Hydraulic Clutch System Description and Operation SWBRHD
Concentric Actuator Cylinder Operation (3.6L) Engine
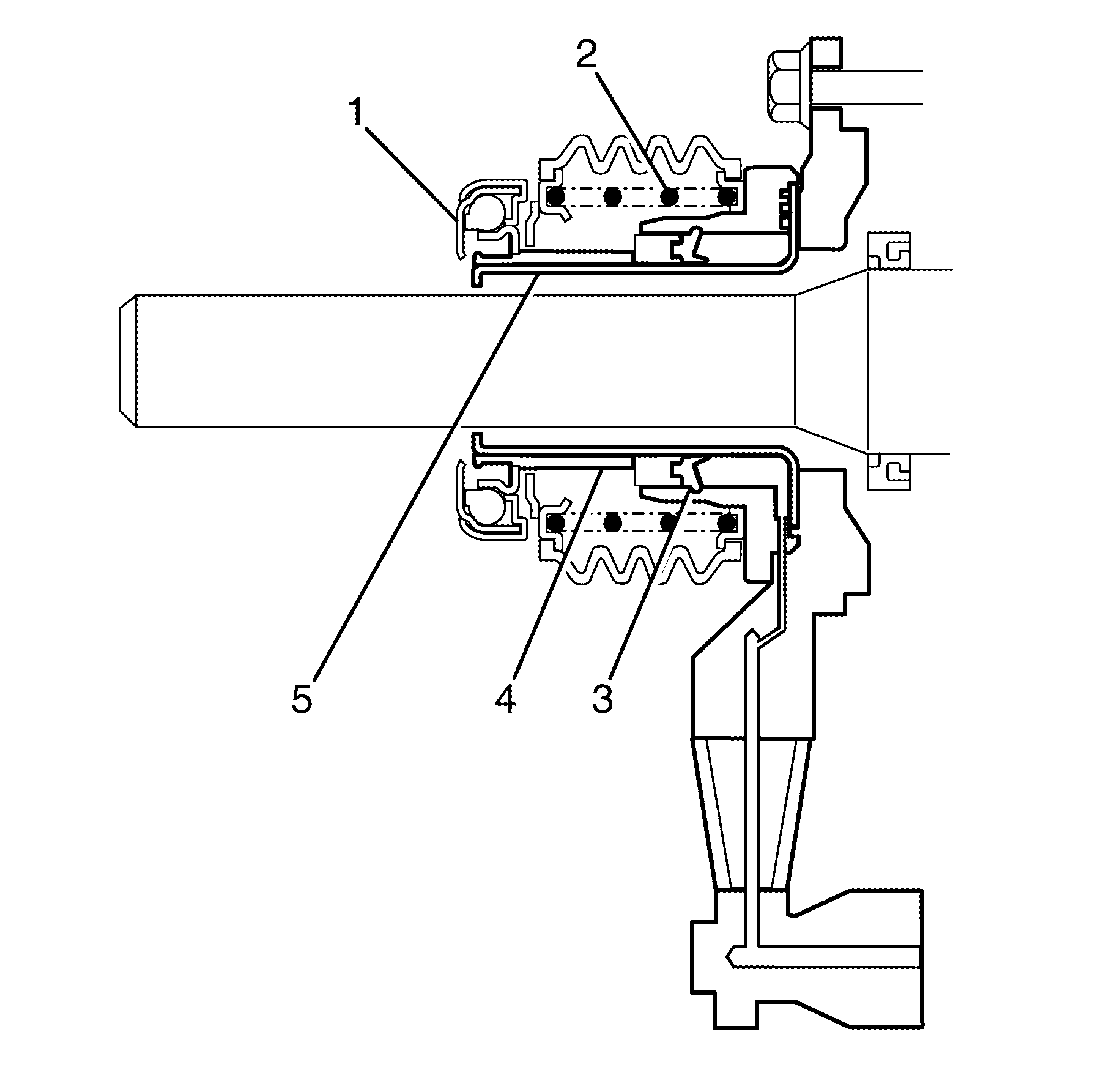
The pressurised fluid acts upon the seal (3) which then moves stroking the sleeve (4) in front of it. The release bearing (1) is also attached to the sleeve which means it also moves with the seal, in turn forcing the fingers of the pressure plate to move against the spring force. The concentric actuator cylinder sleeves continues to move the cylinder body, the pressure plate diaphragm spring guide (2) starts to pivot due to the force being applied. When this happens the clutch driven plate is allowed to spin. As this action takes place the flywheel and transmission input shaft friction link is broken which then allows smooth gear changing. The release bearing and actuating sleeve are moved back along the actuating body cylinder guide (5) by releasing the clutch pedal which in turn operates the pressure plate diaphragm spring force. As the clutch pressure plate is self-adjusting, the "at rest position of the release bearing and concentric slave cylinder sleeve remains relatively the same throughout the life of the assembly.
