Perform a compression test in order to determine the cylinder
compression pressure. Use a compression test in order to diagnose lack of
power, excessive oil consumption, or poor fuel economy.
- Verify that the battery is fully charged or close to fully charged.
Notice: This engine is equipped with an aluminum cylinder head. Allow the engine
to cool before removing spark plugs. Removing the spark plugs from an engine
at operating temperature may damage the spark plug threads in the cylinder
head. Also be sure to clean any dirt or debris from around spark plug holes
prior to removing spark plugs.
Important: The engine should be at room temperature.
- Remove the secondary (spark plug) wires from the spark plugs.
- Remove the spark plugs from the cylinder head.
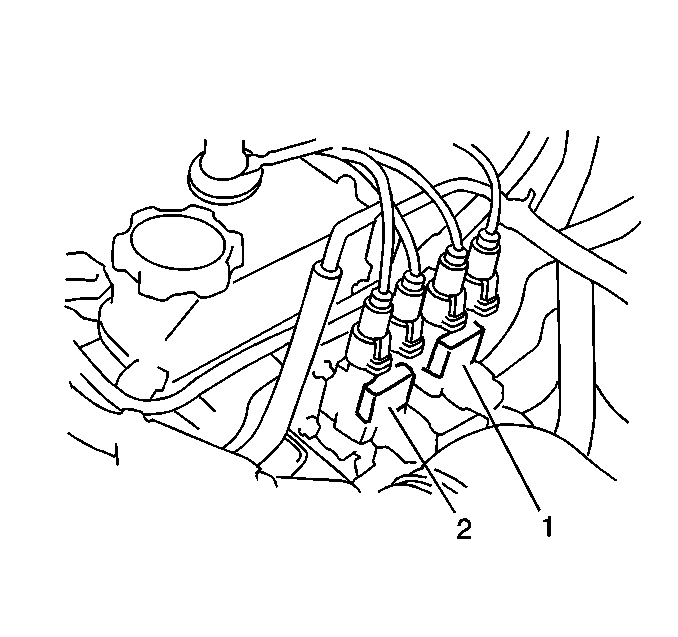
- Disconnect the electrical
connectors at both ignition coils (1,2).
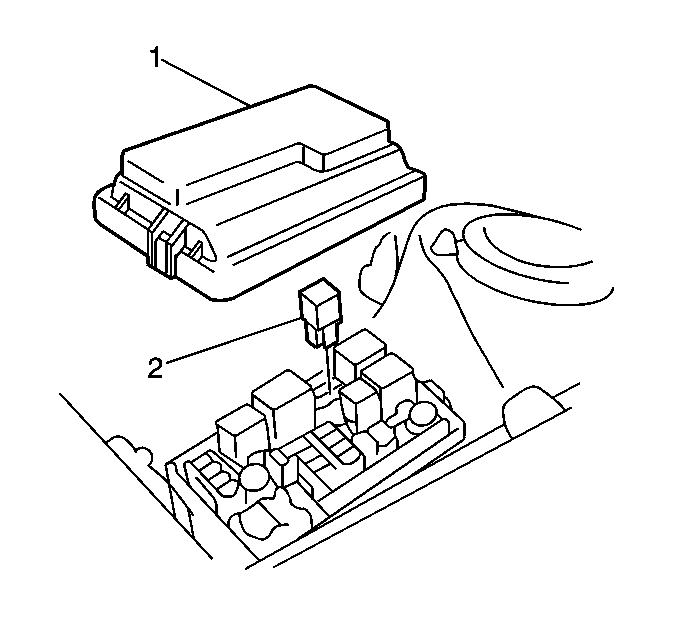
- Remove the EFI Main Relay
(2) from the Fuse/Relay Block 1.
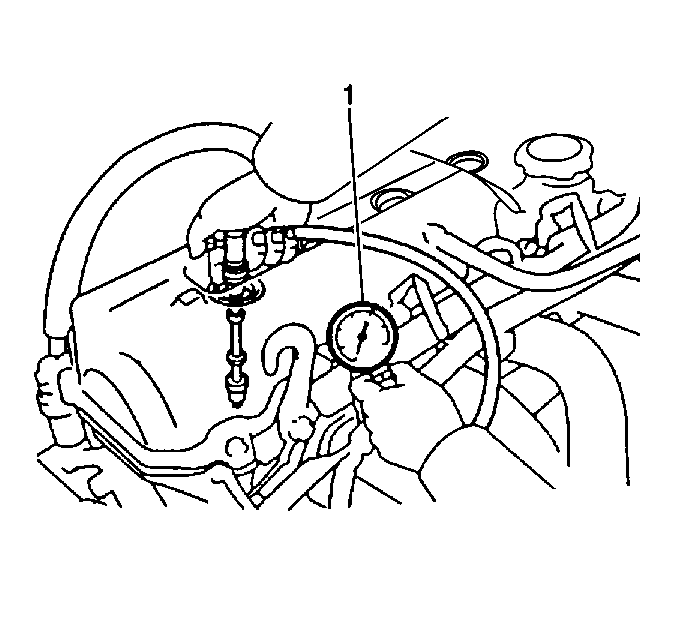
- Install a compression
gage into a spark plug hole.
- Depress the clutch pedal (on vehicles that are equipped with a
manual transmission).
- Depress the accelerator pedal to the floor for a wide open throttle.
- Crank the engine through four compression strokes for each cylinder
being tested.
Important: The maximum allowable compression pressure difference between any two
cylinders is 100 kPa (15 psi).
- Measure the highest pressure reading on the compression gage.
| - | The standard compression pressure is 1,500 kPa (218 psi). |
| - | The minimum allowable compression pressure is 1,000 kPa
(145 psi). |
- Repeat the compression test procedures for the remaining three
cylinders.
- Remove the compression gage from the engine.
- Install the four spark plugs.

- Reconnect the electrical
connectors at both ignition coils(1,2).

- Reconnect the EFI Main
Relay (2) to the Fuse/Relay Block 1.
- Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | The pistons, piston rings and valves are operating normally if the cylinder
compression pressure increases quickly and evenly to the compression standard
(1,500 kPa (218 psi). |
| • | The following actions indicate that the piston rings are faulty: |
| • | The cylinder compression is low on the first stroke. |
| • | The cylinder compression increases on the following strokes but
does not reach the compression standard. |
| • | The following actions indicate that the valves are faulty: |
| • | The cylinder compression is low on the first stroke. |
| • | The cylinder compression does not increase on the following strokes. |





