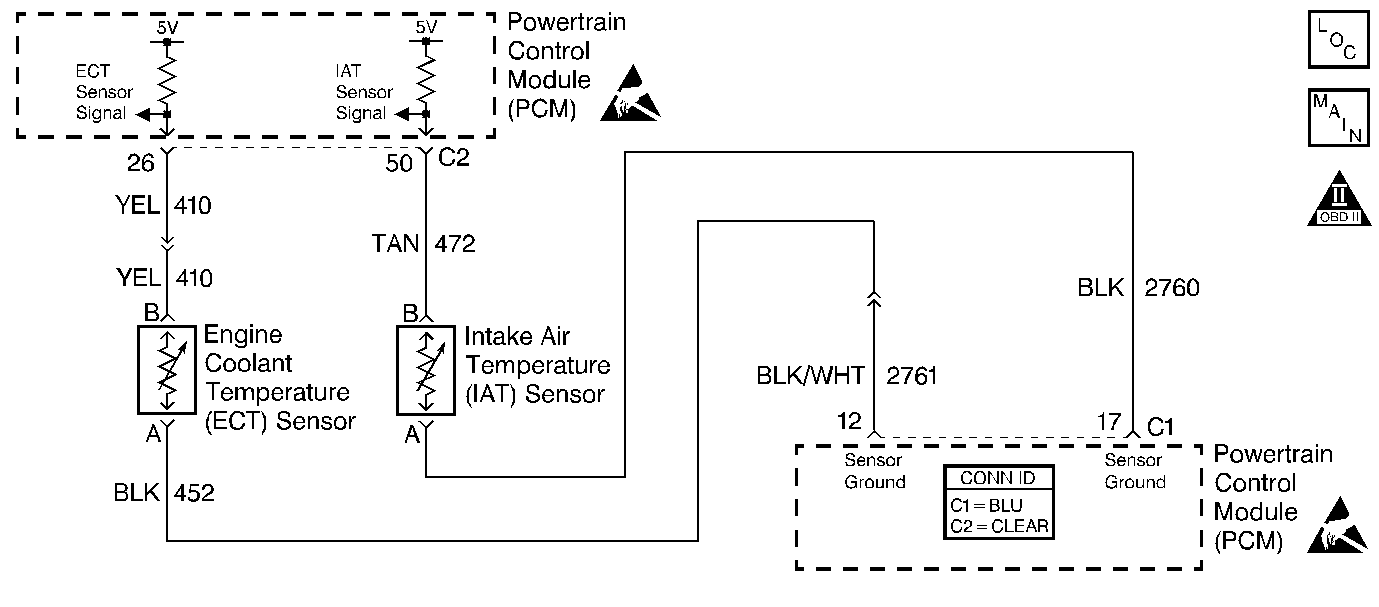
Circuit Description
To provide the best possible combination of driveability, fuel economy, and emission control, a closed loop air/fuel metering system is used. When the vehicle is first started, the PCM controls fuel delivery in open loop, ignoring the HO2S signals and calculating air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the engine coolant temperature, throttle position, and mass air flow sensors. The PCM will begin using the HO2S 1 signal for controlling fuel delivery (Closed Loop). when the following conditions have been met:
| • | The HO2S output signal is varying, indicating that the sensor is hot enough to operate properly. |
| • | The Engine Coolant Temperature sensor indicates coolant temperature above 20°C (68°F). |
| • | Time since start-up is at least 15 seconds for a warm engine or 90 seconds for a cold engine. |
The PCM monitors the amount of time for the cooling system to achieve closed loop operating temperature. This diagnostic is broken into three temperature regions. The diagnostic uses the ECT and IAT Sensors to determine which region to operate in. The time to achieve closed loop temperature is monitored. A time based decision is made depending on the temperature region. The diagnostic will monitor the following conditions prior to setting the DTC:
| • | Total airflow must exceed a calibrated amount. |
| • | Engine idle time must be less than a calibrated amount. |
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active IAT or ECT Sensor DTCs present. |
| • | Minimum air temperature is greater than -7°C (19°F). |
| • | Start-up engine coolant temperature is below 50°C (122°F). |
| • | Region 1--air temperature above 10°C (50°F) and the start up coolant temperature above 10°C (50°F) . |
| • | Region 2--air temperature above -7°C (20°F) and the start up coolant temperature between -7°C (20°F) and 10°C (50°F). |
| • | Region 3--air temperature above -7°C (20°F) and the start up coolant temperature between -40°C (-40°F) and -7°C (20°F). |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Region 1:
| • | Engine run time over 127 seconds to achieve closed loop temperature of 21°C (70°F). |
| • | Calibrated minimum amount of total airflow has been exceeded. |
| • | Maximum idle time less than 95 seconds. |
Region 2:
| • | Engine run time over 280 seconds to achieve closed loop temperature of 21°C (70°F). |
| • | Calibrated minimum amount of total airflow has been exceeded. |
| • | Maximum idle time less than 210 seconds. |
Region 3:
| • | Engine run time over 439 seconds to achieve closed loop temperature of 21°C (70°F). |
| • | Calibrated minimum amount of total airflow has been exceeded. |
| • | Maximum idle time less than 329 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P0125 set indicates a skewed ECT sensor. Comparing the engine coolant temperature displayed on a scan tool with actual coolant temperature measured with a thermometer may isolate this condition. If the displayed engine coolant temperature is not close to the actual coolant temperature, replace the ECT sensor. Refer to Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Replacement .
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at PCM. Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis Repairing Connector Terminals and Connector Repairs . |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs . |
If DTC P0125 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Fail Records data can be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain OBD System Check performed? | -- | ||
Does Eng. Cool. Temp. increase to above the specified value within 9 minutes? | 21°C (70°F). | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
3 | Are any ECT sensor DTCs set? | -- | Go to applicable ECT sensor DTC chart | |
4 |
Are the cooling fans off? | -- | Go to Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor Control Circuit Diagnosis | |
5 | Check the cooling system coolant level. Is the coolant level OK? | -- | ||
6 | Check for proper operation of the thermostat. Refer to Thermostat Diagnosis . Is the thermostat operating correctly? | -- | ||
7 | Compare Eng. Cool. Temp. displayed on the scan tool to the actual coolant temperature measured with a thermometer. Is the scan tool Eng. Cool. Temp. indication close to the measured temperature? | -- | ||
8 | Check for high resistance in wiring related to the ECT sensor. Also, check for poor connections at ECT sensor and PCM. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
9 | Repair condition as necessary. Refer to Loss of Coolant in Engine Cooling. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 | Replace the faulty terminals or repair faulty wiring as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Replace the ECT sensor. Refer to Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Does Eng. Cool. Temp. increase to above the specified value within 9 minutes? | 21°C (70°F) | System OK |
