Circuit Description
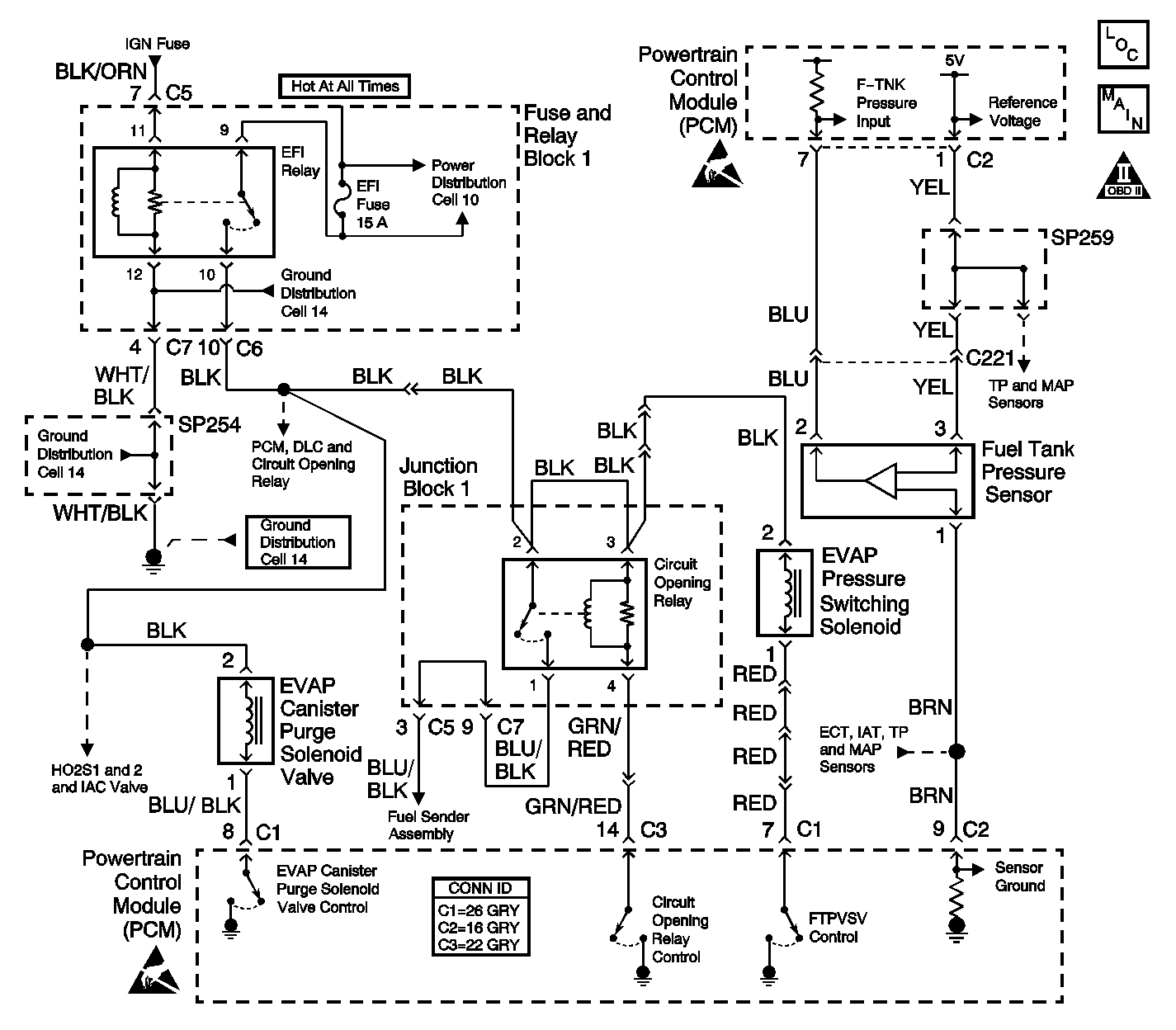
The Evaporative Emission (EVAP) control system prevents the emission of the fuel vapors. The fuel vapor generated in the fuel tank while driving or idling enters the EVAP canister where a charcoal element absorbs and stores the fuel vapor. When certain engine operating conditions are met the PCM purges the EVAP canister of stored vapors by turning ON the EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid Valve.
Emissions laws require that the PCM detect any leakage within the EVAP system. The PCM monitors the Fuel Tank Pressure sensor in order to detect any abnormalities within the EVAP system.
The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage, a sensor ground and an input signal circuit to the Fuel Tank Pressure sensor.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine has been running less than 10 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The fuel tank pressure sensor signal indicates less than -1.2 in. Hg for 7 seconds.
OR
The fuel tank pressure sensor signal indicates greater than +0.6 in. Hg for 7 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information is stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL turns OFF after three consecutively passing trips without a fault present. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
If DTCs P0105, P0110, P0115, and P0120 are also set, the malfunction may be in the sensor ground circuit.
If DTCs P0105 and P0120 are also set, the malfunction may be in the reference voltage circuit.
To perform a functional check of the fuel tank pressure sensor, refer to Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis .
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the fuel tank pressure sensor electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals. |
| • | Improper mating of terminals. |
| • | Broken electrical connectors locks. |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Faulty terminal to wire connections. |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation. |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals. |
Repair any electrical circuit faults that were found. Refer to Wiring Repairs .
The information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining the vehicle operating conditions when the DTC first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the Diagnostic Table.
-
The OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step checks whether the fuel tank pressure sensor malfunction is present or intermittent. The input signal voltage of the fuel tank pressure sensor should indicate atmospheric pressure, 3.0 to 3.6 volts, with the fuel tank filler cap removed. The fuel tank pressure sensor voltage will vary with atmospheric pressure. A typical voltage at sea level is 3.2-3.3 volts.
-
This step determines if DTC P0450 is the result of a hard failure or an intermittent condition. Operating the vehicle in check mode enhances the PCM's diagnostic capabilities. For additional information on check mode operation refer to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis.
-
This step checks whether there is trapped negative or positive pressure at the fuel tank pressure sensor.
-
Checks for an open or a short in the fuel tank pressure sensor 5 volt reference.
-
Checks for an open or short in the fuel tank pressure sensor input circuit.
-
Checks for an open in the fuel tank pressure sensor ground circuit.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||
Is the voltage within the specified value? | 3.0-3.6 volts | |||||||||
Does the DTC P0450 set? | -- | Fault Not Present-Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
Is the voltage within the specified value? | 3.0-3.6 volts | |||||||||
5 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
Does the DMM read the specified value? | 5.0 volts | |||||||||
Measure the voltage from the fuel tank pressure sensor connector cavity 2 (harness side), using a DMM. Does the DMM read near the specified value? | 4.9 volts | |||||||||
8 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
9 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
10 | Probe the fuel tank pressure sensor connector cavity 1 (harness side), with a test lamp connected to battery voltage. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
11 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
12 | Replace the fuel tank pressure sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
13 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
14 |
Are any DTCs displayed on scan tool? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
