Active Test
| • | The engine operates for greater than 5 minutes. |
| • | Manifold vacuum is greater than 45 kPa. |
| • | Vehicle is not in Park/Neutral. |
| • | Engine speed is greater than 900 RPM. |
| • | Air flow is less than 15 g/s. |
| • | ECT is greater than 75°C (167°F). |
| • | Accumulate 40 seconds of time in Fuel Trim Cell 2 (steady state cruise) with EVAP Purge active. |
| • | Ignition voltage is greater than 11.0 volts. |
| • | Fuel system operating in Closed Loop. |
| • | Active Test fails if the HO2S 1 voltage does not fall below a voltage threshold for a calibrated amount of time. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
If a total of 4 Active and/or Passive Test failures, P0410 is set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
The following may cause an intermittent:
Many situations may lead to an intermittent condition. Perform each inspection or test as directed.
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Loose terminal connection |
| - | Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| - | Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Inspect the powertrain control module (PCM) and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
If the condition is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Snapshot or Freeze Frame/Failure Records may be useful in determining when the DTC or condition was identified.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
DTC P0412 AIR Solenoid Valve Control Circuit and P0418 AIR Pump Relay Control Circuit should be diagnosed first if either are set.
-
Begins testing for a short to ground in the AIR pump feed circuit.
-
Listen for a running motor. Command both the ON and OFF states. Repeat the commands as necessary.
-
Begins testing for a short to voltage in the pump feed circuit.
-
Tests for voltage at the AIR pump relay switch feed circuit.
-
Bypasses the relay.
-
Tests for voltage on the AIR pump feed circuit.
-
Tests for an open on the pump ground circuit.
-
The AIR Pump is not designed to run continuously. If the pump needs to be replaced, inspect for conditions that may cause continuous pump operation.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||
Are DTCs P0412 or P0418 set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | ||||||
Is the AIR pump relay switch feed fuse OK? | -- | |||||||
With a scan tool, command the AIR pump ON and OFF. Does the AIR pump turn ON and OFF with each command? | -- | |||||||
Does the AIR pump run continuously? | -- | |||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||||||
With a fused jumper wire, jumper the relay switch feed circuit to the AIR pump feed circuit. Does the AIR pump operate? | -- | |||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||||||
Connect a test lamp between the feed circuit of the pump and the ground circuit of the pump. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||||||
10 |
Is air flow present at the AIR pump outlet? | -- | ||||||
11 |
Is air flow present at the AIR hose/pipe outlet? | -- | ||||||
12 | Visually inspect the following:
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||
13 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||
14 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||
15 |
Does the fuse open? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||
16 | Disconnect the AIR pump relay. Is the pump still running? | -- | ||||||
17 | Repair the open relay switch feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
18 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||
19 | Repair the open/high resistance in the AIR pump ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
20 | Repair the short to ground in the relay switch feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
21 | Repair the short to ground in the AIR pump feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
22 | Visually inspect the following and repair as necessary:
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
23 | Repair the vacuum system as necessary. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
24 | Repair the short to voltage in the AIR pump feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
25 | Replace the AIR pump relay. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
26 | Replace the AIR combination valve. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
27 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||
Replace the AIR pump. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||
29 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||
30 | With a scan tool, review Captured Info. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table
| System OK |
