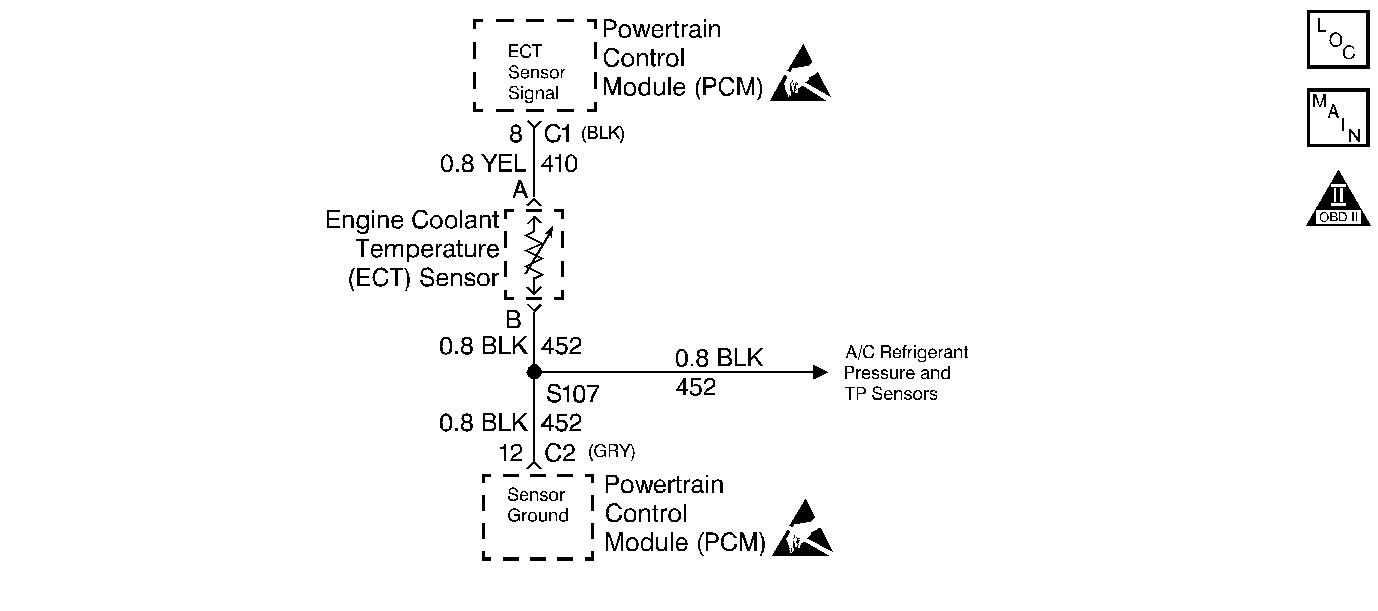
System Description
When the engine coolant temperature is below 20° C (68° F), the fuel delivery system will operate in an Open Loop. The PCM ignores the oxygen sensor signal. The PCM calculates the air to fuel ratio based on inputs from the engine coolant temperature, the throttle position and the manifold absolute pressure sensors.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
| • | The ECT sensor is less than 60° C (140° F). |
| • | The IAT sensor is greater than 20° C (68° C). |
| • | The vehicle speed is greater than 5 mph. |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 363 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminates after 2 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers stores this information. |
| • | A history DTC is stored. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will turn OFF after 3 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
A poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation may cause an intermittent.
| • | Check for a poor connection or damaged harness: Inspect the PCM harness for backed out terminals and for improper mating, broken locks, and damaged harness. |
| • | Perform an intermittent test. Whenever the connections and the harness checks OK, monitor a digital voltmeter connected between the ECT signal circuit and the ECT ground circuit on the PCM harness while moving related connectors and wiring harness. Whenever a fault is induced, the resistance reading will change. This may help to isolate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | Use the table below to check for a skewed sensor. Refer to Temperature vs Resistance . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame Data and the Failure records on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. This information on the scan tool can be referred to later.
-
Allow the engine to cool to ambient and compare the ECT sensor to the IAT sensor. The IAT sensor and ECT sensor should read within 4° C of each other. This step checks the initial operation of the ECT sensor.
-
Before replacing the PCM, check terminals for improper mating, broken locks, or physical damage to the wiring harness. Reprogram the replacement PCM. Refer to the latest Techline information for programming procedures.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | |||
Are the temperatures readings close to each other? | -- | |||
3 |
Does the ECT sensor accurately reflect the actual engine coolant temperature sensor. | -- | ||
4 | Disconnect the ECT electrical connector. Is the ECT sensor value less than the specified value? | -30° C (-22° F) | ||
5 | Jumper the ECT signal circuit and the sensor ground circuit together at the ECT sensor. Is the ECT sensor value greater than the specified value? | 130° C (266° F) | ||
6 |
Was a repair made? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
7 |
Was a repair made? | -- | ||
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
9 | Replace the ECT sensor. Refer to Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | 90°-95° C | ||
11 | Check if any additional DTCs are set. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
