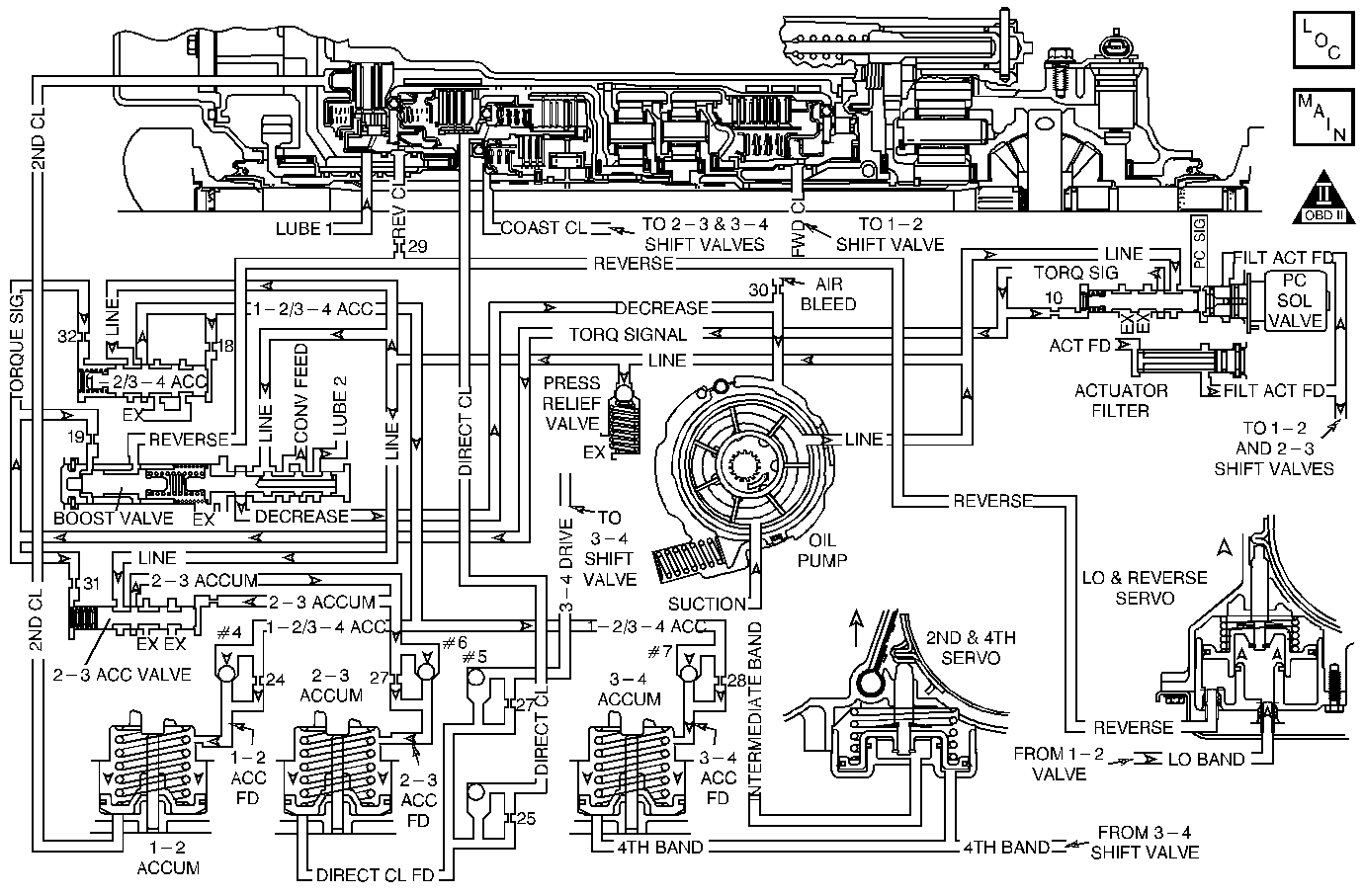
The PCM modifies the transmission line pressure through the pressure
control (PC) solenoid valve, in order to control shift execution time
and shift consistency. The PCM monitors various inputs, and modifies
the shift execution and timing by applying a calculated duty cycle
to the PC solenoid valve. The PCM alters the shifting based on driving
habits, transmission load, and internal transmission condition.
When the PCM detects long shifts that cannot be shortened by shift adapts
during the same ignition cycle, then DTC P1811 sets. DTC P1811
is a type D DTC.
The shift time is greater than 0.65 second two times during the
same ignition cycle.
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
DTC P1811 Maximum Adapt and Long Shift (2.4 L and 3.1L)
Step
| Action
| Value(s)
| Yes
| No
|
1
| Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check performed?
| --
|
Go to Step
2
| Go to
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
(2.4L) or
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
(3.1L)
|
2
| Was the Transmission Fluid Checking Procedure performed?
| --
|
Go to Step 3
| Go to
Transmission Fluid Check
|
3
|
- Install the Scan Tool
.
- Turn the ignition switch to the RUN position.
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record the Failure
Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Failure Records from the
PCM.
- Record the Failure Records.
- Clear the DTCs.
- Use the scan tool snapshot mode in order to record the shift times.
