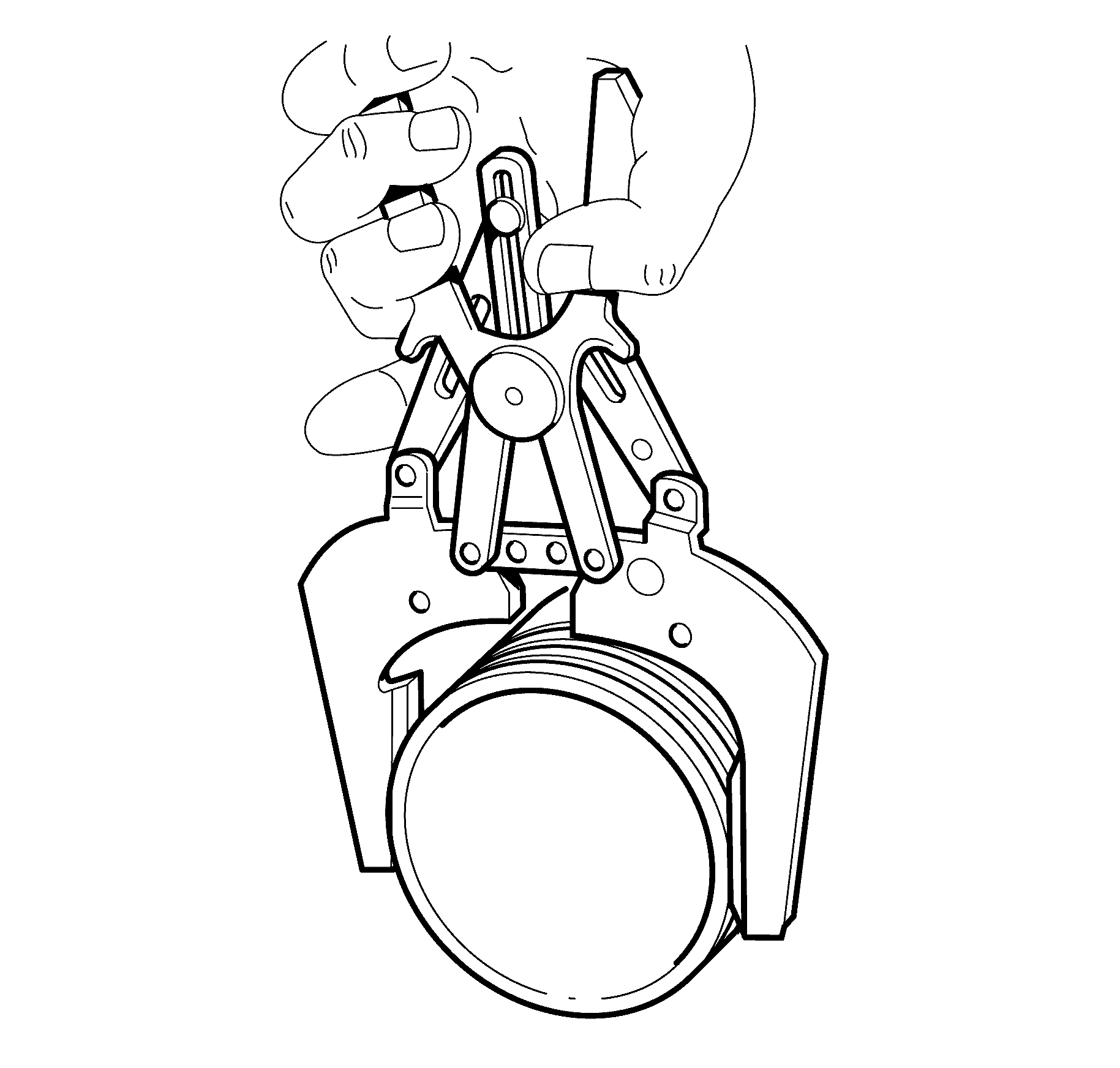Piston, Pin, and Piston Rings
Caution: Refer to Safety Glasses Caution in the Preface section.
Important:
| • | Replace pistons, pins, and connecting rods that are damaged or show signs
of above acceptable wear. |
| • | The piston and pin are to be serviced as an assembly. |
| • | Do not wire brush any part of the piston. |
| • | Measurement of the components should be taken with the components at normal
room temperature. |
- Clean the varnish and carbon from the piston using cleaning solvent.
- Dry the components with compressed air.
- Clean the piston ring grooves with a suitable ring
groove cleaning tool.
- Clean the oil lubrication holes and slots.
