Your new vehicle comes with high-quality tires made by a leading tire manufacturer. If you ever have questions about your tire warranty and where to obtain service, see your GM Warranty booklet for details. For additional information refer to the tire manufacturer's booklet included with your vehicle's Owner's Manual.
Caution:
• Poorly maintained and improperly used tires are dangerous. • Overloading your tires can cause overheating as a result of too much
friction. You could have an air-out and a serious accident. See
Loading the Vehicle
. • Underinflated tires pose the same danger as overloaded tires. The resulting
accident could cause serious injury. Check all tires frequently to maintain the
recommended pressure. Tire pressure should be checked when your tires are cold. • Overinflated tires are more likely to be cut, punctured or broken by
a sudden impact, such as when you hit a pothole. Keep tires at the recommended pressure. • Worn, old tires can cause accidents. If your tread is badly worn, or
if your tires have been damaged, replace them.
Winter Tires
If you expect to drive on snow or ice covered roads often, you may want to get winter tires for your vehicle. All season tires provide good overall performance on most surfaces but they may not offer the traction you would like or the same level of performance as winter tires on snow or ice covered roads. If you choose to use winter tires:
| • | Use tires of the same brand and tread type on all four wheel positions. |
| • | Use only radial ply tires of the same size as your original equipment tires. |
See Buying New Tires .
Tire Sidewall Labeling
Useful information about a tire is molded into the sidewall. The following illustration is an example of a typical P-Metric tire sidewall.
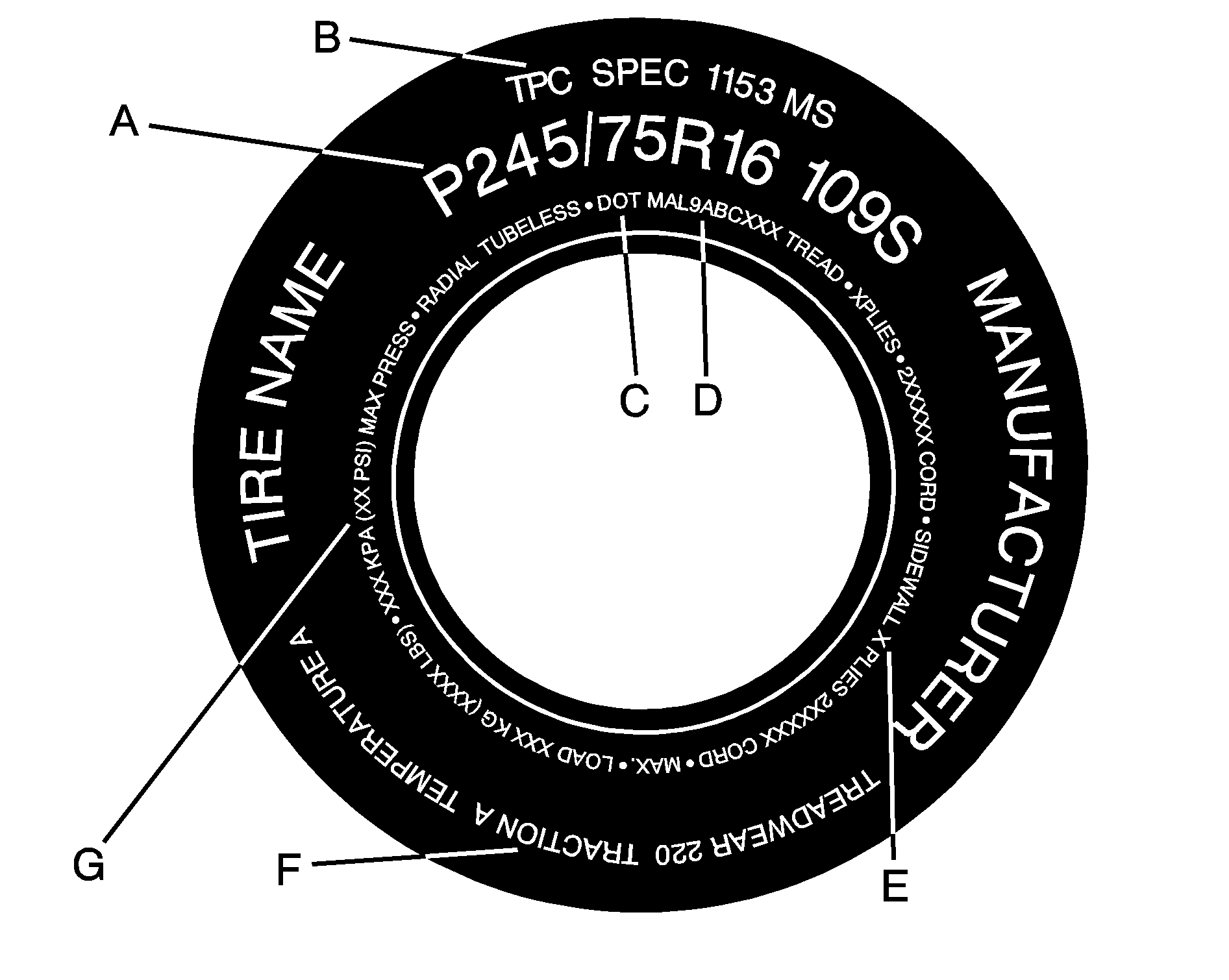
(A) Tire Size: The tire size code is a combination of letters and numbers used to define a particular tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type, and service description. See the Tire Size illustration later in this section for more detail.
