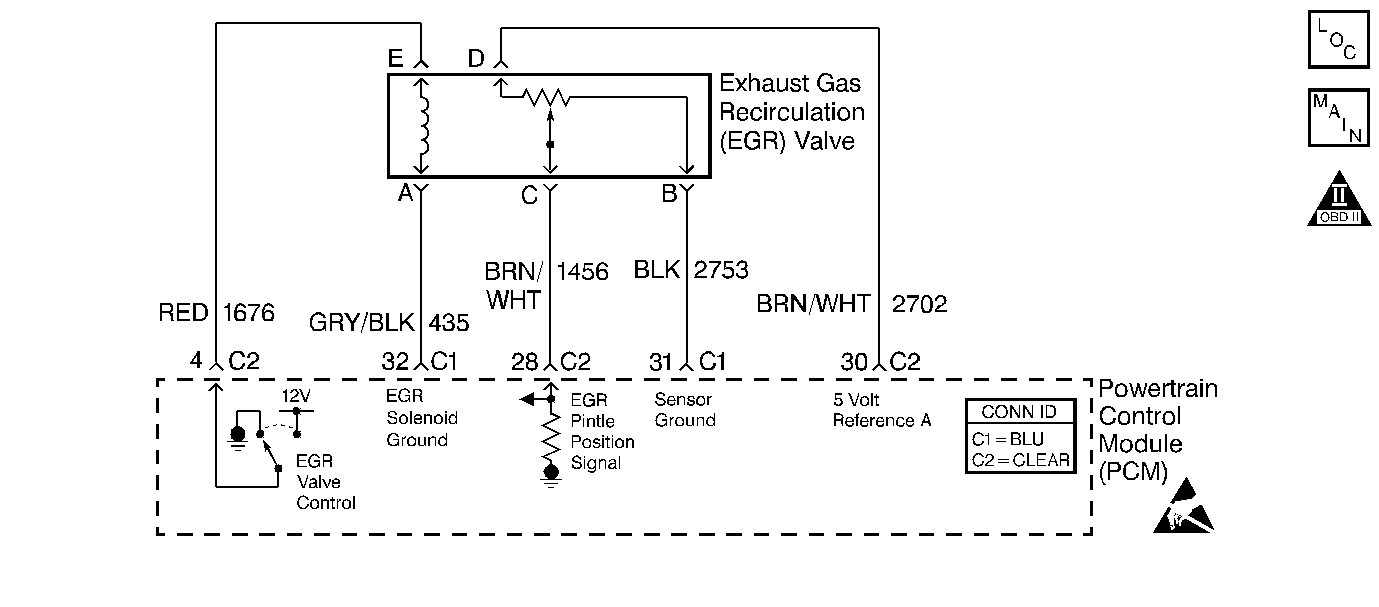
Circuit Description
The PCM monitors the EGR valve pintle position input to ensure that the valve responds properly to commands from the PCM. The Linear EGR valve is controlled by using an ignition positive driver and ground circuit within the PCM. The driver has the ability to detect an electrical malfunction in the ignition positive or ground circuit. If an electrical malfunction occurs, the driver signals the PCM to set DTC P0403.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No TP, IAT, MAP, ECT, CKP, MAF sensor, VSS, Misfire, Idle Speed, Fuel Injector, or DTCs set. |
| • | Engine coolant temperature is greater than 75°C (167°F). |
| • | Engine run time met. The time ranges from 20 seconds to 6 minutes depending upon engine coolant temperature at startup. |
| • | TP angle is greater than 2%. |
| • | Vehicle speed is greater than 2 mph (3.2 km/h) |
| • | System voltage is between 10 volts and 16 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The PCM detects an electrical malfunction in the control circuit for the EGR Valve. |
| • | The condition is present for 20 second. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will disable EGR for the ignition cycle. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Fail Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL off during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear Info function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Poor connection at PCM or EGR Valve. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis . |
| Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis , Repairing Connector Terminals , and Connector Repairs . |
| • | Damaged harness. Refer to Wiring Repairs . |
| Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, connect J 39200 DMM and check circuit continuity while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the EGR valve. A change in the display will indicate the location of the malfunction. Refer to Wiring Repairs . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
Verifies that the malfunction is present.
-
If DTC P0403 will only set under certain conditions, the malfunction may be intermittent; refer to Diagnostic Aids. If an intermittent wiring problem is not present, check for a poor connection at the PCM or the EGR valve.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is being replaced, the new PCM must be programmed.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain OBD System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Does the solenoid turn on and off with each command? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 3 | |
3 |
Does the test lamp turn on and off with each command? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 5 |
Does the test lamp turn on and off with each command? | -- | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 10 | |
5 | Does the test lamp remain illuminated with each command? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 6 |
6 | Test the control circuit of the solenoid for a short to ground or an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 9 |
7 | Test the control circuit of the solenoid for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 9 |
8 | Inspect for poor connections at the EGR. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis and Connector Repairs in Wiring systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 |
9 | Inspect for poor connections at the PCM. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 |
10 | Repair the ground circuit of the solenoid. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
11 | Replace the EGR. Refer to EGR Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
12 |
Important: : The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
13 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
