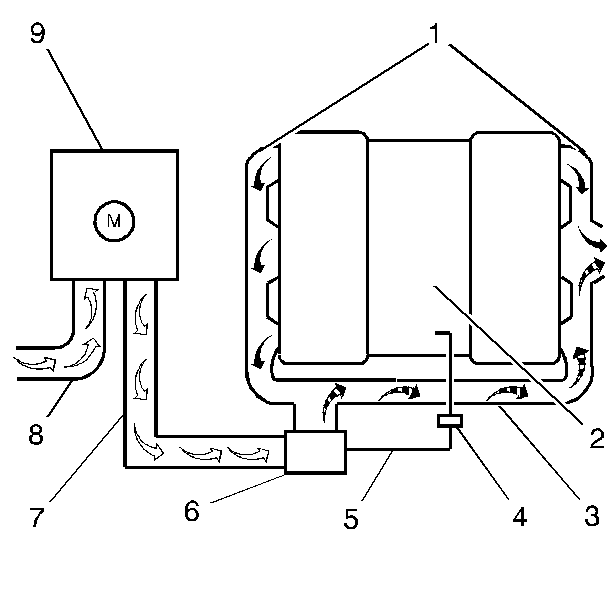
Certain vehicles may be equipped with a Secondary Air Injection
(AIR) System. This system is used to lower tail pipe emissions on start-up.
The PCM grounds the AIR pump relay control circuit, which energizes the
AIR pump. The PCM also grounds the AIR Solenoid Valve control circuit,
which energizes the AIR Solenoid Valve. The PCM enables both circuits
when AIR system operation is desired. DTC P0412 applies to the AIR solenoid
control circuit. DTC P0418 applies to the AIR pump relay control circuit.
DTC P0410 sets if an air flow problem is detected.