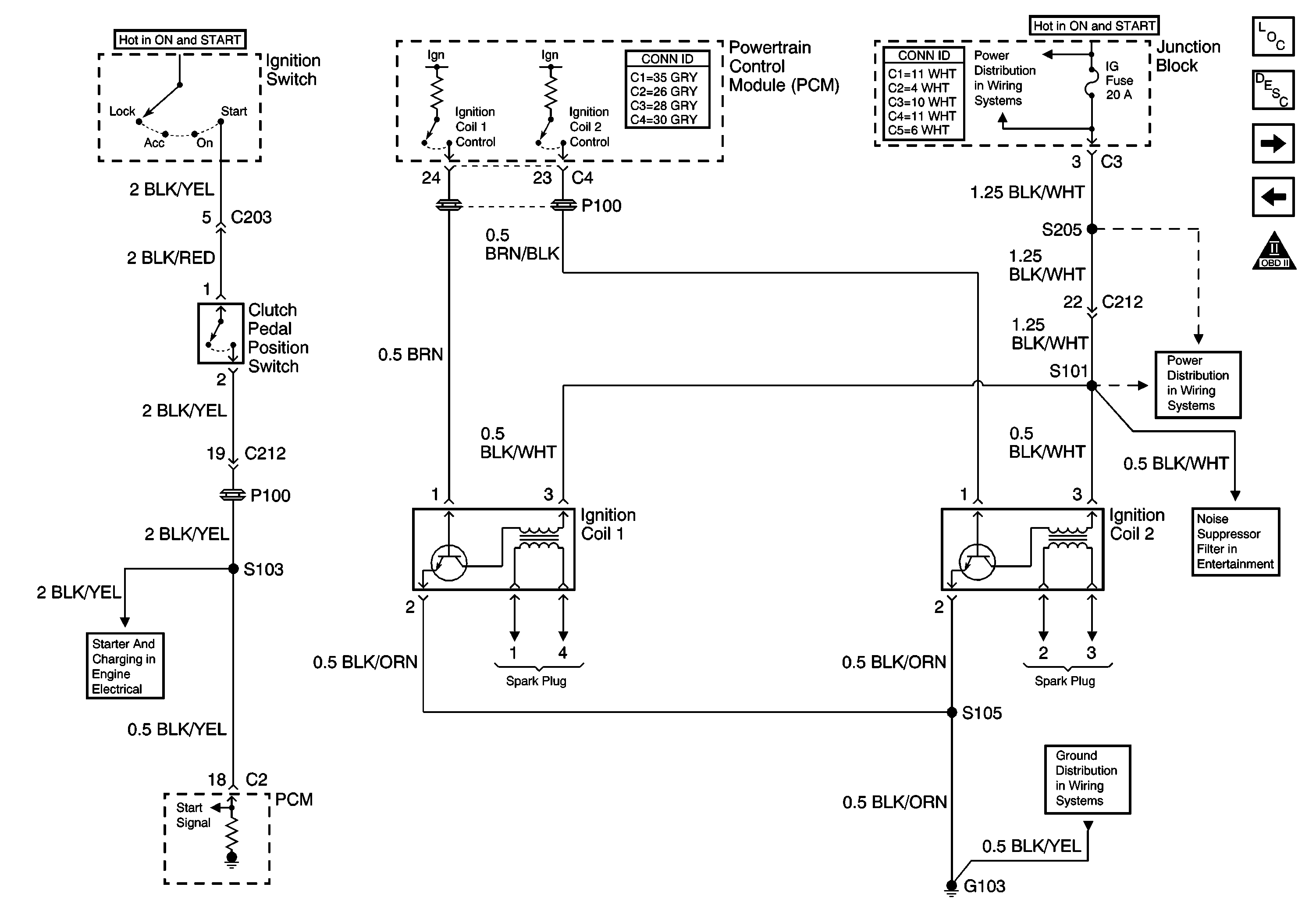
Circuit Description
The 1.6L ignition system has two ignition coils. The ignition coils have a pair of high voltage output terminals that provide spark to two engine cylinders at the same time. Battery voltage is applied to the ignition coils when the ignition switch is turned to the ON or START positions. The ignition control module circuitry within the coil assemblies toggles the primary windings of the ignition coil in order to induce a high voltage in the secondary windings of the ignition coil. The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the ignition event based on numerous inputs including the crankshaft position sensor. The high voltage induced in the secondary windings of the ignition coils is applied through the spark plug wires and coil boots to the spark plugs.
Diagnostic Aids
If the operation of the ignition system is intermittent, check for a reliable reference signal from the camshaft position (CMP) sensor while cranking the engine. The PCM relies on the CMP sensor for engine reference. Without continuous accurate reference signals, there is no reliable spark or fuel injector pulse. The scan tool engine speed display should be more than 200 RPM while cranking. If erratic values, such as sudden spikes in engine speed are displayed, the engine reference signal may not be stable enough for the engine to start and run properly. Inspect the CMP sensor signal circuit for electromagnetic interference (EMI) or poor electrical connections.
A vehicle that starts and runs after being brought to the shop for an engine cranks but will not run concern, may have an ignition system that is susceptible to moisture. Spray water on the ignition system components and wiring in order to check for an engine miss or stall.
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a problem in the ignition system electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for an intermittent condition. Refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
If there is a fault in the CMP sensor circuit, the ignition system can malfunction. Repair the cause of a DTC P0340 first.
-
This step checks for a condition that can cause a loss of spark, even though the test in step 3 indicated that there was good spark.
-
This step checks whether the engine will start and run. A repair that has been performed leading to this step may only have been a contributing cause of a no start condition. Returning to the Engine Cranks But Does Not Start diagnostic table will locate additional causes of the no start condition.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference:
| ||||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check--Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||
Install a scan tool and check for DTCs. Is a DTC P0340 set? | -- | Go to DTC P0340 | Go to Step 3 | |||||||||
3 |
Did the test of each cylinder indicate a good crisp blue spark while cranking the engine? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||||
4 | Inspect the ignition coils and spark plug boots for the following conditions:
Did you find any of the listed conditions? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||||
5 |
Did you replace a faulty part? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||||
6 |
Does the known good ignition coil assembly provide a crisp blue spark while cranking the engine? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||||
7 | Replace the faulty ignition coil assembly. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 15 | -- | ||||||||
8 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||
9 | Connect a test lamp from B+ to the ground circuit on the harness side of the ignition coil. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||
10 | Repair the open or the faulty connection in the ignition coil ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 15 | -- | ||||||||
11 | Repair the open in the ignition positive voltage circuit of the ignition coil. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 15 | -- | ||||||||
12 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 13 | ||||||||
13 |
Important:: The replacement PCM must be reprogrammed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 15 | -- | ||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 15 | -- | |||||||||
Does the engine start and run? | -- | Go to Step 16 | ||||||||||
16 | Check for DTCs. Are any DTCs set? | -- | System OK | |||||||||