| Table 1: | EGR Valve Terminal (Pin) Location |
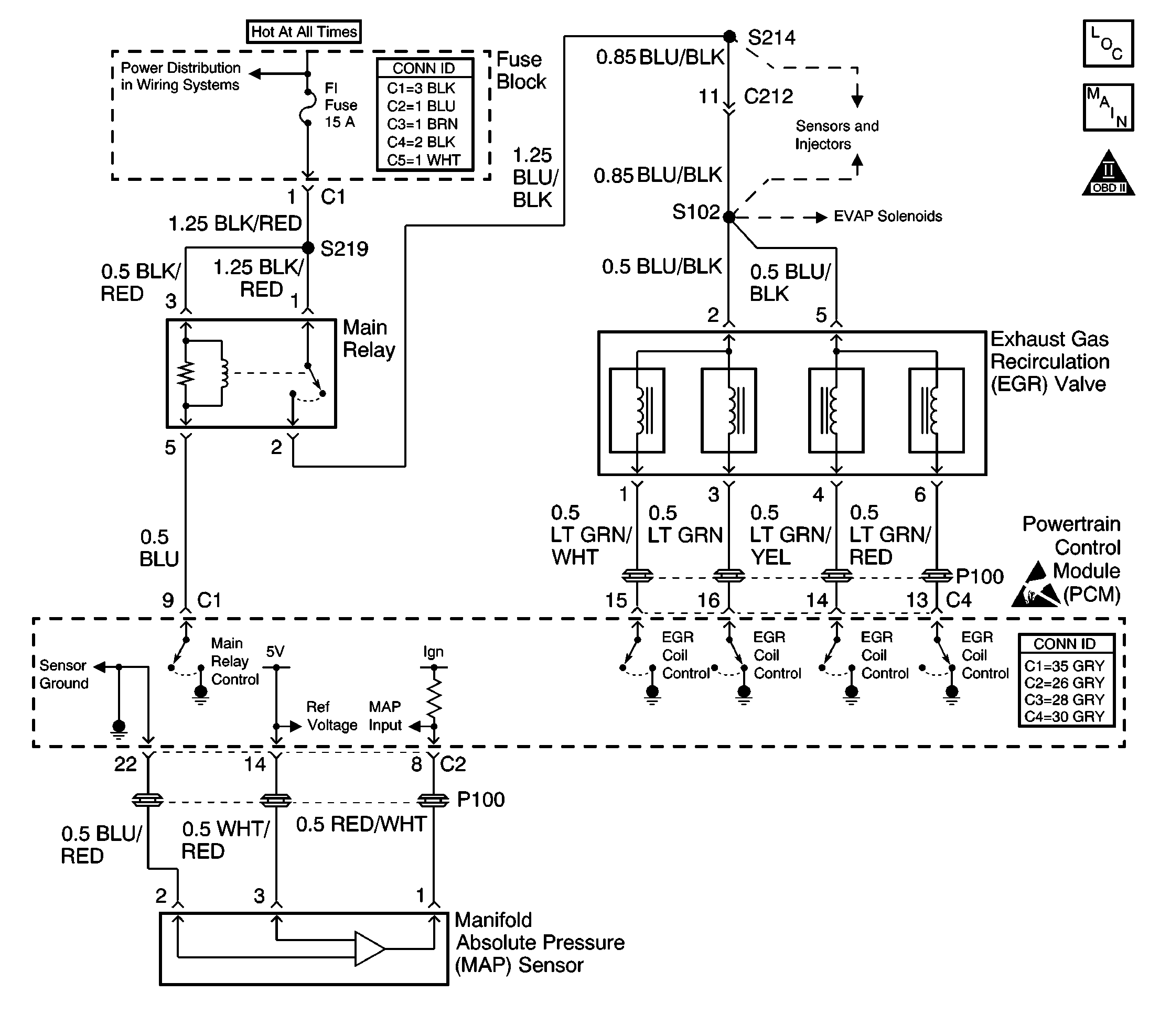
Circuit Description
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system controls the formation of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions by recirculating the exhaust gases into the combustion chamber. The EGR valve is a stepper motor design. The stepper motor moves a spring loaded plunger that controls the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. The plunger movement is controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM). By turning the stepper motor in different directions, the PCM controls the opening of the exhaust gas passage to the intake manifold. The stepper motor has four coil windings that control the motor movement.
Diagnostic Aids
A normal engine operating temperature is specified as 80°C (176°F) or more.
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the EGR control system electrical circuits.
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing an intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating of terminals |
| • | Broken electrical connector locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Improper terminal to wire connections |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals |
Refer to the following procedures in Wiring Systems:
Use the following table in order to locate the correct terminals to test during diagnosis. The table layout corresponds to the pin location of the EGR valve electrical terminals.
Lock Tab | ||
3 | 2 | 1 |
6 | 5 | 4 |
Test Description
The number below refer to the step number in the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step checks for an EGR valve that is leaking, stuck open, or turned on at idle. A normal engine operating temperature is specified as 80°C (176°F) or more.
-
This step checks the operation of the EGR valve. The EGR duty cycle output control is disabled by the PCM when any DTCs are stored and when engine temperature is less than 80°C (176°F).
-
This step checks for a physically stuck EGR valve or plugged EGR passages.
-
This step checks the ignition positive voltage supply to the EGR coils.
-
This step determines whether an electrical fault is the cause of the EGR valve staying open. A grounded EGR valve control circuit can cause the EGR valve to be open all the time.
-
This step checks for an EGR valve control circuit that is shorted to ground. If the circuit wiring is OK, a faulty PCM with an internally shorted circuit can cause the EGR valve to be open.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | ||||||||||
2 | Are DTC P0400 or DTC P0403 set? | -- | Go to DTC P0400 EGR Flow Malfunction or DTC P0403 Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid Control Circuit | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||
Does the engine run rough, or is the idle unstable? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 4 | |||||||||
Does the engine run rough or stall? | -- | System OK | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||
5 |
Does the EGR valve pass both tests? | 5 % | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||
6 |
Does the EGR valve pass both tests? | 5 % | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||
7 |
Does the EGR valve pass all the resistance tests? | 20-24 ohms at 20°C (68°F) | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 15 | |||||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate on both circuits? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 13 | |||||||||
With the engine running, disconnect the EGR valve electrical connector. Does the engine performance improve when the EGR valve is disconnected? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 11 | |||||||||
11 |
Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | ||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 16 | |||||||||
13 | Repair the ignition positive voltage supply to the EGR valve. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | ||||||||
14 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 16 | ||||||||
15 | Replace the EGR valve. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | ||||||||
16 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | ||||||||
17 | Operate the vehicle within the conditions in which the customer concern was first noticed. Is the customer concern still present? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
