The 5.3 Liter V8 Engine
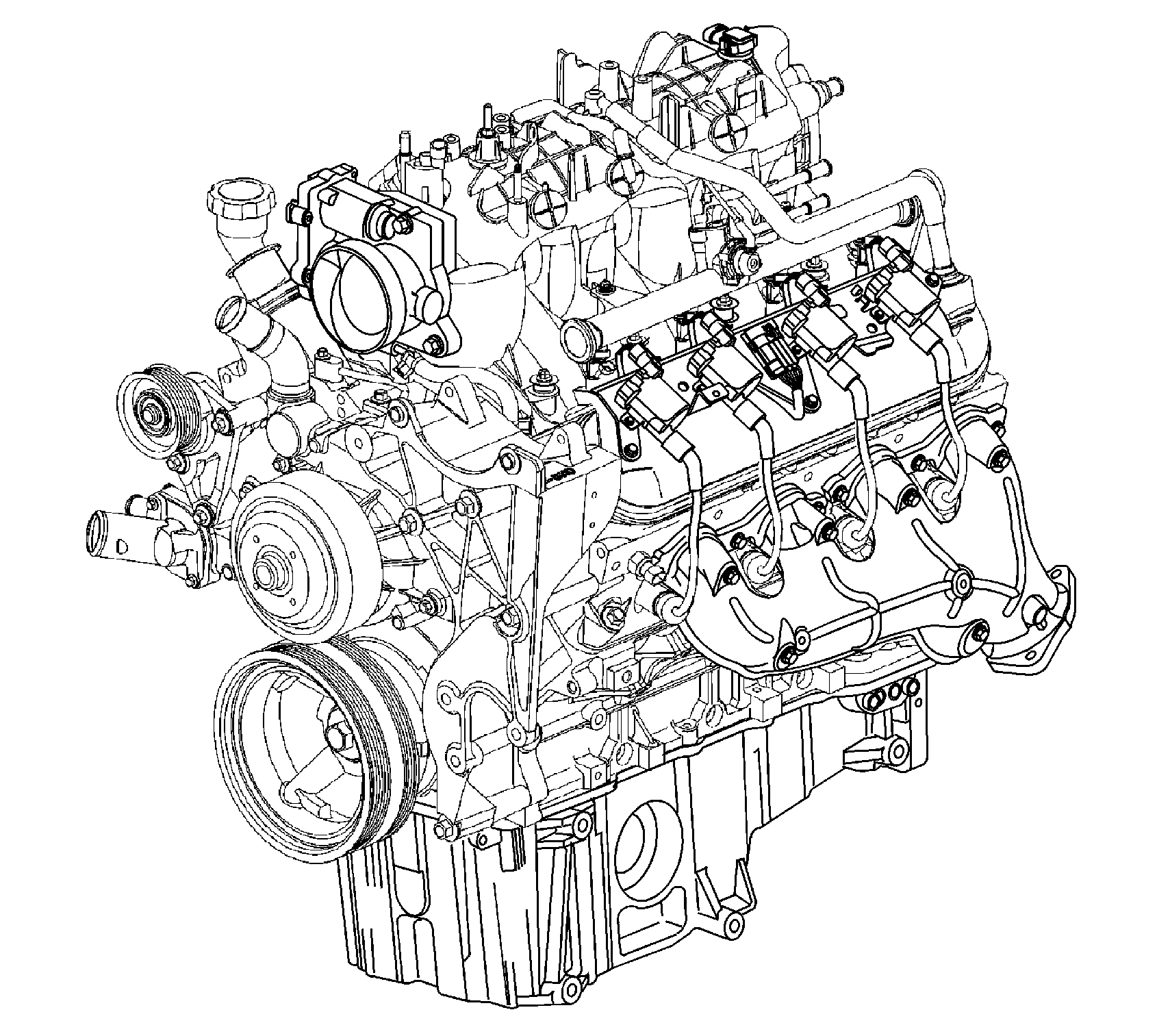
The 5.3 Liter V8 engine is identified as RPO LM4 VIN P.
Camshaft and Drive System
A billet steel one piece camshaft is supported by five bearings pressed into the engine block. The camshaft has a machined camshaft sensor reluctor ring incorporated between the fourth and fifth bearing journals. The camshaft timing sprocket is mounted to the front of the camshaft and is driven by the crankshaft sprocket through the camshaft timing chain. The splined crankshaft sprocket is positioned to the crankshaft by a key and keyway. The crankshaft sprocket splines drive the oil pump driven gear. A retaining plate mounted to the front of the engine block maintains camshaft location.