Concentric Actuator Cylinder Operation (6.0L Engine)
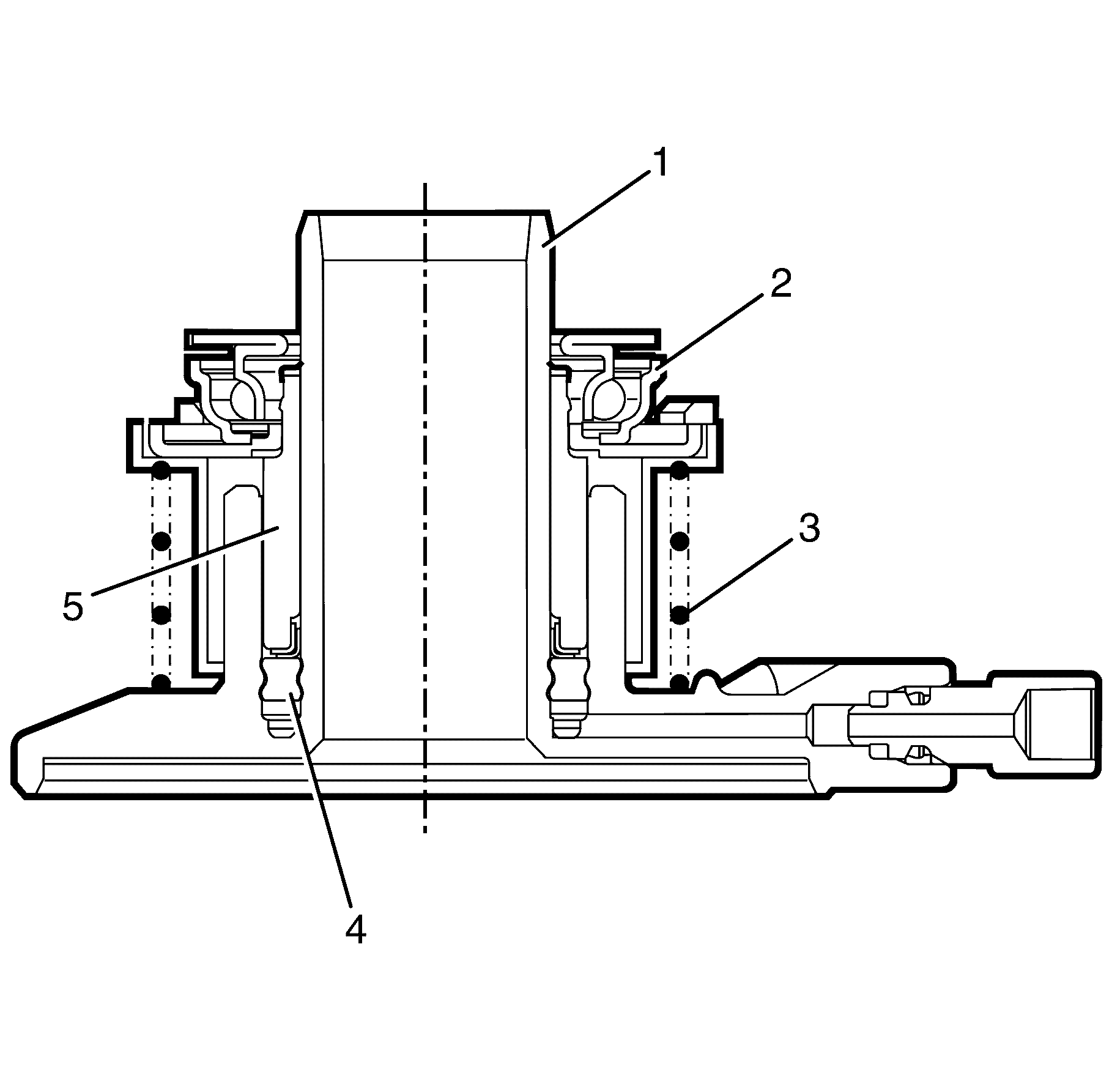
The pressurised fluid acts upon the seal upon the seal (4) which then moves stroking the sleeve in front of it. The release bearing (2)) is also attached to the sleeve (5) which means it also moves with the seal (4), in turn forcing the fingers of the pressure plate to move against the spring force. As the concentric actuator cylinder continues to move on the cylinder body, (1) the pressure plate diaphragm spring starts to pivot due to the force being applied. When this happens the clutch driven plate is allowed to spin. As this action takes place the flywheel and transmission input shaft friction link is broken which then allows smooth gear changing. The release bearing and actuating sleeve are moved back along the actuating body cylinder guide by releasing the clutch pedal which in turn operates the pressure plate diaphragm spring (3) force. As the clutch pressure plate is self-adjusting, the "at rest position of the release bearing and concentric slave cylinder sleeve remains relatively the same throughout the life of the assembly.
Master Cylinder Operation
As the clutch pedal is depressed, force is transmitted via the clutch pedal push rod to the clutch master cylinder piston moving it down the cylinder bore. When the piston stars to move, the primary seal covers the compensation port and the resultant build up in pressure, seats the relief valve in the end of the piston. As hydraulic pressure develops, the fluid is displaced and moves the piston in the concentric actuator cylinder against the return spring and clutch pressure plate diaphragm spring forces, to stroke the concentric actuator cylinder push rod. In turn, this action moves the clutch release lever and bearing, releasing the clutch pressure plate.