(B) Tire Performance Criteria Specification (TPC Spec): Original equipment tires designed to GM's specific tire performance criteria have a TPC specification code molded onto the sidewall. GM's TPC specifications meet or exceed all federal safety guidelines.
(C) Department of Transportation (DOT): The Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
(D) Tire Identification Number (TIN): The letters and numbers following the DOT code are the Tire Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the tire, although only one side may have the date of manufacture.
(E) Tire Ply Material: The type of cord and number of plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG): Tire manufacturers are required to grade tires based on three performance factors: treadwear, traction, and temperature resistance. For more information, see Uniform Tire Quality Grading .
(G) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit: Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load. For information on recommended tire pressure see Inflation - Tire Pressure and Loading the Vehicle .
Tire Size
The following illustration shows, an example of, a typical passenger car tire size.
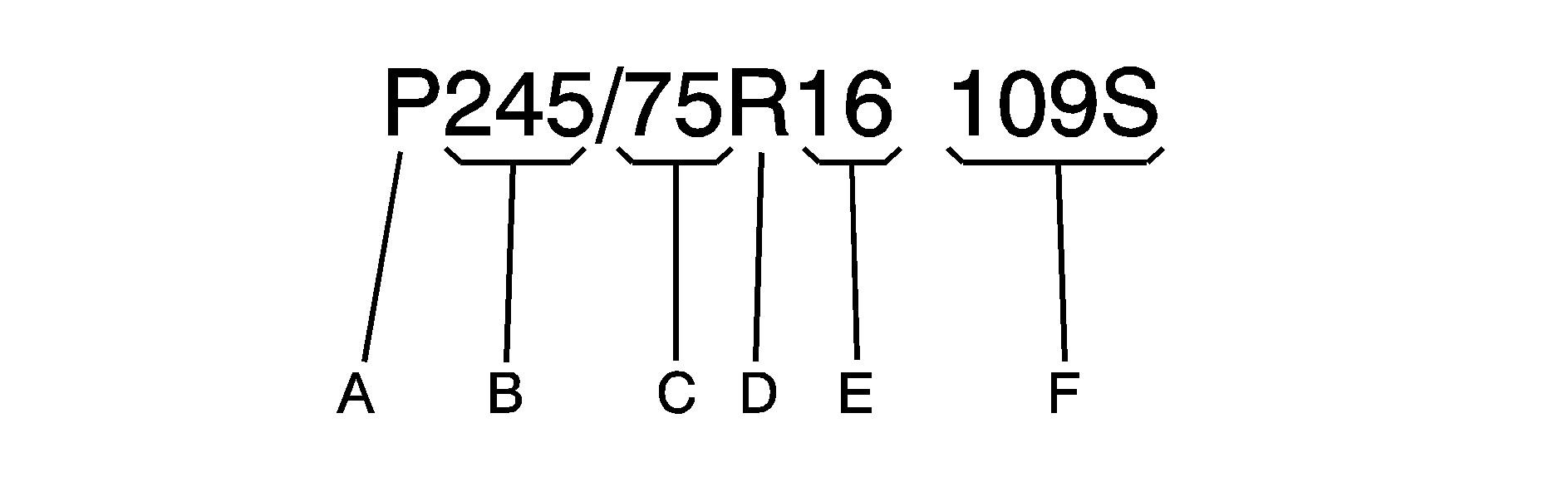
(A) Passenger (P-Metric) Tire: The United States version of a metric tire sizing system. The letter "P" as the first character in the tire size means a passenger vehicle tire engineered to standards set by the U.S. Tire and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width: The three-digit number indicates the tire section width in millimeters from sidewall to sidewall.
(C) Aspect Ratio: A two-digit number that indicates the tire height-to-width measurements. For example, if the tire size aspect ratio is 75, as shown in item C, of the illustration, it would mean that the tire's sidewall is 75 percent as high as it is wide.
