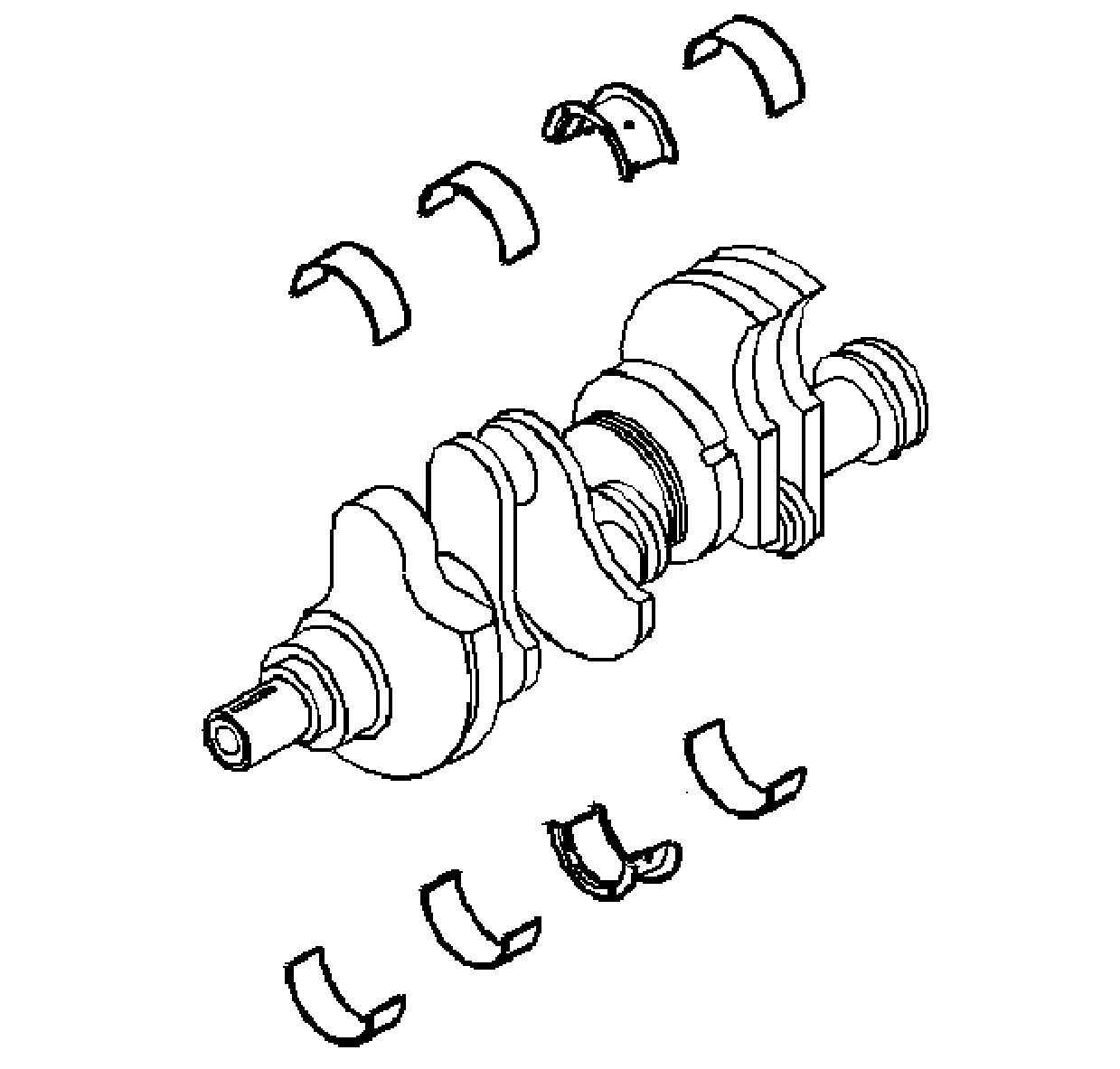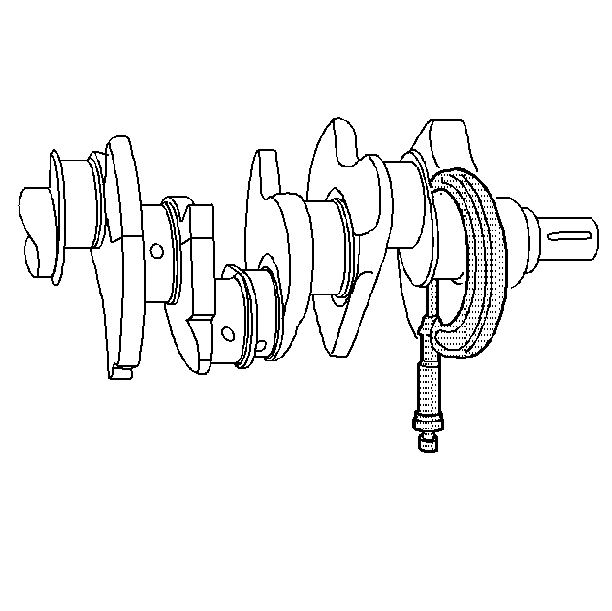Crankshaft and Bearing Cleaning and Inspection Bearing Selection
Tools Required
