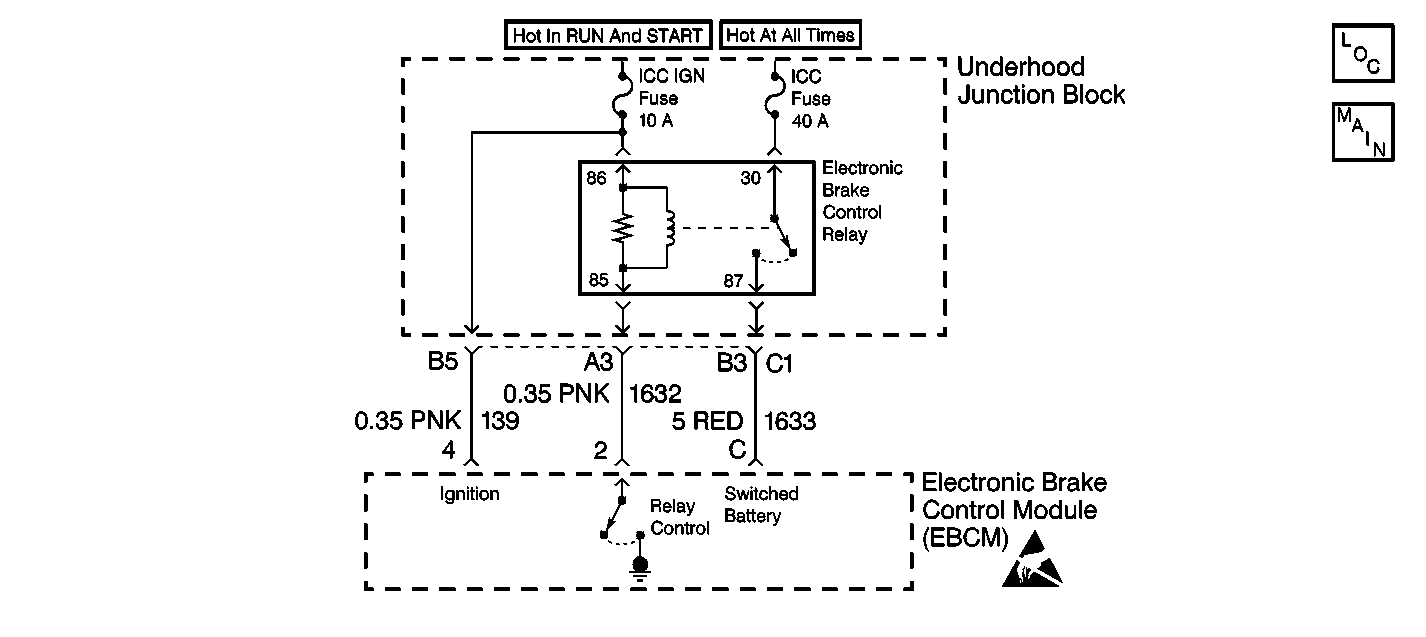
Circuit Description
Ignition voltage is supplied to terminal 86 of the Electronic Brake Control Relay. The above condition enables the EBCM to energize the pullin coil by completing the ground circuit at connector terminal 2 of the EBCM. The magnetic field created closes the Electronic Brake Control Relay contacts. The magnetic field also allows battery voltage and current through the Electronic Brake Control Relay terminal 30 to be supplied to the EBCM through connector terminal C. Connector terminal C supplies power to the EBCM, which supplies power to the motors and solenoids.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC C1217 can set before the EBCM commands the Electronic Brake Control Relay ON.
DTC C1217 determines if the Electronic Brake Control Relay energizes when the Electronic Brake Control Relay should not energize. The above malfunction would not allow the Electronic Brake Control Relay to remove power to the ABS system.
If a second malfunction occurs, that requires the Electronic Brake Control Relay to turn OFF, the second malfunction cannot be removed if the Electronic Brake Control Relay cannot be controlled.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC stores. |
| • | The ABS does not disable. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition responsible for setting the DTC no longer exists and the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function is used. |
| • | 100 drive cycles pass with no DTCs detected. A drive cycle consists of starting the vehicle, driving the vehicle over 16 km/h (10 mph), stopping and then turning the ignition OFF. |
Diagnostic Aids
Use the enhanced diagnostic function of the Scan Tool in order to measure the frequency of the malfunction.
Clear the DTCs after completing the diagnosis.
Test drive the vehicle for three drive cycles in order to verify that the DTC does not reset.
Use the following procedure in order to complete one drive cycle:
- Start the vehicle.
- Drive the vehicle over 16 km/h (10 mph).
- Stop the vehicle.
- Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position.
Test Description
-
This test determines if the EBCM is capable of controlling the electronic brake control relay as commanded.
-
This test ensures that the electronic brake control relay or control circuit are not shorted to ground.
-
This test ensures that the electronic brake control relay or control circuit are not shorted to ground.
-
This test determines if the malfunction is due to the EBCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Important: Zero the J 39200 test leads before making any resistance measurements. Refer to the J 39200 user's manual. | ||||||||||||||
1 | Was the ABS Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||||||||||||
Do not start the engine. Does the Scan Tool indicate that the Electronic Brake Control Relay is off, and is the voltage within the specified range? | 0-5 V | |||||||||||||
Do not start the engine. Is the voltage within the specified voltage? | 0-1 V | |||||||||||||
4 |
Are there signs of poor terminal contact, corrosion, or damaged terminals? | -- | ||||||||||||
Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the EBCM connector terminal 2 and ground. Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | |||||||||||||
Do not start the engine. Does DTC C1217 set as a current DTC? | -- | |||||||||||||
7 |
Is the voltage less than or equal to the specified range? | 0-1 V | ||||||||||||
8 | Replace all of the terminals or connectors that exhibit signs of poor terminal contact, corrosion, or damaged terminal(s). Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
9 | Repair the short to ground in CKT 1632. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
10 | Replace the Electronic Brake Control Relay. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Relay Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
11 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
12 | The malfunction is intermittent or is not present at this time. Refer to Diagnostic Aids for more information. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | ||||||||||