(D) Construction Code: A letter code is used to indicate the type of ply construction in the tire. The letter "R" means radial ply construction; the letter "D" means diagonal or bias ply construction; and the letter "B" means belted-bias ply construction.
(E) Rim Diameter: Diameter of the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description: The service description indicates the load range and speed rating of a tire. The load index can range from 1 to 279. Speed ratings range from A to Z.
Tire Terminology and Definitions
Air Pressure: The amount of air inside the tire pressing outward on each square inch of the tire. Air pressure is expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or kilopascal (kPa).Accessory Weight: This means the combined weight of optional accessories. Some examples of optional accessories are, automatic transmission, power steering, power brakes, power windows, power seats, and air conditioning.
Aspect Ratio: The relationship of a tire's height to its width.
Belt: A rubber coated layer of cords that is located between the plies and the tread. Cords may be made from steel or other reinforcing materials.
Bead: The tire bead contains steel wires wrapped by steel cords that hold the tire onto the rim.
Bias Ply Tire: A pneumatic tire in which the plies are laid at alternate angles less than 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread.
Cold Inflation Pressure: The amount of air pressure in a tire, measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or kilopascals (kPa) before a tire has built up heat from driving. See Inflation - Tire Pressure .
Curb Weight: This means the weight of a motor vehicle with standard and optional equipment including the maximum capacity of fuel, oil and coolant, but without passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings: A code molded into the sidewall of a tire signifying that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation motor vehicle safety standards. The DOT code includes the Tire Identification Number (TIN), an alphanumeric designator which can also identify the tire manufacturer, production plant, brand and date of production.
GVWR: Gross Vehicle Weight Rating, see Loading the Vehicle .
GAWR FRT: Gross Axle Weight Rating for the front axle, see Loading the Vehicle .
GAWR RR: Gross Axle Weight Rating for the rear axle, see Loading the Vehicle .
Intended Outboard Sidewall: The side of an asymmetrical tire, that must always face outward when mounted on a vehicle.
Kilopascal (kPa): The metric unit for air pressure. There are 6.9 kilopascals (kPa) to one psi.
Light Truck (LT-Metric) Tire: A tire used on light duty trucks and some multipurpose passenger vehicles.
Load Index: An assigned number ranging from 1 to 279 that corresponds to the load carrying capacity of a tire.
Maximum Inflation Pressure: The maximum air pressure to which a cold tire may be inflated. The maximum air pressure is molded onto the sidewall.
Maximum Load Rating: The load rating for a tire at the maximum permissible inflation pressure for that tire.
Maximum Loaded Vehicle Weight: The sum of curb weight; accessory weight; vehicle capacity weight; and production options weight.
Normal Occupant Weight: The number of occupants a vehicle is designed to seat multiplied by 150 pounds (68 kg). See Loading the Vehicle .
Occupant Distribution: Designated seating positions.
Outward Facing Sidewall: The side of a asymmetrical tire that has a particular side that faces outward when mounted on a vehicle. The side of the tire that contains a whitewall, bears white lettering or bears manufacturer, brand, and or model name molding that is higher or deeper than the same moldings on the other sidewall of the tire.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire: A tire used on passenger cars and some light duty trucks and multipurpose vehicles.
Recommended Inflation Pressure: Vehicle manufacturer's recommended tire inflation pressure and shown on the tire placard. See Inflation - Tire Pressure and Loading the Vehicle .
Radial Ply tire: A pneumatic tire in which the ply cords that extend to the beads are laid at 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread.
Rim: A metal support for a tire and upon which the tire beads are seated.
Sidewall: The portion of a tire between the tread and the bead.
Speed Rating: An alphanumeric code assigned to a tire indicating the maximum speed at which a tire can operate.
Traction: The friction between the tire and the road surface. The amount of grip provided.
Tread: The portion of a tire that comes into contact with the road.
Treadwear Indicators: Narrow bands, sometimes called wear bars, that show across the tread of a tire when only 2/32 inch of tread remains. See When It Is Time for New Tires .
UTQGS: Uniform Tire Quality Grading Standards, a tire information system that provides consumers with ratings for a tire's traction, temperature, and treadwear. Ratings are determined by tire manufacturers using government testing procedures. The ratings are molded into the sidewall of the tire. See Uniform Tire Quality Grading .
Vehicle Capacity Weight: The number of designated seating positions multiplied by 150 pounds (68 kg) plus the rated cargo load. See Loading the Vehicle .
Vehicle Maximum Load on the Tire: Load on an individual tire due to curb weight, accessory weight, occupant weight and cargo weight.
Vehicle Placard: A label permanently attached to a vehicle showing the original equipment tire size and recommended inflation pressure. See Loading the Vehicle .