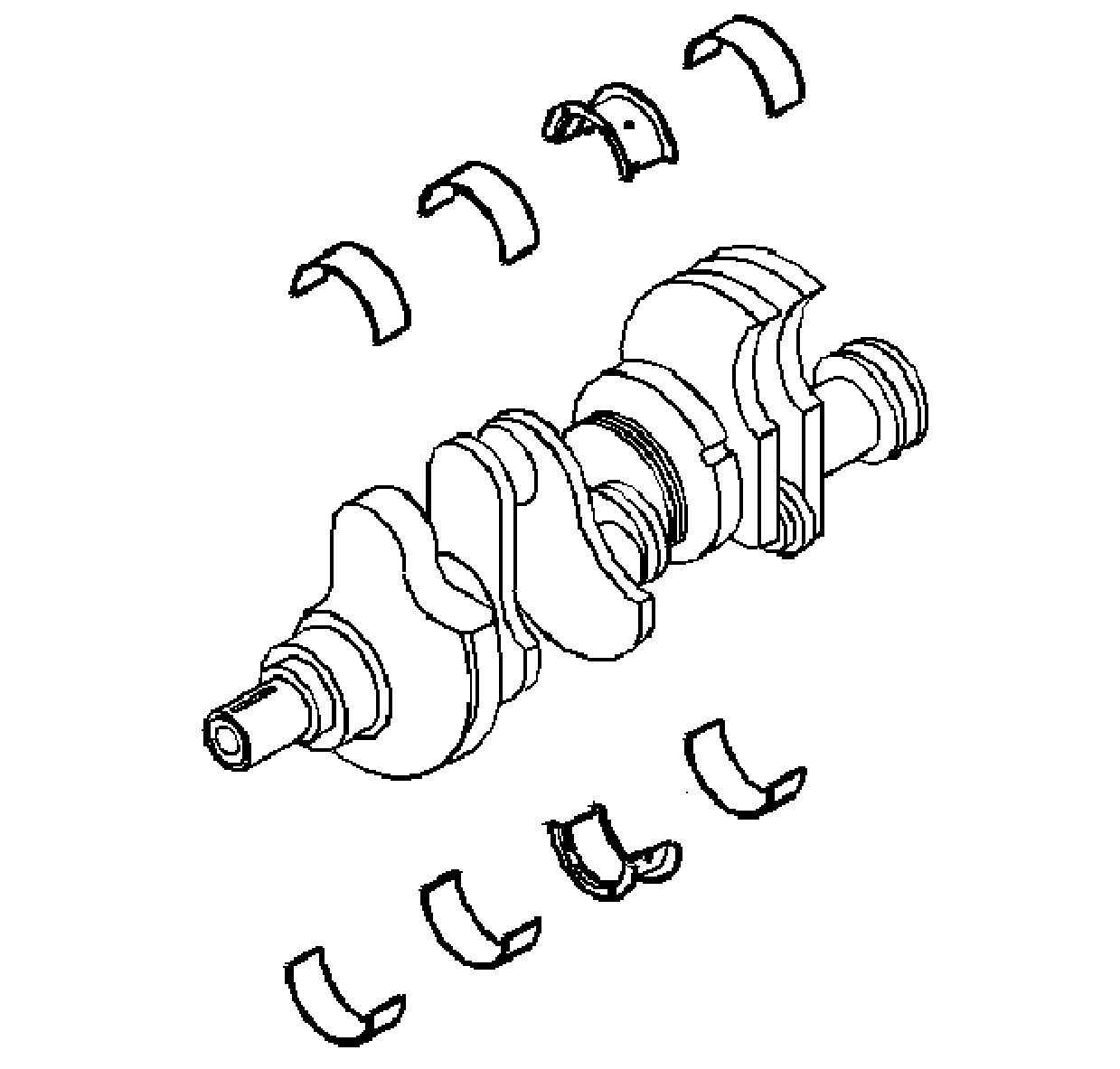
- Clean the crankshaft of
the following elements:
- Inspect the crankshaft oil passages for obstructions.
