The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated pressure relief valve consisting of a diaphragm (3), a spring (2), and a valve (4). The fuel pressure regulator keeps the fuel pressure applied to the fuel injector at a pressure much more than
the pressure in the intake manifold.
The pressure applied to chamber A (2) of the fuel pressure regulator is the intake manifold pressure. The pressure applied to chamber B (5) of the fuel pressure regulator is fuel pressure. When the fuel pressure rises at least 210 kPa (30 psi)
higher than the intake manifold pressure, the fuel pushes a valve in the regulator open and excess fuel (6) returns to the fuel tank via the fuel return pipe.
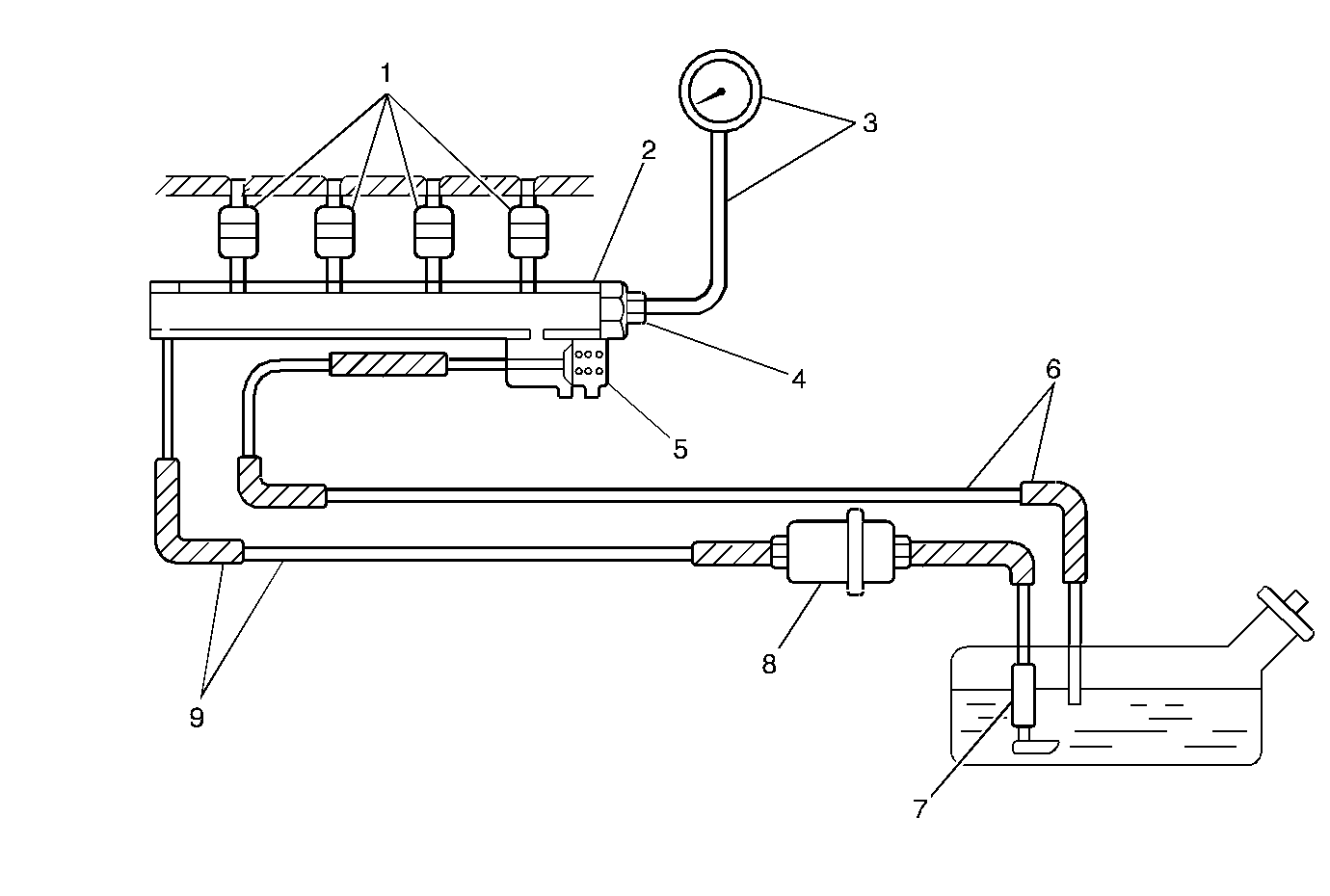
The fuel feed, return pipes and hoses carry the fuel from the fuel tank to the fuel injectors and back to the fuel tank. These pipes and hoses are attached to the chassis of the vehicle, and should be inspected periodically for kinks or dents that
may restrict the fuel flow.
The fuel vapor pipe and hoses carry the fuel vapors from the fuel tank to the evaporative emission canister. The fuel vapors are stored in the canister when the engine is not running. When the engine is running at the normal operating temperature
and the accelerator pedal is depressed, the powertrain control module (PCM) will command the evaporative emission canister purge valve to open and allow the stored fuel vapors to be purged into the intake manifold where they will be burned in the combustion
process.
The on-board refueling vapor recovery (ORVR) system is an on-board vehicle system designed to recover fuel vapors during the vehicle refueling operation. Instead of allowing fuel vapors to escape to the atmosphere the ORVR system transports the
vapor to the EVAP canister for use by the engine. The flow of liquid fuel down the fuel filler neck provides a liquid seal that prevents fuel vapor from leaving the fuel system. The ORVR system architecture varies from platform to platform. Some of the
items listed below are optional depending on the platform application. The following is a list of all the ORVR system components with a brief description of their operation:
The accelerator control system is cable-operated. When the accelerator pedal is depressed, the cable pulls the throttle lever open, increasing the throttle plate opening. When the accelerator pedal is released, the throttle lever spring pressure returns
the throttle lever to the idle position, decreasing the throttle plate opening.
The function of the fuel metering system is deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions. Fuel is delivered to each cylinder by the fuel injectors. The fuel injectors are controlled sequentially by the powertrain
control module (PCM). The PCM bases the control of the fuel injectors on several important engine parameters. These engine parameters include the following:
The two most important inputs for fuel control are the mass air flow (MAF) sensor and the fuel control heated oxygen sensors (HO2S). The MAF sensor provides the powertrain control module (PCM) with engine air intake quantity, while the fuel control
HO2S provides the PCM with exhaust stream oxygen content information. Determining air density is critical to proper air/fuel management. Air density is primarily derived from the MAF sensor input. The MAF sensor measures the air volume and determines
the air density. Larger volumes of air and denser air masses require additional fuel. The information from the MAF sensor is used by the PCM in order to modify the fuel injector pulse width.
The PCM modifies the air/fuel mixture by changing the injector pulse width signal sent to the injectors. By constantly measuring the air intake and the exhaust oxygen content and adjusting the injector pulse width, the air fuel ratio is kept very
close to the optimal 14.7:1. This is the range at which the three-way catalytic converter (TWC) operates most effectively and at which the emissions of this vehicle are kept to a minimum. The constant tailoring of the air/fuel ratio is based upon feedback
from the HO2S and is referred to as closed loop operation.