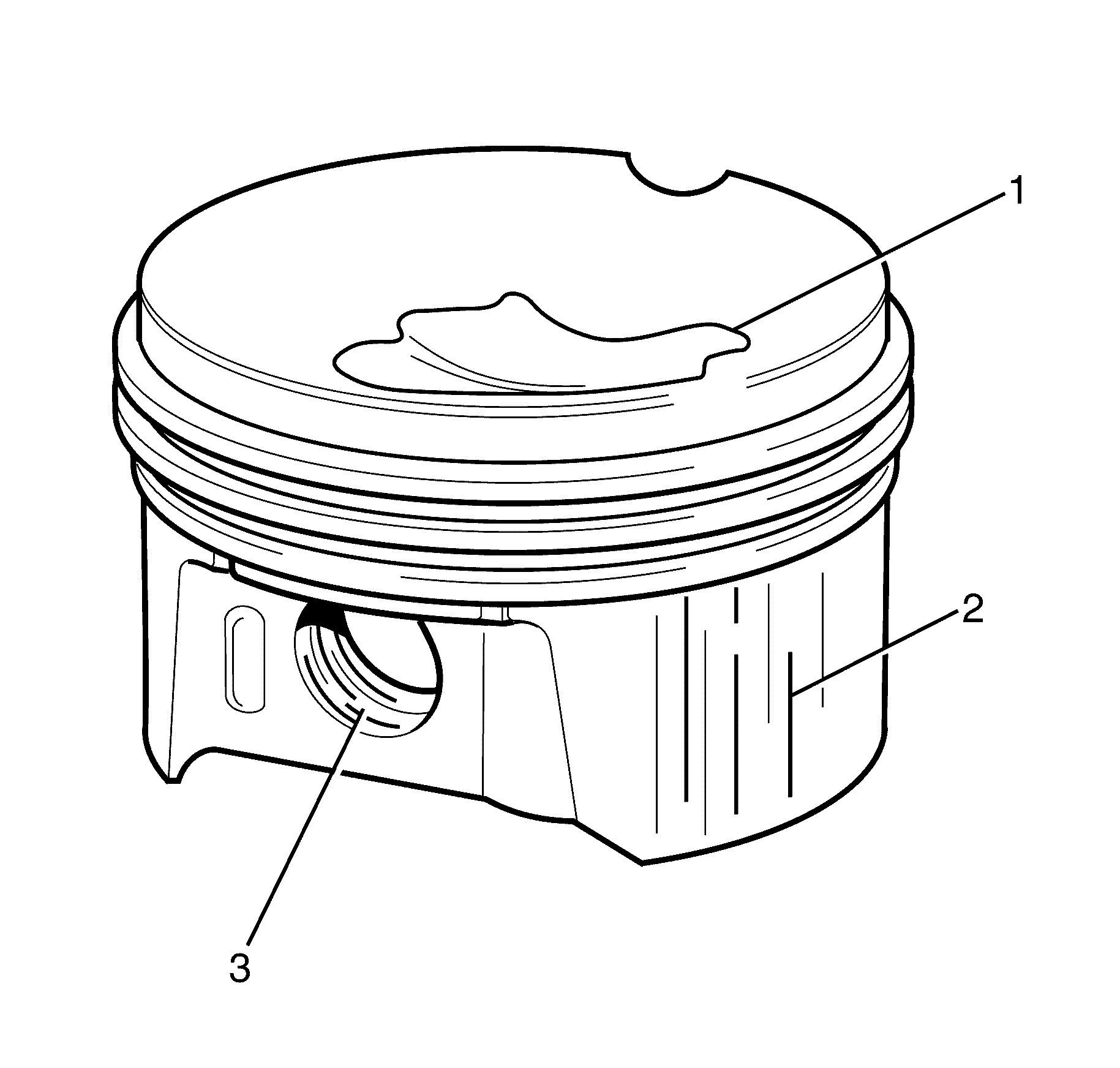
- Inspect the piston for the following conditions and
replace as necessary:
| • | Cracks in the piston ring lands, the piston skirt, or pin bosses. |
| • | Piston ring grooves for nicks, burrs, or warpage which may cause the piston
ring to bind. |
| • | MINOR imperfections may be removed from the piston with
a fine file. |
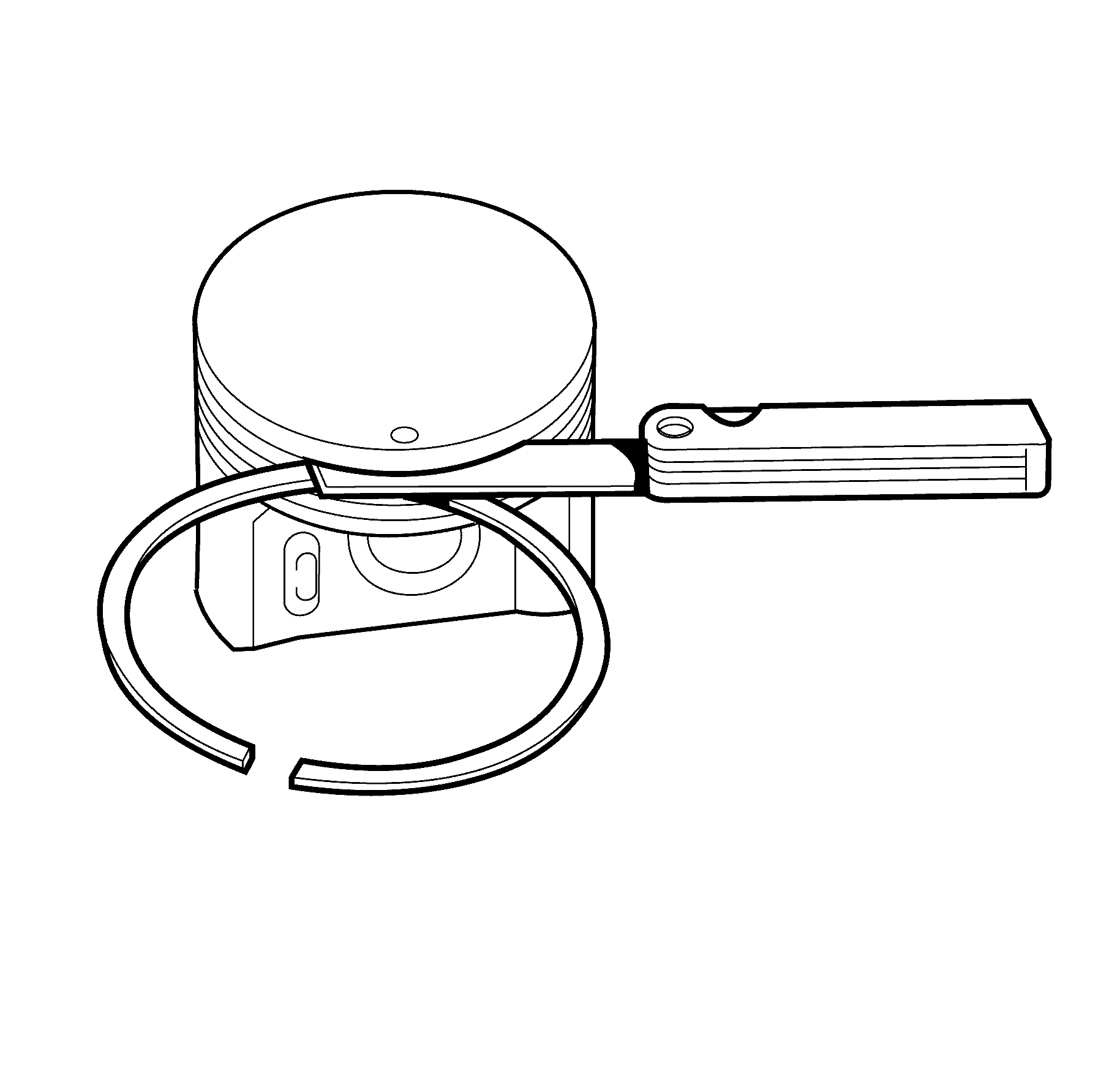
| • | Scuffed or damaged skirts (2). |