- Inspect the crankshaft keyway for nicks or wear.
- Inspect the crankshaft threads.
Important: If cracks, severe gouges or burned spots are found, the crankshaft must
be replaced. Slight roughness may be removed with a fine polishing cloth soaked
in clean engine oil. Burrs may be removed with a fine oil stone.
- Inspect the crankshaft bearing journals and the crankshaft thrust surfaces
for the following conditions:
| • | Overheating (discoloration) |
- Inspect the corresponding crankshaft bearings for embedded foreign
material and determine the source.
Important: Note the location of the crankshaft main bearing high spots. If they
are not in line, the crankshaft is bent and must be replaced.
- Inspect the crankshaft bearings for uneven side-to-side wear. This may
indicate a bent crankshaft or a tapered bearing journal.
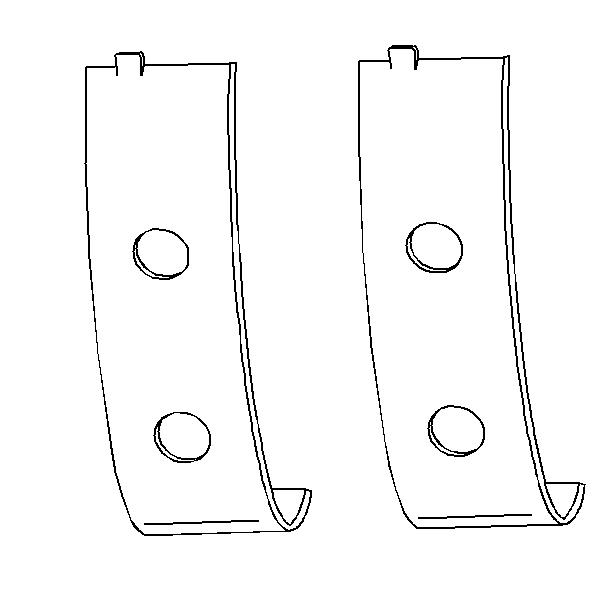
- The crankshaft bearings
are of the precision insert type. The crankshaft bearings are available in
standard and various undersizes.
Notice: Do not scrape, shim, or file bearing inserts. If the bearing surface
of the insert is touched with bare fingers, the skin oil and acids will etch
the bearing surface.
- Inspect the outer surfaces of the crankshaft bearings for the
following conditions:
| • | Wear - surface wear indicates either movement of the insert or
high spots in the surrounding material (spot wear). |
| • | Overheating or discoloration |
| • | Looseness or rotation indicated by flattened tangs and wear grooves |
- Inspect the thrust surfaces of the main thrust bearing for the
following conditions:
| • | Grooving (Grooves are caused by irregularities of the crankshaft
thrust surface.) |
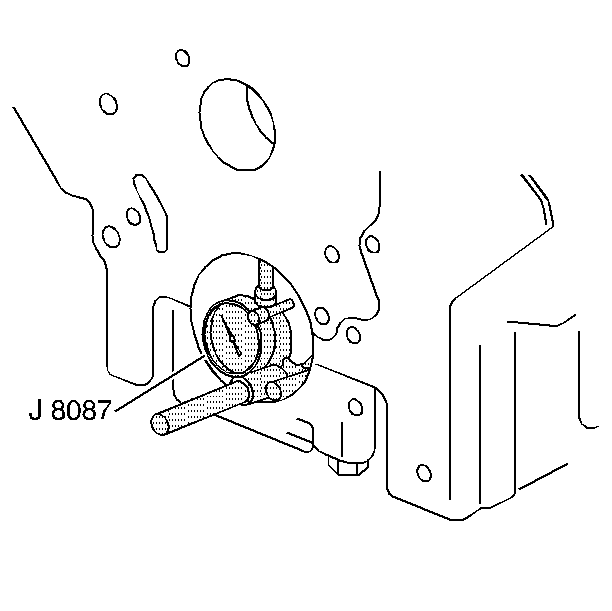
Important: If crankshaft bearing failure is due to other than normal wear, investigate
the cause. Inspect the crankshaft or connecting rod bearing bores.