Hydraulic Clutch System Description and Operation SWBLHD
Concentric Actuator Cylinder Operation (6.0L Engine)

The pressurised fluid acts upon the seal upon the seal (4) which then moves stroking the sleeve in front of it. The release bearing (2)) is also attached to the sleeve (5) which means it also moves with the seal (4), in turn forcing the fingers of the pressure plate to move against the spring force. As the concentric actuator cylinder continues to move on the cylinder body, (1) the pressure plate diaphragm spring starts to pivot due to the force being applied. When this happens the clutch driven plate is allowed to spin. As this action takes place the flywheel and transmission input shaft friction link is broken which then allows smooth gear changing. The release bearing and actuating sleeve are moved back along the actuating body cylinder guide by releasing the clutch pedal which in turn operates the pressure plate diaphragm spring (3) force. As the clutch pressure plate is self-adjusting, the "at rest position of the release bearing and concentric slave cylinder sleeve remains relatively the same throughout the life of the assembly.
Master Cylinder Operation
As the clutch pedal is depressed, force is transmitted via the clutch pedal push rod to the clutch master cylinder piston moving it down the cylinder bore. When the piston stars to move, the primary seal covers the compensation port and the resultant build up in pressure, seats the relief valve in the end of the piston. As hydraulic pressure develops, the fluid is displaced and moves the piston in the concentric actuator cylinder against the return spring and clutch pressure plate diaphragm spring forces, to stroke the concentric actuator cylinder push rod. In turn, this action moves the clutch release lever and bearing, releasing the clutch pressure plate.