| • | Eroded areas at the top of the piston (1). |
| • | Scoring to the full-floating design piston pin bore (3) or piston
pin. |
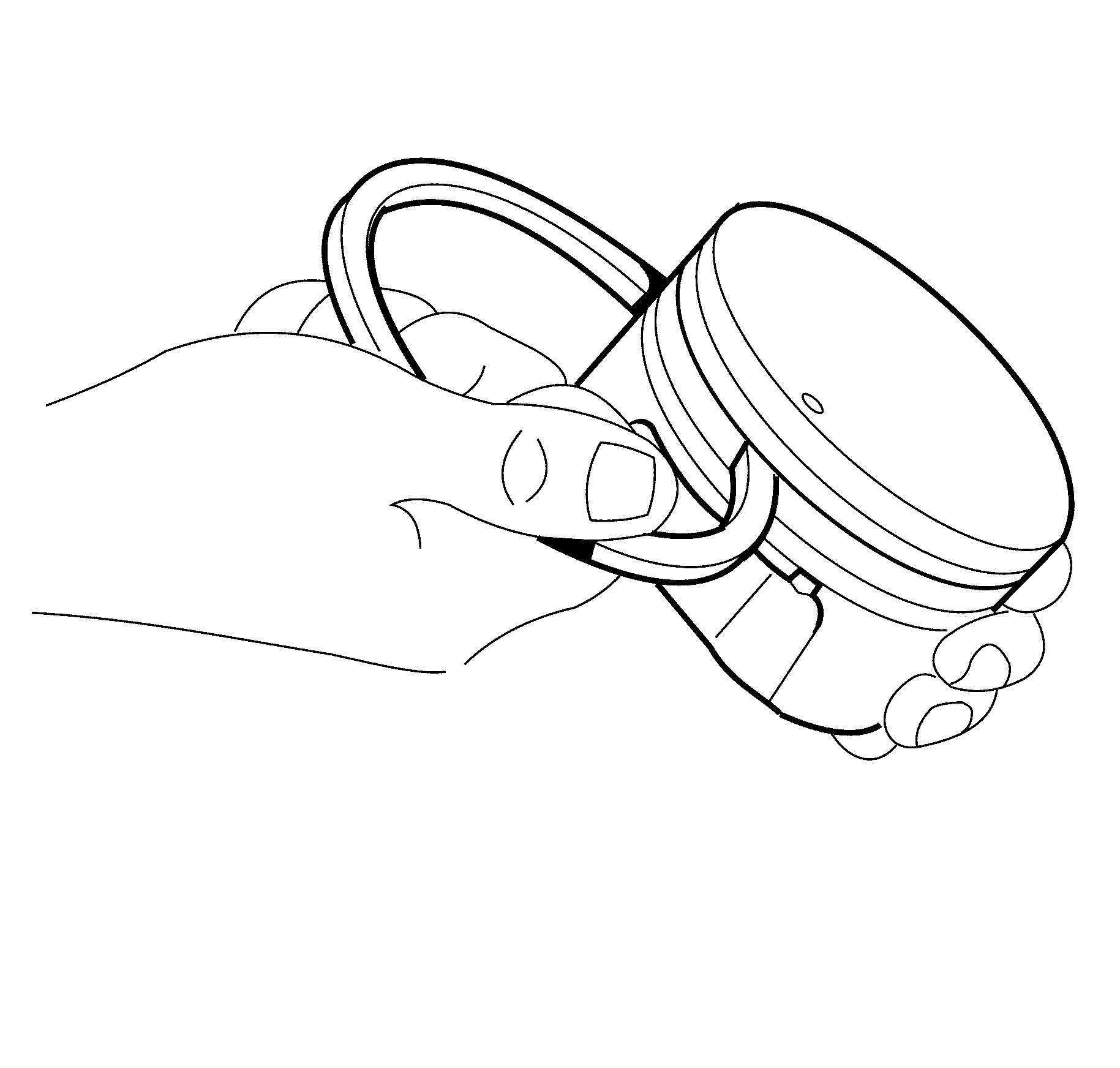
- Insert the edge of the piston ring into the piston
ring groove.
Roll the piston ring completely around the piston. If binding
is caused by distorted ring groove, MINOR imperfections may be removed with a fine
file. If binding is caused by a distorted piston ring, replace the rings, as required.