- Inspect the connecting rod bearing bores or crankshaft main bearing
bores using the following procedure:
| 11.1. | Tighten the bearing cap to specification. |
| 11.2. | Measure the bearing bore for taper and out-of-round using the J 8087
. No taper or out-of-round
should exist. |
Bearing Selection
Measure the bearing clearance to determine the correct replacement bearing
insert size. There are two methods to measure bearing clearance. Method
A gives more reliable results and is preferred.
| • | Method A yields measurement from which the bearing clearance can
be computed. |
| • | Method B yields the bearing clearance directly. Method B does
not give any indication of bearing run-out. |
Method A
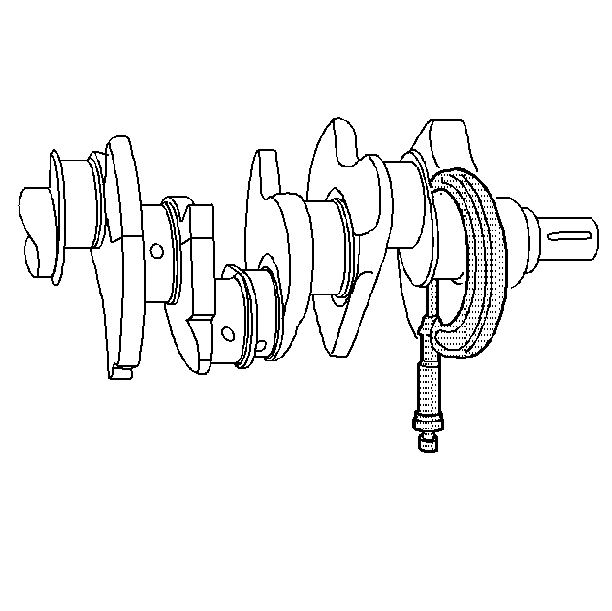
Important: Do not mix inserts of different nominal size in the same bearing bore.
- Measure the crankshaft bearing journal diameter with a micrometer in
several places, 90 degrees apart. Average the measurements.
- Measure the crankshaft bearing journal taper and runout.
- Install the crankshaft bearing inserts. Tighten the bearing cap
bolts to specification. Refer to Fastener Tightening Specifications.
- Measure the connecting rod inside diameter in the same direction
as the length of the rod with an inside micrometer.
- Measure the crankshaft main bearing inside diameter with an inside
micrometer.
- Select a set of bearing inserts that will produce the desired
clearance.
- If the specified clearances cannot be met, the crankshaft journals
must be reconditioned and undersized bearing inserts installed.
Method B
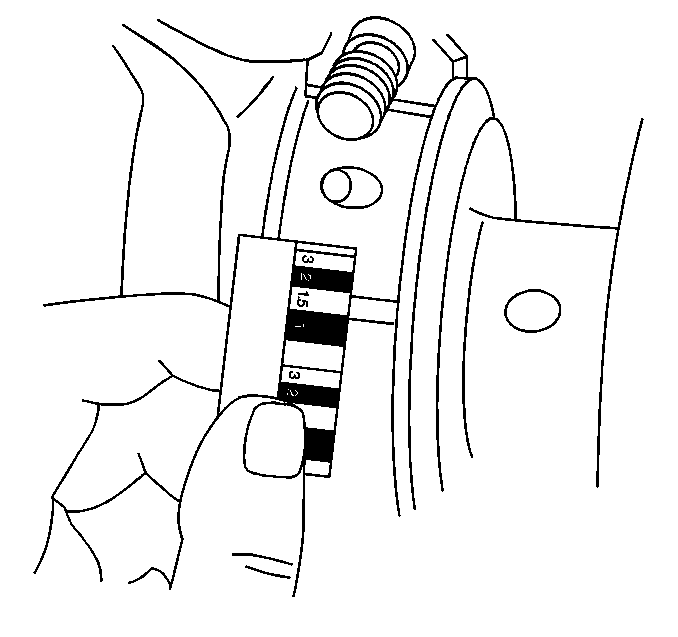
Important: Do not mix inserts of different nominal size in the same bearing bore.
- Clean the used bearing inserts.
- Install the used bearing inserts.
- Place a piece of gauging plastic across the entire bearing width.
