| Table 1: | Discharge High Pressure Abnormally High |
| Table 2: | Discharge Pressure Abnormally Low |
| Table 3: | Suction Low Pressure Abnormally Low |
| Table 4: | Suction Pressure Abnormally High |
| Table 5: | Suction Pressure Abnormally High |
| Table 6: | Suction and Discharge Pressure Abnormally High |
| Table 7: | Suction and Discharge Pressure Abnormally Low |
| Table 8: | Refrigerant Leaks |
Symptom | Checks | Actions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
After stopping the compressor, the pressure drops about 299 kPa (28 psi) quickly, then falls gradually | There is air in the system. | Recover, evacuate, and recharge the system with the specified amount of refrigerant. | |||
The condenser is excessively hot. | There is excessive refrigerant in the system. | Recover, evacuate, and recharge the system with the specified amount of refrigerant. | |||
Reduced or no airflow through the condenser. | The condenser or the radiator fins are clogged. | Clean the condenser or the radiator fins. | |||
The condenser or the radiator fan is not working properly. |
| ||||
The line to the condenser is excessively hot. | Restricted flow of refrigerant in the system. | Locate and repair the restriction. |
Symptom | Checks | Actions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The condenser is not hot. | Insufficient refrigerant in the system |
| ||||
High and low pressures are balanced soon after stopping the compressor. Low-side pressure is higher than normal. | Faulty compressor pressure relief valve | Repair or replace the compressor. | ||||
Faulty compressor seal | ||||||
The outlet of the expansion valve is not frosted, low pressure gage indicates vacuum | Faulty expansion valve | Replace the expansion valve. | ||||
Moisture in the system | Recover, evacuate, and recharge the system. |
Symptom | Checks | Actions |
|---|---|---|
The condenser is not hot. | Insufficient refrigerant in the system | Repair the leaks. Recover, evacuate, and recharge the system. |
The expansion valve is not frosted and the low pressure line is not cold. The low pressure gage indicates a vacuum. | Frozen expansion valve | Replace the expansion valve. |
Faulty expansion valve | ||
The discharge temperature is low and the air flow from the vents is restricted. | The evaporator is frozen. | Clear the restricted evaporator case drain. |
The expansion valve is frosted. | The expansion valve is clogged. | Clean or replace the expansion valve. |