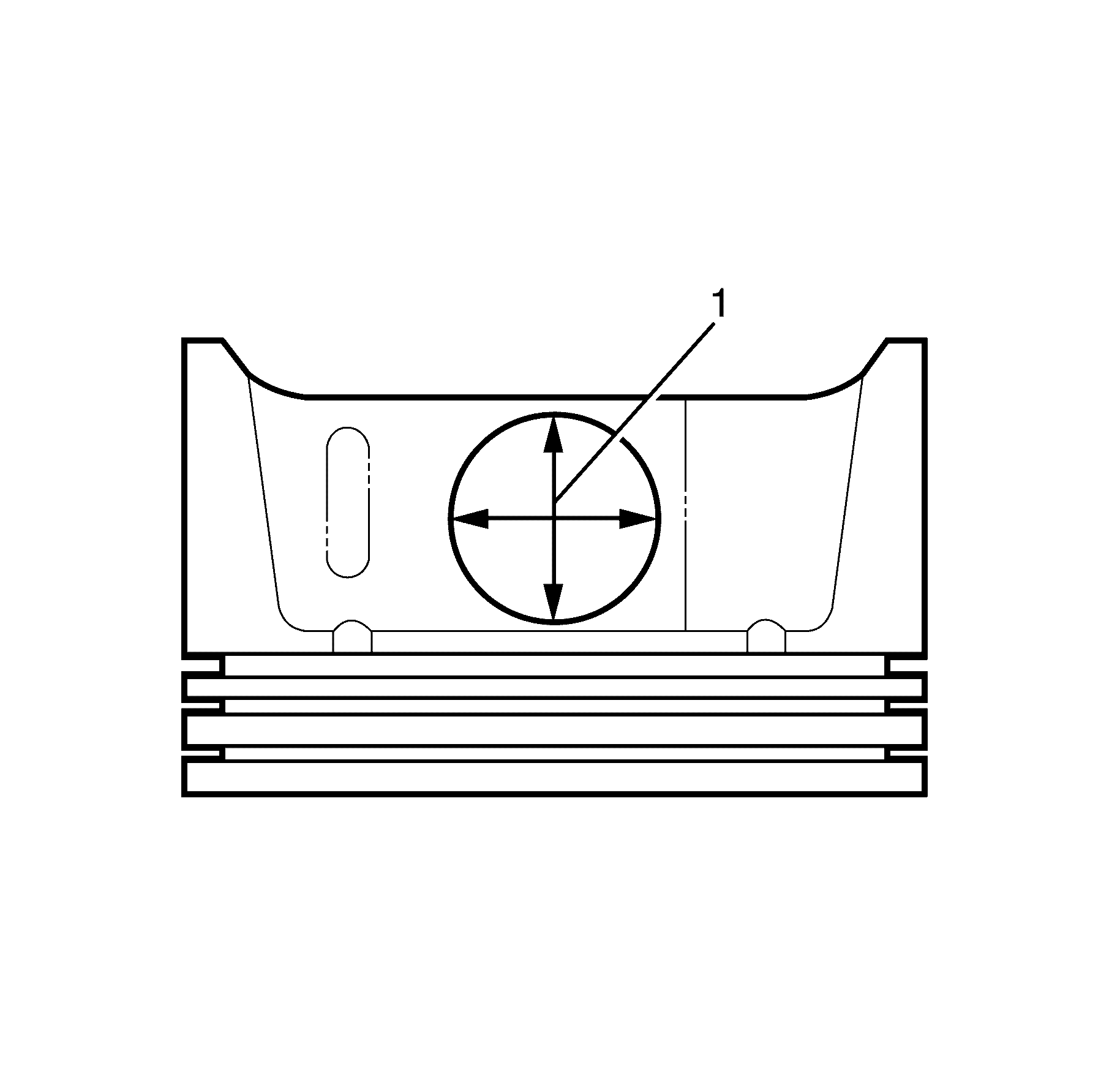
- Measure the piston ring side clearance with a feeler
gauge. If side clearance is not within specifications, try another piston ring. If
the correct ring-to-groove clearance cannot be obtained, replace the piston and pin
as an assembly. Refer to
Engine Mechanical Specifications.
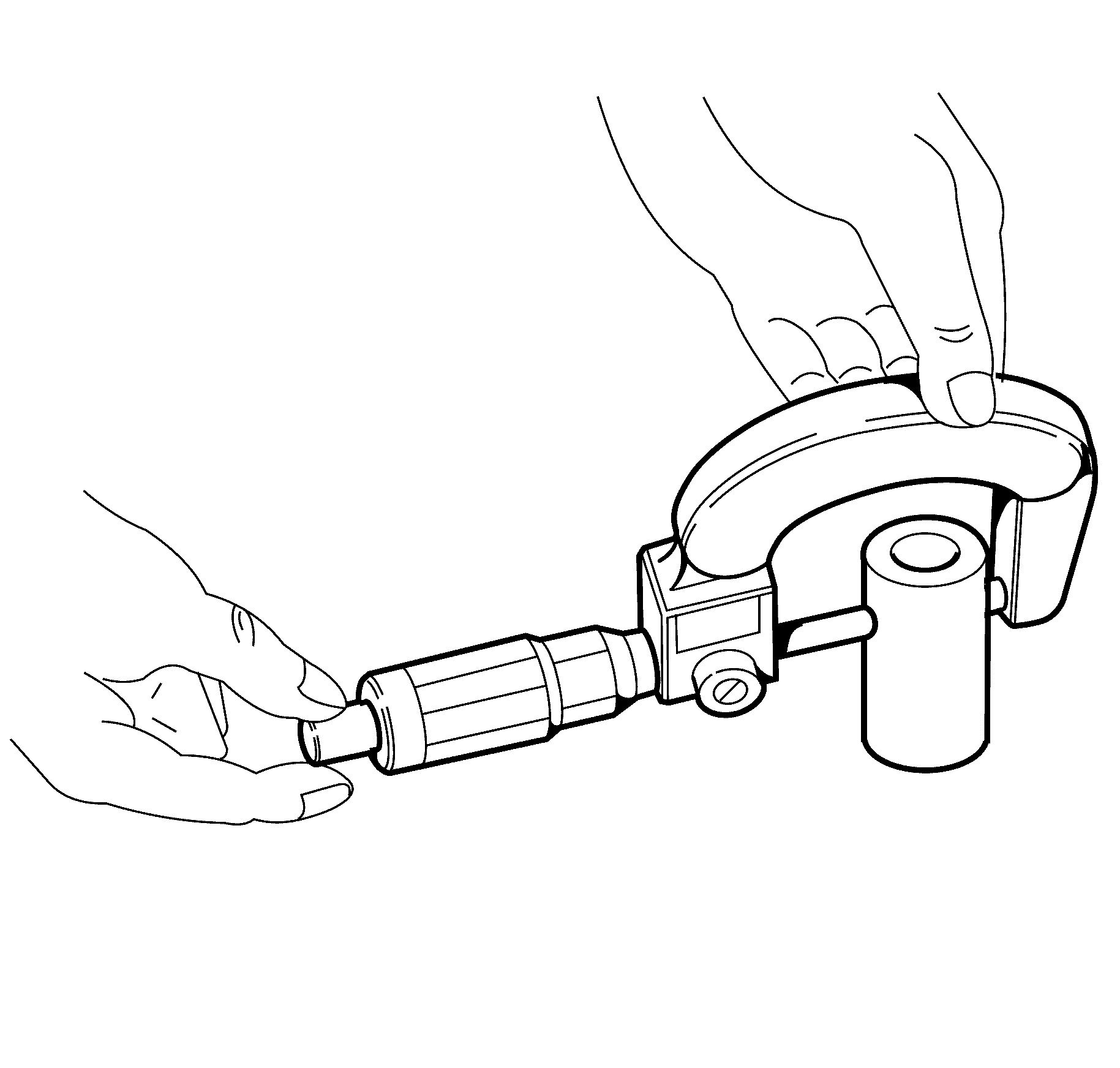
- To determine piston pin-to-bore clearance, use a micrometer
and measure the piston pin outside diameter (OD).
