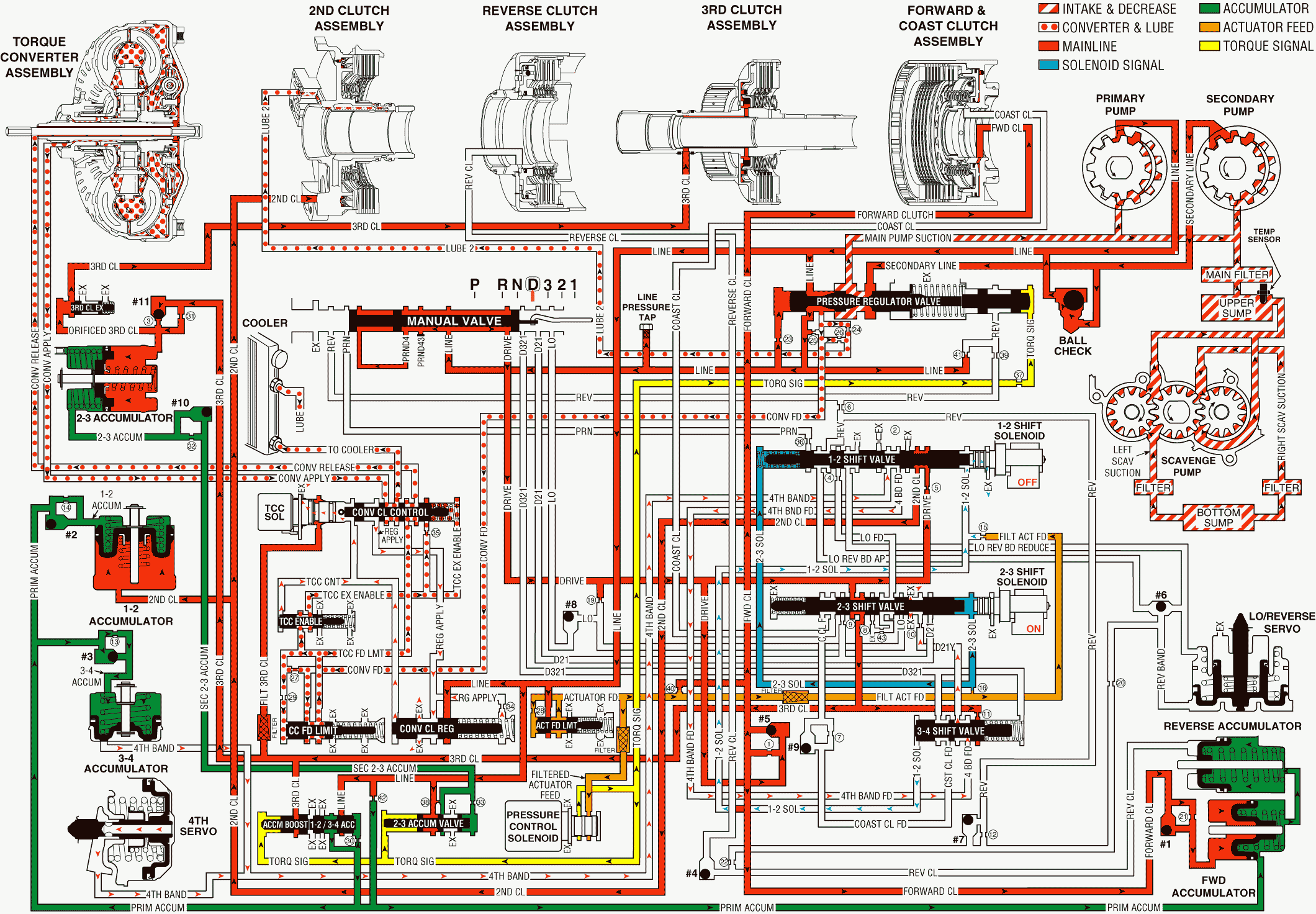
When the transmission is operating in Fourth gear, a 4-3 downshift occurs if there is a significant change or increase in the throttle position, or if the load on the engine is increased. The torque converter clutch releases prior to the downshift occurring, which results in the following changes in the hydraulic system:
Line Pressure Increases
Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid Valve
The change in throttle position (increase in percentage of travel) signals the PCM to increase the PC solenoid valve's OFF cycle time. When this occurs, higher filtered actuator feed pressure passes through the PC solenoid valve into the torque signal fluid passage.
Pressure Regulator Valve
Torque signal fluid, acting on the end of the valve, causes the valve to move against orificed line pressure at the other end of the valve. This movement of the valve increases line pressure in the hydraulic circuits.
Actuator Feed Limit Valve
Increased line pressure passes through the valve and the pressure enters the actuator feed circuit. Actuator feed fluid is routed through the force motor feed filter and then the fluid is routed into the filtered actuator feed circuit. Filtered actuator feed is then sent to the PC solenoid valve.
Torque Converter Clutch Releases
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid
As the throttle position changes, the throttle position sensor provides input to the PCM indicating throttle angle. The PCM then lowers the ON/OFF cycle time. Then the PCM de-energizes the TCC solenoid, thereby letting the filtered third clutch fluid exhaust through the solenoid. With filtered third clutch fluid exhausting, the converter clutch control valve moves into the released position.
Converter Clutch Control Valve
When spring force moves the converter clutch control valve to the released position, the valve directs TCC feed limit fluid into the converter release circuit. Converter release fluid is then routed to the torque converter pressure plate and disengages the torque converter clutch. Converter apply fluid from the torque converter clutch pressure plate is then routed back through its circuit to the converter clutch control valve. Converter apply fluid passes through the valve and enters the cooler circuit.
Fourth Band Releases
1-2 Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve
The 1-2 SS valve de-energizes, allowing fluid pressure from the 1-2 SS valve (acting on the end of the 3-4 shift valve) to exhaust through the solenoid. With low fluid pressure in the 1-2 SS valve, spring force acting on the opposite end of the valve moves the 3-4 shift valve.
Fourth Servo Assembly
Spring force actuates the fourth servo piston and returns the piston to its band released position. This movement forces fourth band fluid from the other side of the piston back through its circuit to the 1-2 shift valve.
1-2 Shift Valve
Spring force and pressure from the 2-3 shift solenoid (SS) valve hold the 1-2 shift valve in the upshifted position. Fourth band fluid is routed back through the valve and into the fourth band feed circuit. Fourth band feed is then routed to the 3-4 shift valve.
3-4 Shift Valve
Spring force holds the 3-4 shift valve in the downshifted position. Fourth band fluid from the 1-2 shift valve is routed through the valve into the orificed D21Y fluid passage. Orificed D21Y fluid is then routed to the 2-3 shift valve where the fluid exhausts.
Overdrive Range, 4-3 Downshift