The receiver/drier outlet is cool and the inlet is warm. | The receiver/drier is clogged. | Replace the receiver/drier. |
Symptom | Checks | Actions |
|---|---|---|
The low pressure hose and check joint are cooler than the temperature around the evaporator. | The expansion valve is opened for too long. | Replace the expansion valve. |
A capillary tube is loose. |
Symptom | Checks | Actions |
|---|---|---|
Suction pressure is lowered when the condenser is cooled by water. | There is excessive refrigerant in the system. | Recover, evacuate, and recharge the system. |
High and low pressure are equalized as soon as the compressor is stopped and both gages fluctuate while the compressor is running. | A gasket is faulty. | Repair or replace the compressor. |
The high pressure valve is faulty. | ||
Foreign particles are stuck in the high pressure valve. |
Symptom | Checks | Actions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Reduced airflow through the condenser | The condenser or the radiator fins are clogged. | Clean the condenser and the radiator. | |||
The radiator cooling fans are not working properly. |
| ||||
The condenser is excessively hot. | There is excessive refrigerant in the system. | Recover, evacuate, and recharge the system. |
Symptom | Checks | Actions |
|---|---|---|
The low pressure hose and metal end areas are cooler than the evaporator. | Clogged or kinked low pressure hose | Repair or replace the low pressure hose. |
The temperature around the expansion valve is low compared to that around the receiver/dryer. | The high pressure line is clogged. | Repair or replace the high pressure line. |
Symptom | Checks | Actions |
|---|---|---|
The compressor clutch is dirty. | The compressor shaft seal is leaking. | Repair or replace the compressor. |
The compressor bolts are dirty. | Leaking around a compressor housing bolt. | Tighten the bolt(s) or replace the compressor. |
The compressor gasket is wet with oil. | The compressor gasket is leaking. | Repair or replace the compressor. |
Low and High Side Pressure Relationship Chart
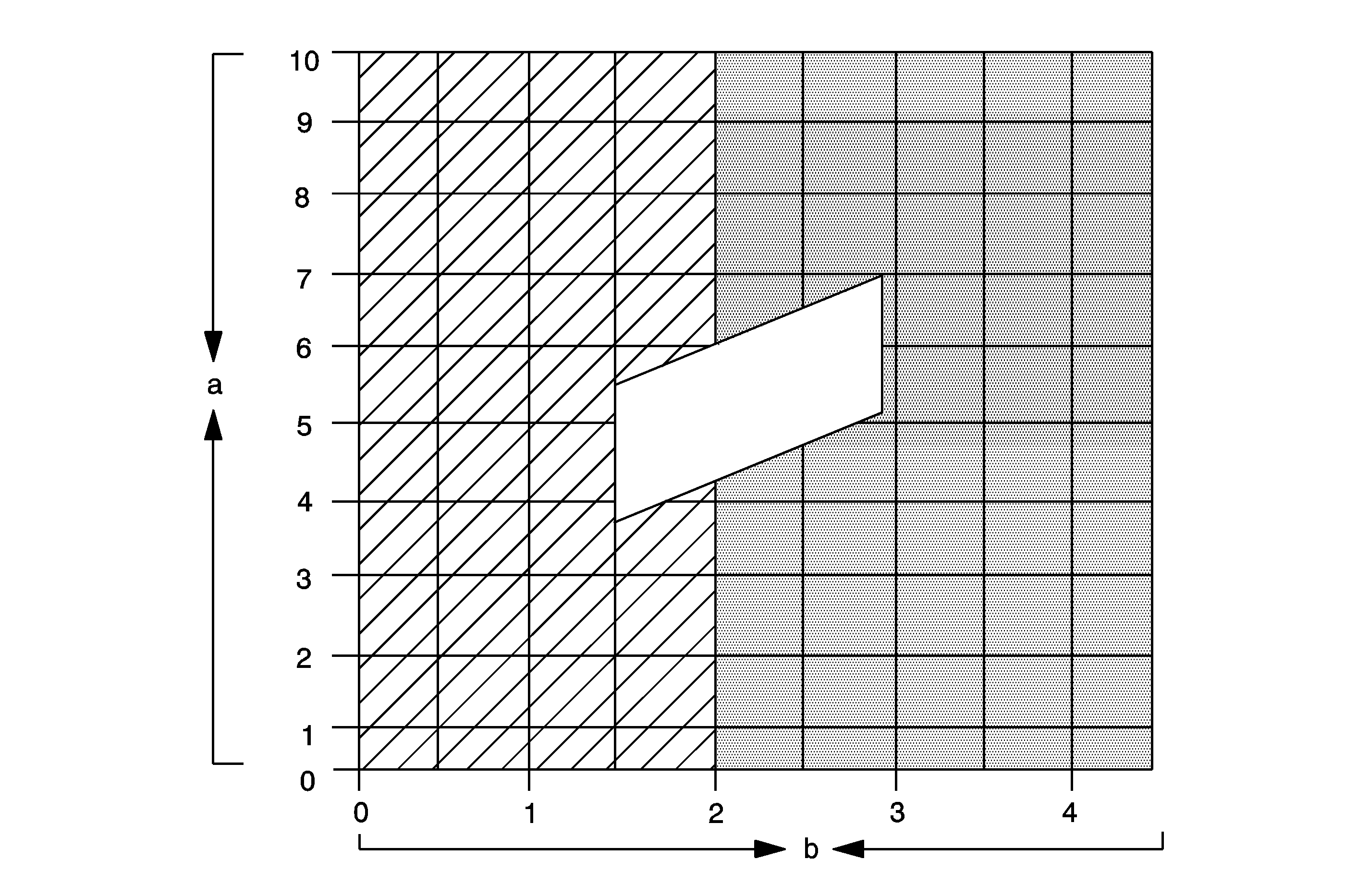
Low Side Pressure (a)
- 70 kPa (10 psi)
- 138 kPa (20 psi)
- 207 kPa (30 psi)
- 276 kPa (40 psi)
- 345 kPa (50 psi)
- 414 kPa (60 psi)
- 483 kPa (70 psi)
- 552 kPa (80 psi)
- 621 kPa (90 psi)
- 690 kPa (100 psi)
High Side Pressure (b)
- 690 kPa (100 psi)
- 1379 kPa (200 psi)
- 2069 kPa (300 psi)
- 2758 kPa (400 psi)