- To determine the piston pin-to-bore clearance, use
an inside micrometer and measure the piston pin bore inside diameter (ID).
- Subtract the piston pin OD measurement from the piston pin bore ID measurement
to determine pin-to-bore clearance. Refer to
Engine Mechanical Specifications.
Measuring Piston Ring End Gap
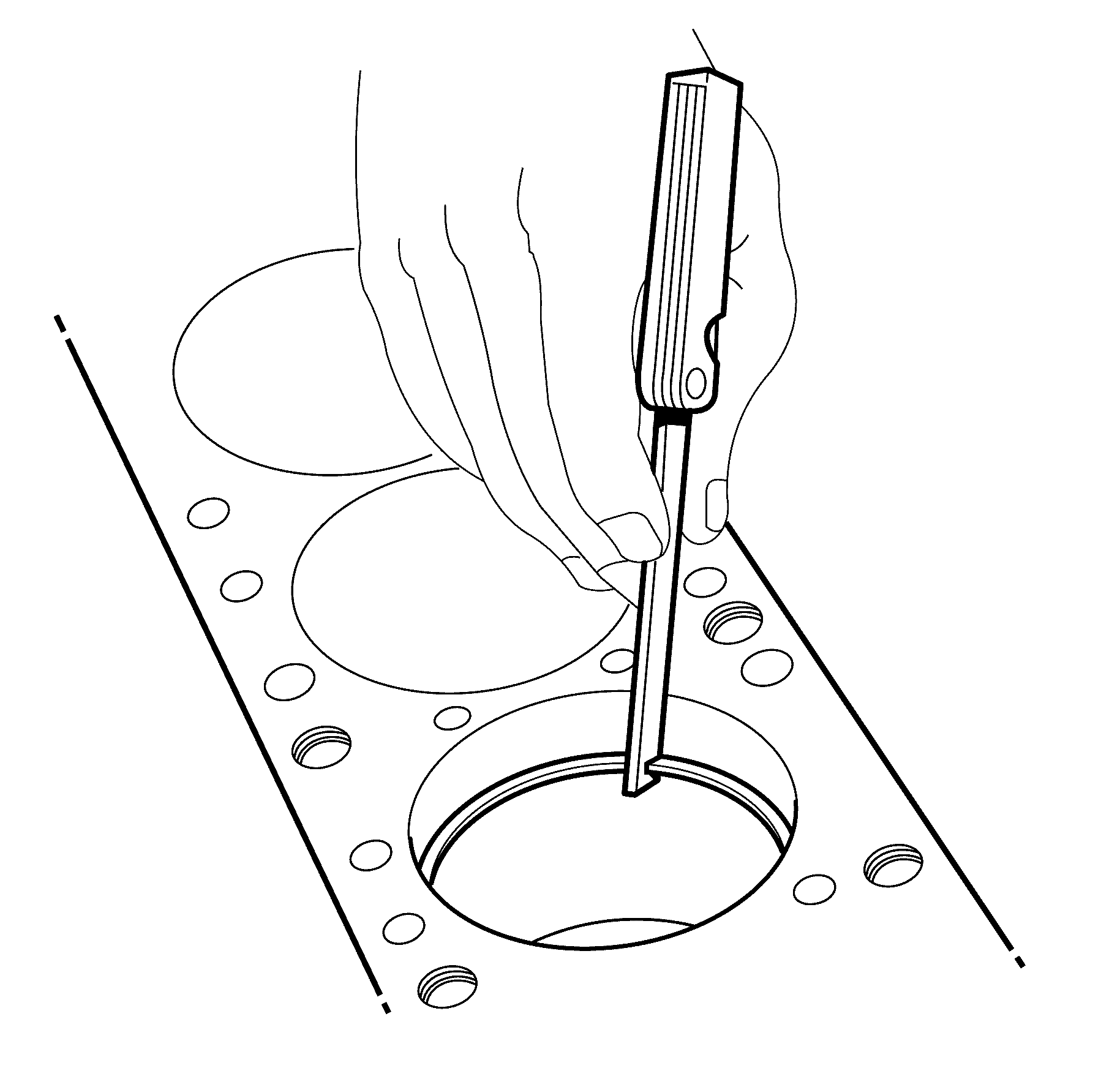
Important:
| • | Do not attempt to file the end of the piston ring to achieve the correct
end gap clearance. |
| • | Measure the piston ring in the cylinder in which it will be used. |
- Place the piston ring into the cylinder bore 6.5 mm (0.25 in)
below the top of the ring travel area. Both rings should be installed with the orientation
marks facing the top of the piston.
