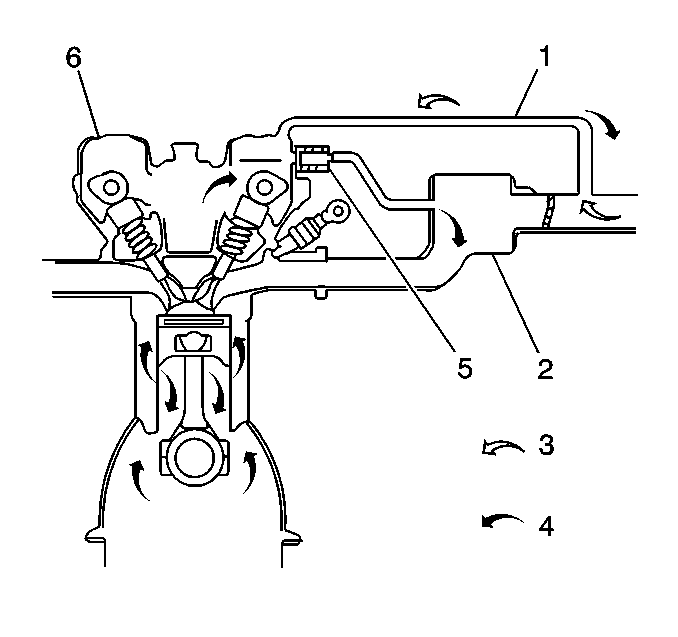
The compressed combustion gas
which escapes past the piston rings into the crankcase is known as blowby
gas. Blowby gas contains large amounts of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbon
(HC). The positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system prevents the blowby
gas from being emitted into the atmosphere. The PCV system routes crankcase
blowby gas back into the intake system where it becomes part of the combustion
process. The PCV system consists of the following components:
The primary control of engine crankcase blowby gas is the PCV valve.
The PCV valve meters the flow of blowby gas according to the manifold vacuum
signal.