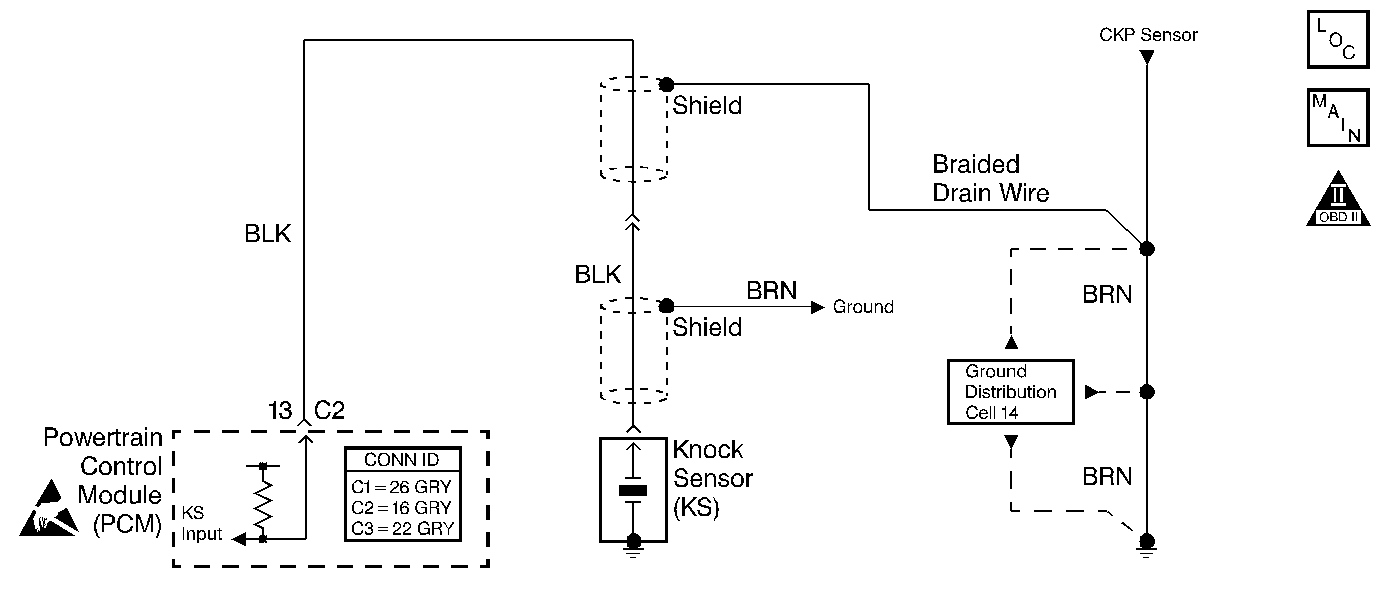
Circuit Description
The knock sensor (KS) is used to detect engine detonation. The KS is constructed of a piezoelectric element which generates an AC signal when vibrated. Normal engine operation will cause the KS to generate a signal of a certain known frequency. When engine knock is present, the KS frequency changes which signals the PCM to retard ignition timing. By retarding the ignition timing, the engine detonation detected should be reduced.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Engine speed is 1,200 RPM or more. |
| • | VSS and TP sensor indicate that the vehicle is accelerating. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The KS signal (voltage) detected, is below specifications, for more than 20 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the MIL. |
| • | The PCM stores the conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame Data. |
| • | The PCM enters the Fail-Safe Function and defaults to maximum spark retard. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the MIL on the third consecutive trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and the fault condition is no longer present. |
| • | The DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a fault. |
| • | A DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
A loose KS can cause a loss of the KS signal. Check the KS for proper torque. The correct KS sensor torque is 39 N·m (29 lb ft).
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the KS sensor electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals. |
| • | Improper mating of terminals. |
| • | Broken electrical connectors locks. |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Faulty terminal to wire connections. |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation. |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals. |
Repair any electrical circuit faults that were found. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
The information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining the vehicle operating conditions when the DTC first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the Diagnostic Table.
-
The OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step checks whether the DTC P0325 is the result of a hard failure or an intermittent condition. Operating the vehicle in check mode enhances the PCM's diagnostic capabilities. For additional information on check mode operation refer to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis .
-
This step checks the knock sensors ability to output the correct frequency signal for a given engine speed.
-
This step checks if the fault is the knock sensor input wiring.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||
Does the DTC P0325 set? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Is the A/C frequency near the second specified value? | 4,000 RPM 12.5 kHz | |||
Is the A/C frequency near the second specified value? | 4,000 RPM 12.5 kHz | |||
5 |
Ensure that the terminal connection at the knock sensor is good. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
6 | Replace the Knock Sensor. Refer to Knock Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Are any DTCs displayed on the scan tool? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