- Insert a feeler gauge and measure the piston ring end gap. Refer to
Engine Mechanical Specifications.
Connecting Rod and Bearings
Important:
| • | The powdered metal connecting rod and cap are machined for correct clearances.
The connecting rod and cap must be used as an assembly with no repair or modifications
to either mating surface. Do not attempt to repair the rod or cap. If service is required,
replace the piston and pin as an assembly. |
| • | Do not attempt to repair the bolt hole threads of the connecting rod. |
- Clean the connecting rod and cap in solvent.
Caution: Refer to Safety Glasses Caution in the Preface section.
- Dry the components with compressed air.
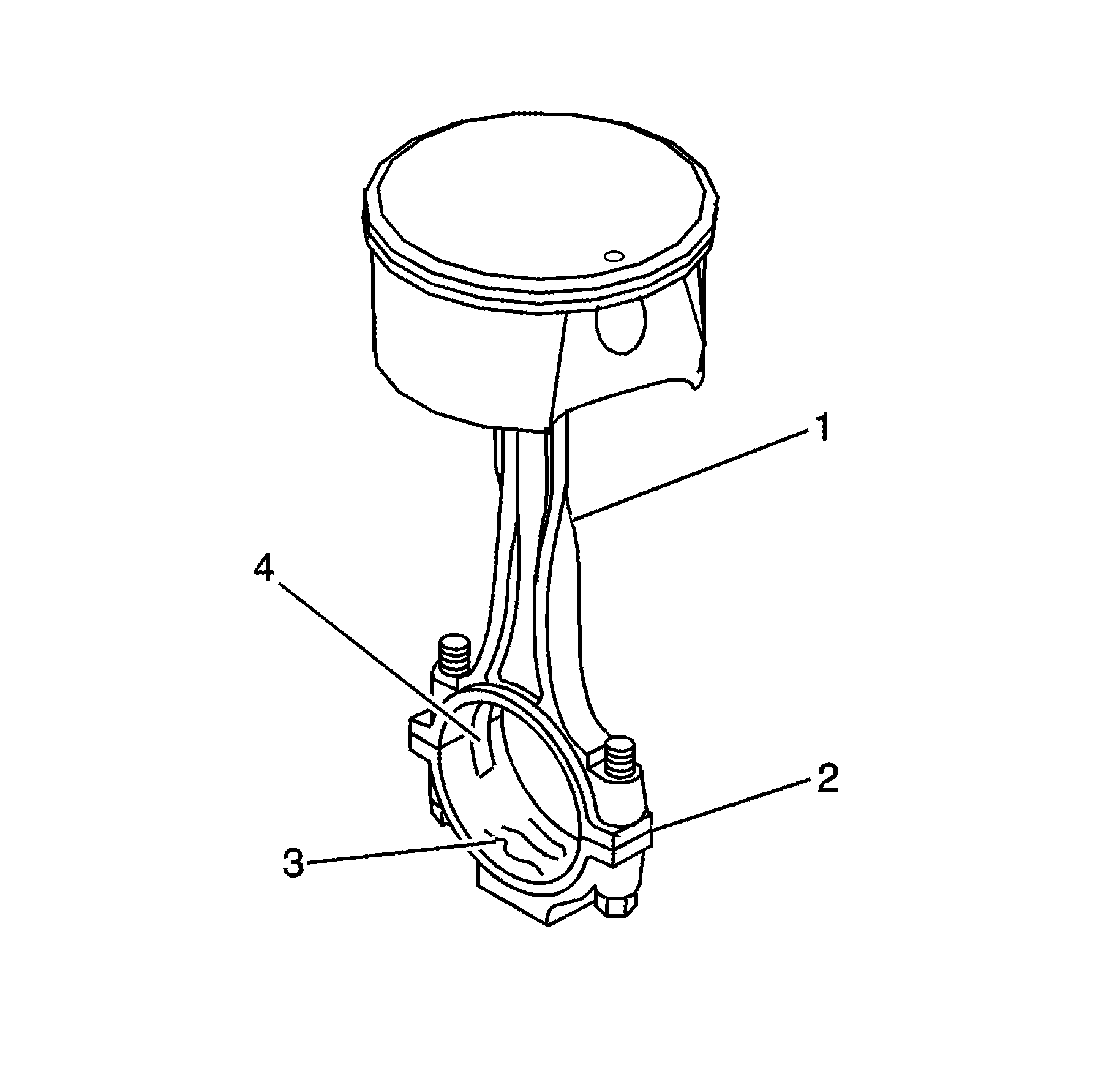