Crankshaft
The crankshaft is cast nodular iron. The crankshaft is supported by five crankshaft bearings. The bearings are retained by crankshaft bearing caps which are machined with the engine block for proper alignment and clearance. The crankshaft journals are undercut and rolled. The center main journal is the thrust journal. A crankshaft position reluctor ring is press fit mounted at the rear of the crankshaft. The reluctor ring is not serviceable separately. All crankshafts will have a short rear flange at the crankshaft rear oil seal area.
Cylinder Heads
The cylinder heads are cast aluminum and have pressed in place powdered metal valve guides and valve seats. Passages for the engine coolant air bleed system are at the front of each cylinder head. The valve rocker arm covers are retained to the cylinder head by four center mounted rocker arm cover bolts.
Engine Block
The engine block is a cam-in-block deep skirt 90 degree V configuration with five crankshaft bearing caps. The engine block is cast aluminum. The five crankshaft bearing caps each have four vertical M10 and two horizontal M8 mounting bolts. The camshaft is supported by five camshaft bearings pressed into the block. First design engine blocks have different drill and tap depths using both medium length 100 mm (3.94 in) and long 155 mm (6.1 in) M11 cylinder head bolts. Second design engine blocks use only the medium length 100 mm (3.94 in) bolt with a common drill and tap depth.
Exhaust Manifolds
The exhaust manifolds are a one piece cast iron design. The exhaust manifolds direct exhaust gasses from the combustion chambers to the exhaust system. Each manifold also has an externally mounted heat shield that is retained by bolts.
Intake Manifold
The intake manifold is a one piece composite design that incorporates brass threaded inserts for mounting the fuel rail, throttle body, evaporative emission (EVAP) solenoid and wire harness stud. Each side of the intake manifold is sealed to the cylinder head by a nonreusable silicone sealing gasket and nylon carrier assembly. The electronically actuated throttle body bolts to the front of the intake manifold. The throttle body is sealed by a one piece push in place silicone gasket. The fuel rail assembly with eight separate fuel injectors is retained to the intake by four bolts. The injectors are seated into their individual manifold bores with O-ring seals to provide sealing. A fuel rail stop bracket is retained to the rear of the left cylinder head by a mounting bolt. The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is installed and retained to the top rear of the intake manifold and sealed by an O-ring seal. The EVAP solenoid is mounted to the top front of the intake manifold and retained by one bolt. There are no coolant passages within the intake manifold.
Oil Pan
The structural oil pan is cast aluminum. Incorporated into the design are the oil filter mounting boss, drain plug opening, oil level indicator tube opening, and oil pan baffle. An internal tube assembly directs pressurized oil from the engine block to the oil filter which is mounted in the center area of the pan. Filtered oil is then returned to the engine block through the tube assembly into the engine block oil galleries. The alignment of the structural oil pan to the rear of the engine block and transmission bell housing is critical.
Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
The pistons are cast aluminum. The pistons use two compression rings and one oil control ring assembly. The piston is a low friction, lightweight design with a flat or recessed top and barrel shaped skirt. The piston pins are chromium steel, have floating fit in the piston, and are retained by a press fit in the connecting rod. The connecting rods are powdered metal. The connecting rods are fractured at the connecting rod journal and then machined for the proper clearance. 2004 applications use a piston with a graphite coated skirt. The piston, pin, and connecting rod are to be serviced as an assembly. The piston, pin, and connecting rod are to be serviced as an assembly.
Valve Rocker Arm Cover Assemblies
The valve rocker arm covers are cast aluminum and use a pre-molded silicon gasket for sealing. Mounted to each rocker cover are the coil and bracket assemblies. Incorporated into the left cover is the positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system passages. Incorporated into the right cover is the oil fill tube and engine fresh air passages.
Valve Train
Motion is transmitted from the camshaft through the hydraulic roller valve lifters and tubular pushrods to the roller type rocker arms. The nylon valve lifter guides position and retain the valve lifters. The valve rocker arms for each bank of cylinders are mounted on pedestals, pivot supports. Each rocker arm is retained on the pivot support and cylinder head by a bolt. Valve lash is net build.