- Install the bearing caps.
Notice: In order to prevent the possibility of cylinder block or
crankshaft bearing cap damage, the crankshaft bearing caps are tapped into
the cylinder block cavity using a brass, lead, or a leather mallet before
the attaching bolts are installed. Do not use attaching bolts to pull the
crankshaft bearing caps into the seats. Failure to use this process may damage
a cylinder block or a bearing cap.
- Install the bearing cap bolts to specification.
Important: Do not rotate the crankshaft.
- Remove the bearing cap, leaving the gauging plastic in place. It does
not matter whether the gaging plastic adheres to the journal or to the bearing
cap.
- Measure the gauging plastic at the widest point with the scale
printed on the gaging plastic package.
- Remove the gauging plastic.
- Select a set of bearing inserts that will produce the desired
clearance.
Crankshaft and Bearing Cleaning and Inspection Inspection
Tool Required
J 7872 Magnetic Base
Dial Indicator Set
Notice: Use care when handling the crankshaft in order to avoid damaging the
bearing surfaces, crankshaft position reluctor ring and crankshaft position
reluctor ring teeth. Damage to the crankshaft position reluctor ring or crankshaft
position reluctor ring teeth may effect OBD II system performance.
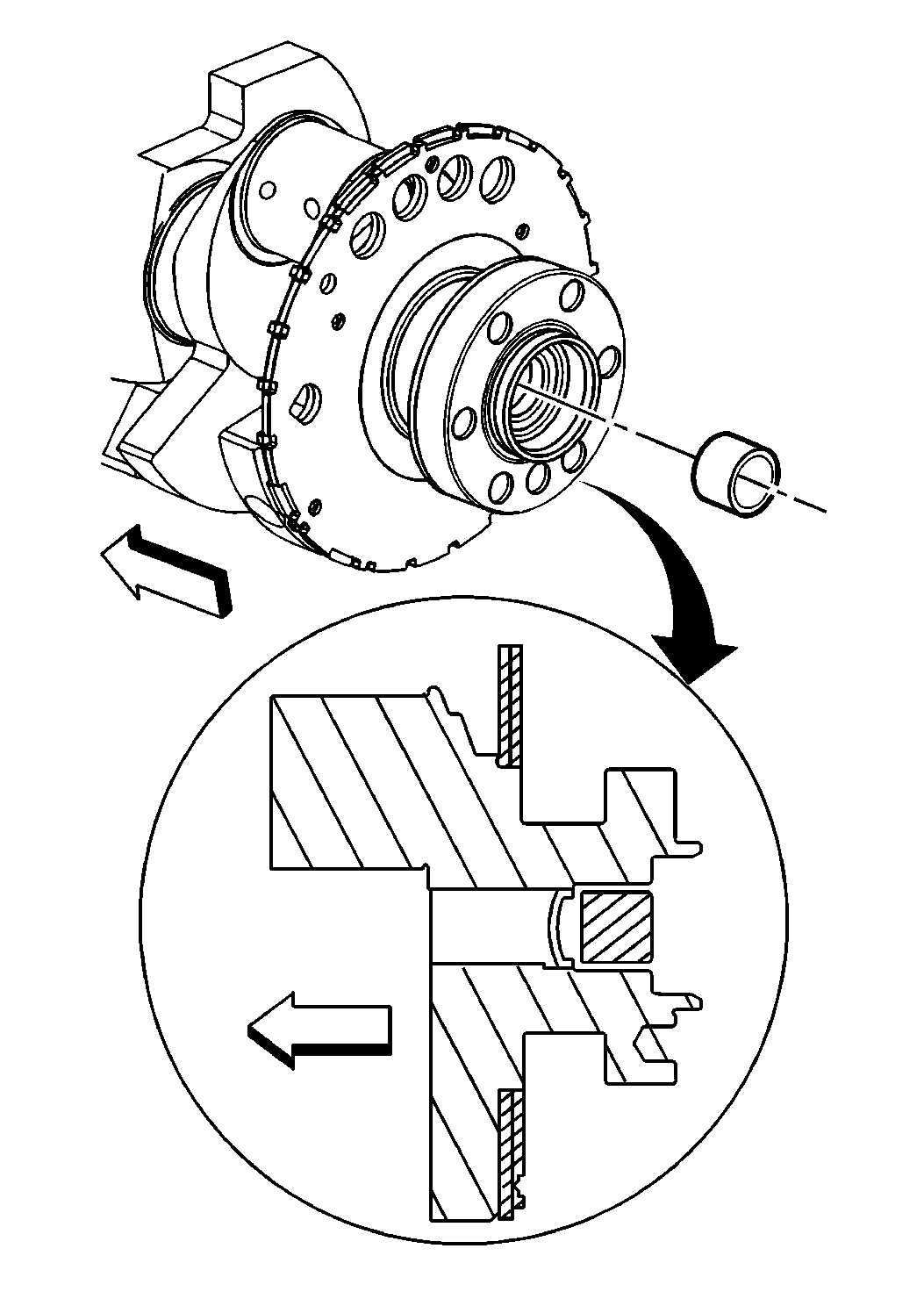
- Remove the clutch pilot bearing.