- Inspect the connecting rod for the following conditions:
| • | Correct fit of the connecting rod and cap mating surfaces (2) |
| • | Nicks or gouges in the bearing bore (3) |
| • | Damage to the bearing locating slots (4) |
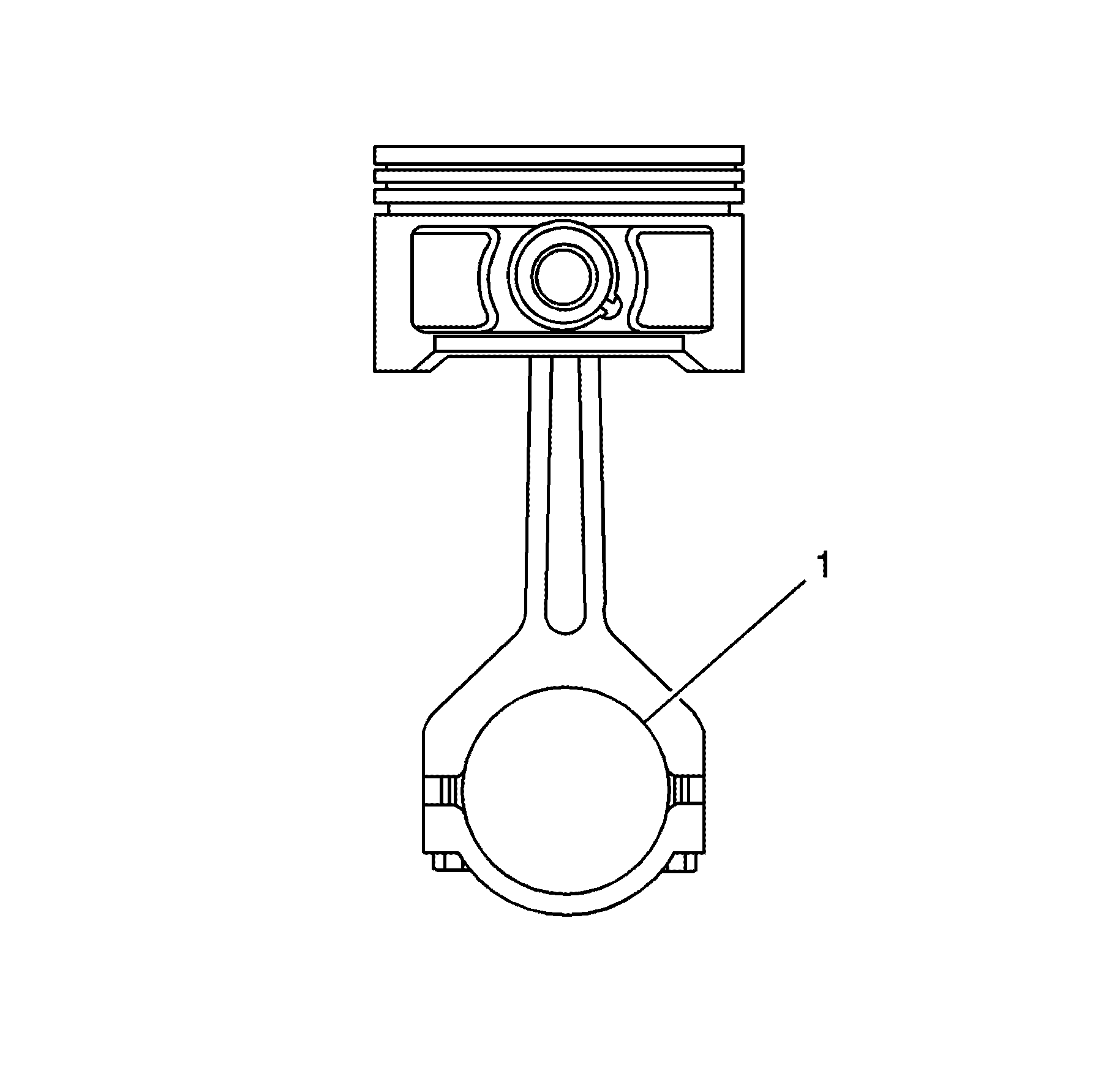
- Measure the connecting rod bearing bore (1)
for an out-of-round condition. Refer to
Engine Mechanical Specifications.

- To determine full-floating piston pin-to-connecting
rod bore clearance, use a micrometer and measure the piston pin outside diameter (OD).
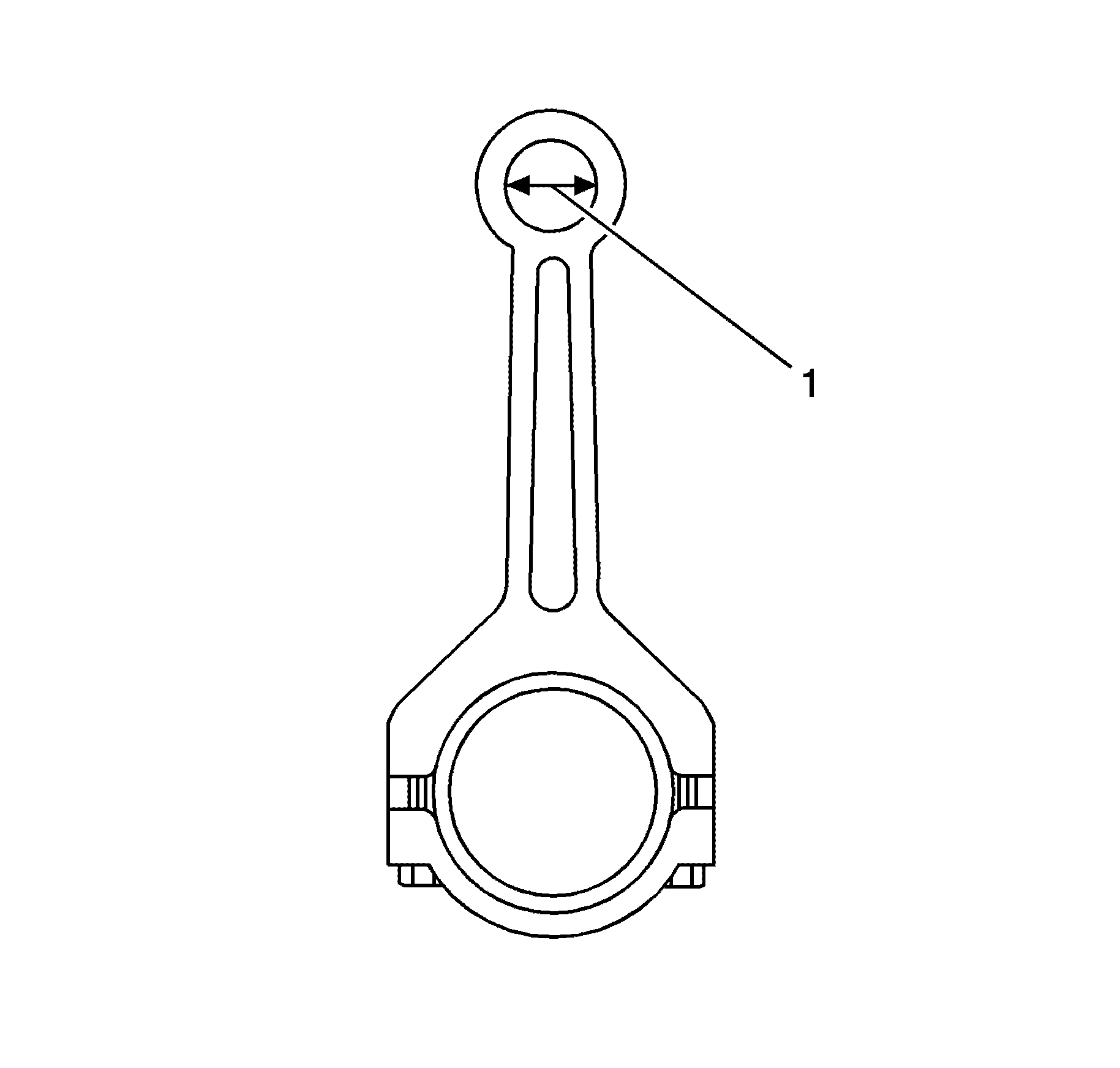
- To determine the full-floating piston pin-to-connecting
rod bore clearance, use a micrometer and measure the connecting rod pin bore (1)
inside diameter (ID).