- Drive the vehicle in D4 in order to obtain 1-2, 2-3, and 3-4 shift
times.
- Record the shift times.
Did all the shift times exceed the specified value?
| 0.65 second
|
Go to Step 4
|
Go to Step 6
|
4
| Perform the Line Pressure Check Procedure.
Refer to
Line Pressure Check
.
Is the line pressure within specifications?
| --
| Go to Diagnostic Aids
|
Go to Step 5
|
5
|
- Inspect the transmission for the following conditions:
| • | Low fluid level caused by external leaks |
| • | Out-of-position fluid filter |
| • | Internal fluid passage leaks |
| • | Casting porosity or damage |
| • | Damaged gasket or spacer plate |
| • | Out-of-position gasket or spacer plate |
| • | Contaminated PC solenoid valve |
| • | Damaged PC solenoid valve |
| • | Stuck PC solenoid valve |
| • | Stuck pressure regulator valve train |
| • | Leaking pressure regulator valve train |
| • | Stuck torque signal valve train |
| • | Leaking torque signal valve train |
| • | Inadequate oil pump suction |
- Repair any of the above items as necessary.
Is the repair complete?
| --
|
Go to Step
11
| --
|
6
| Did the 1-2 shift time exceed the specified value?
| 0.65 second
|
Go to Step 9
|
Go to Step 7
|
7
| Did the
2-3 shift time exceed the specified value?
| 0.65 second
|
Go to Step 10
|
Go to Step
8
|
8
| Did the 3-4 shift time exceed the specified value?
| 0.65 second
|
Go to Step 11
| --
|
9
|
- Inspect the 1-2 shift circuit for the following conditions:
| • | Leaking 1-2 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Rolled 1-2 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Cut 1-2 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Leaking 2nd clutch piston seals |
| • | Rolled 2nd clutch piston seals |
| • | Cut 2nd clutch piston seals |
| • | Burned 2nd clutch plates |
| • | Damaged 2nd clutch plates |
| • | Broken 2nd clutch springs |
| • | Out-of-position 2nd clutch springs |
| • | Damaged 2nd clutch piston |
| • | Leaking driven sprocket support seals |
| • | Damaged driven sprocket support seals |
| • | Internal fluid passage leaks |
| • | Casting porosity or damage |
| • | Damaged gasket or spacer plate |
| • | Out-of-position gasket or spacer plate |
| • | Slipping forward clutch |
| • | Cracked or damaged driven sprocket support |
| • | Damaged sprag clutch (not holding) |
| • | 2nd roller clutch damaged (not holding) |
- Repair the 1-2 shift circuit as necessary.
Is the repair complete?
| --
|
Go to Step
12
| --
|
10
|
- Inspect the 2-3 shift circuit for the following conditions:
| • | Leaking 2-3 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Rolled 2-3 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Cut 2-3 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Leaking direct clutch piston seals |
| • | Rolled direct clutch piston seals |
| • | Cut direct clutch piston seals |
| • | Burned direct clutch plates |
| • | Damaged direct clutch plates |
| • | Broken direct clutch springs |
| • | Out-of-position direct clutch springs |
| • | Damaged direct clutch pistons |
| • | Leaking driven sprocket support seals |
| • | Damaged driven sprocket support seals |
| • | Damaged driven sprocket support |
| • | Damaged (or not holding) sprag clutch |
| • | Internal fluid passage leaks |
| • | Casting porosity or damage |
| • | Damaged gasket or spacer plate |
| • | Out-of-position gasket or spacer plate |
- Repair the 2-3 shift circuit as necessary.
Is the repair complete?
| --
|
Go to Step
12
| --
|
11
|
- Inspect the 3-4 shift circuit for the following conditions:
| • | Leaking 3-4 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Rolled 3-4 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Cut 3-4 accumulator piston seals |
| • | Leaking intermediate/4th servo piston seals |
| • | Rolled intermediate/4th servo piston seals |
| • | Cut intermediate/4th servo piston seals |
| • | Burned intermediate/4th band |
| • | Out-of-position intermediate/4th band |
| • | Damaged intermediate/4th band |
| • | Slipping intermediate/4th band |
| • | Internal fluid passage leaks |
| • | Casting porosity or damage |
| • | Damaged gasket or spacer plate |
| • | Out-of-position gasket or spacer plate |
| • | Damaged intermediate/4th servo pin |
| • | Seized intermediate/4th servo pin |
| • | Damaged intermediate/4th servo piston |
| • | Cracked intermediate/4th servo cover |
| • | Leaking intermediate/4th servo cover |
- Repair the 3-4 shift circuit as necessary.
Is the repair complete?
| --
|
Go to Step
12
| --
|
12
| Perform the following procedure in order to verify the
repair:
- Select DTC.
- Select Clear Info.
- Operate the vehicle under the following conditions:
| • | Drive the vehicle in D4 in order to obtain 1-2, 2-3, and 3-4 shifts. |
| • | Shift times must be less than 0.65 seconds. Refer to Diagnostic
Aid #2. |
- Select Specific DTC.
- Enter DTC P1811.
Has the test run and passed?
| --
| System OK
|
Go to Step
1
|