- Clean the crankshaft with solvent.
- Thoroughly clean all oil passages and inspect for restrictions
or burrs.
Caution: Wear safety glasses in order to avoid eye damage.
- Dry the crankshaft with compressed air.
Important: Reluctor ring teeth should not have imperfections on the rising or falling
edges.
Imperfections of the reluctor ring teeth may effect OBD II system
performance.
- Perform a visual inspection of the crankshaft for damage.
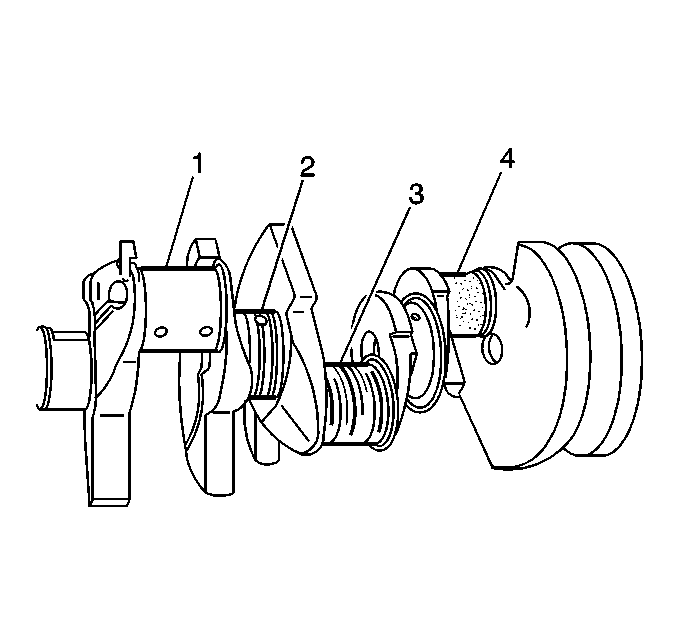
- Inspect the crankshaft
journals for wear (1).
Journals should be smooth with no signs of scoring, wear, or damage.
- Inspect the crankshaft journals for grooves or scoring (2).
- Inspect the crankshaft journals for scratches or wear (3).