- Subtract the piston pin OD measurement from the connecting rod pin bore
ID measurement to determine pin-to-bore clearance. Refer to
Engine Mechanical Specifications.
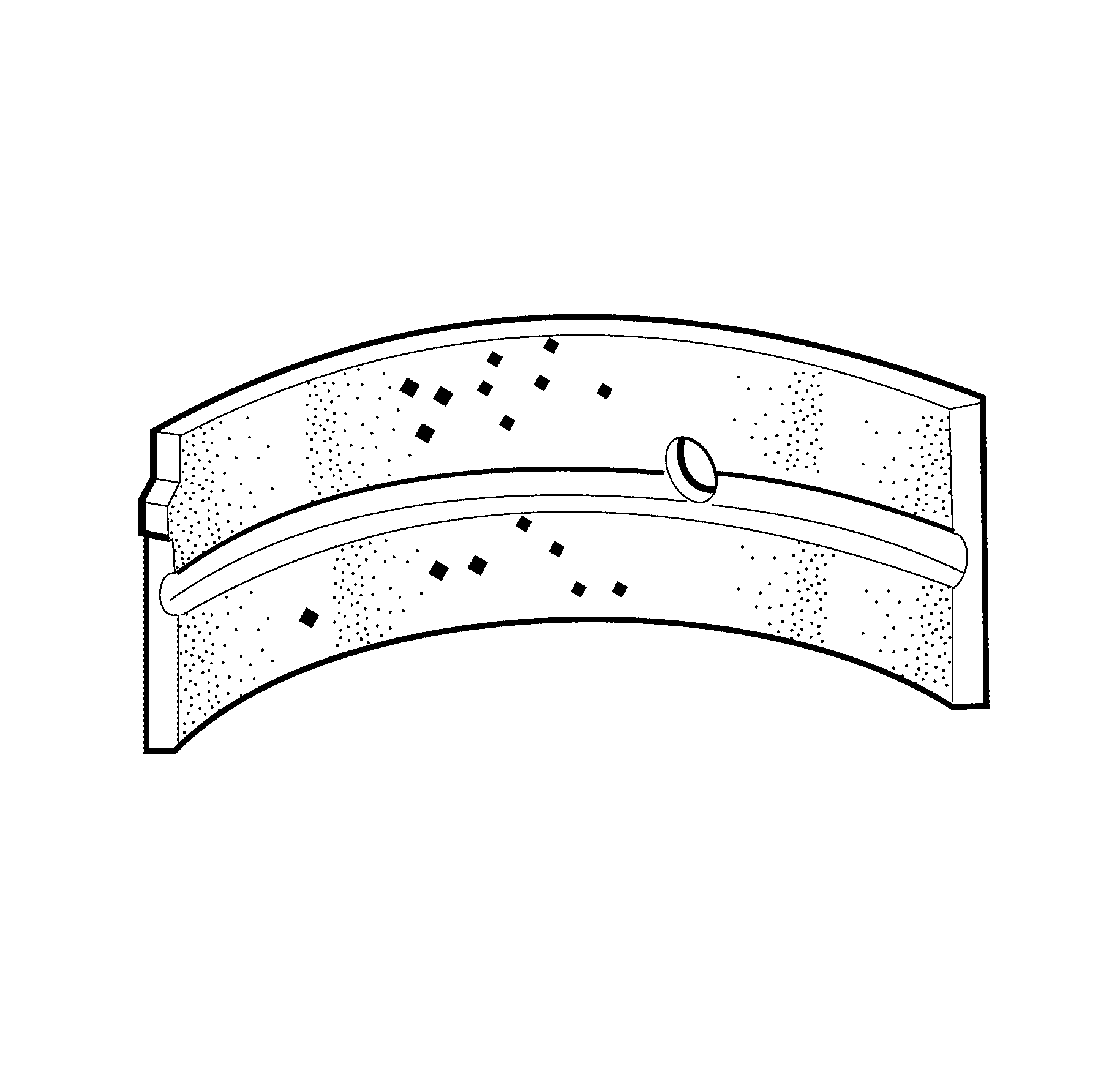
- Inspect the connecting rod bearings for craters or
pockets. Flattened sections on the bearing halves indicate fatigue.

- Inspect the connecting rod bearings for above acceptable
scoring or discoloration.
- Inspect the connecting rod bearings for dirt or debris embedded into the
bearing material.
- Inspect the connecting rod bearings for incorrect
seating indicated by bright, polished sections of the bearing surface.