- Inspect the crankshaft journals for pitting or imbedded bearing
material (4).
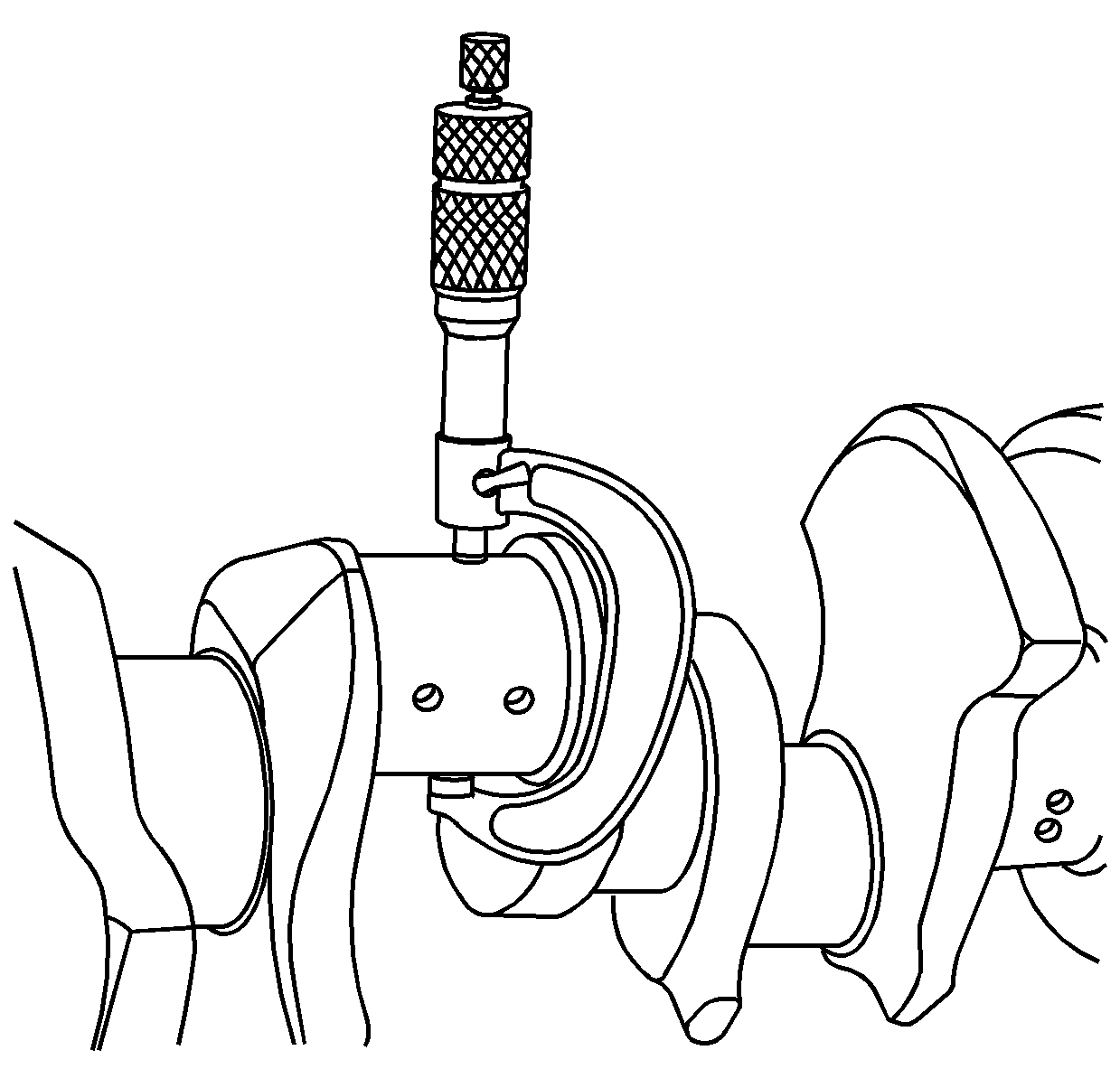
- Measure the crankshaft
journals for out-of-round.
- Measure the crankshaft journals for taper.
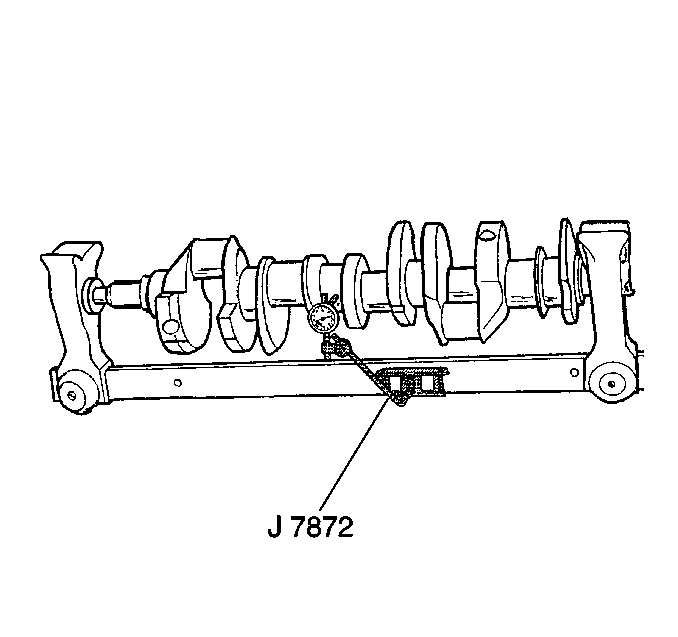
- Measure the crankshaft
runout.
Using wooden V blocks, support the crankshaft on the front and rear
journals.
- Use the J 7872
in order to measure the crankshaft runout at the front and rear intermediate
journals.
- Use the J 7872
in order to measure the runout of the crankshaft rear flange.
| 14.2. | Replace or repair the crankshaft if the measurements are not within
the specifications. |

- Install a new clutch pilot bearing.
A properly installed clutch pilot bearing will be installed until flush
to the face of the crankshaft.
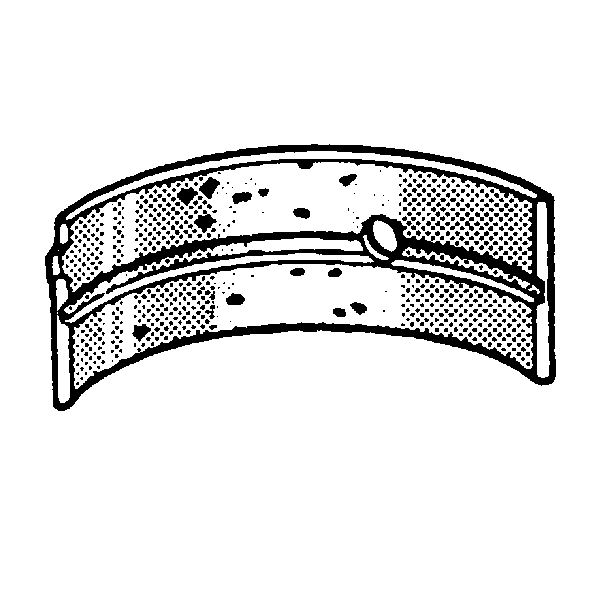
- Inspect crankshaft bearings
for craters or pockets. Flattened sections on the bearing halves also indicate
fatigue.
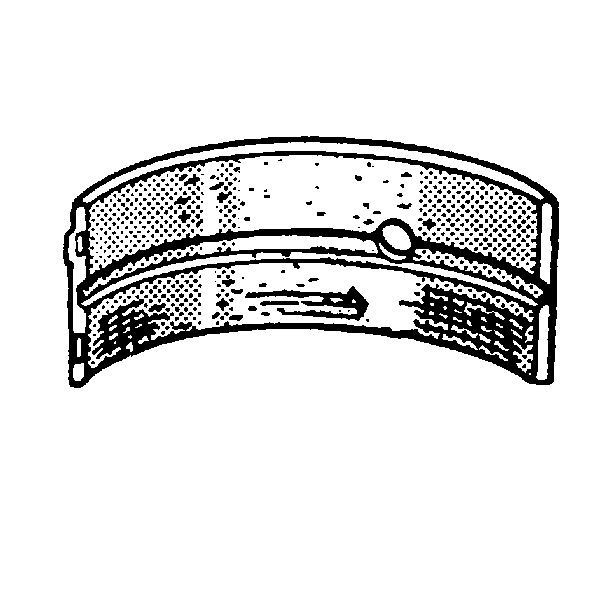
- Inspect the crankshaft
bearings for excessive scoring or discoloration.
- Inspect the crankshaft bearings for dirt or debris imbedded into
the bearing material.
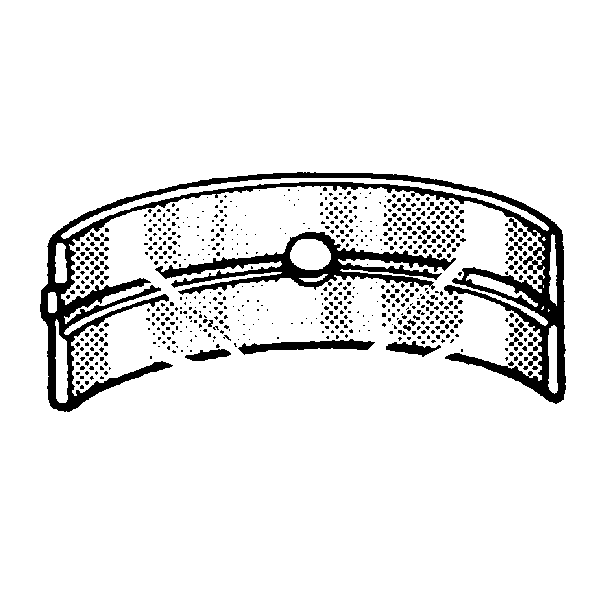
- Inspect the crankshaft
bearings for improper seating indicated by bright, polished sections of the
bearing.
If the lower half of the bearing is worn or damaged, both upper and
lower halves should be replaced.
Generally, if the lower half is suitable for use, the upper half should
also be suitable for us.