For 1990-2009 cars only
| • |
|
| • |
| - | Spark plug fouling - Colder plug |
| - | Pre-ignition causing spark plug and/or engine damage - Hotter plug |
| • |
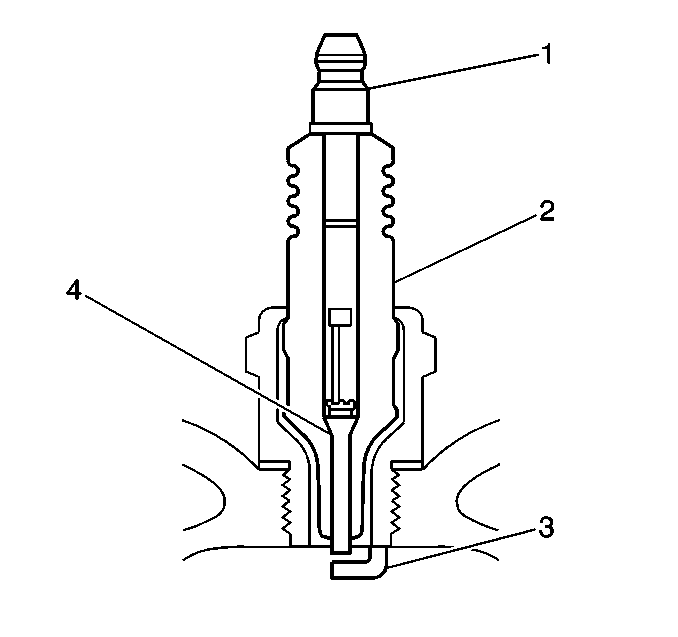
| - | Inspect for a bent or broken terminal post (1) |
| - | Test for a loose terminal post (1) by twisting and pulling the post. The terminal post should not move. |
| • |
|
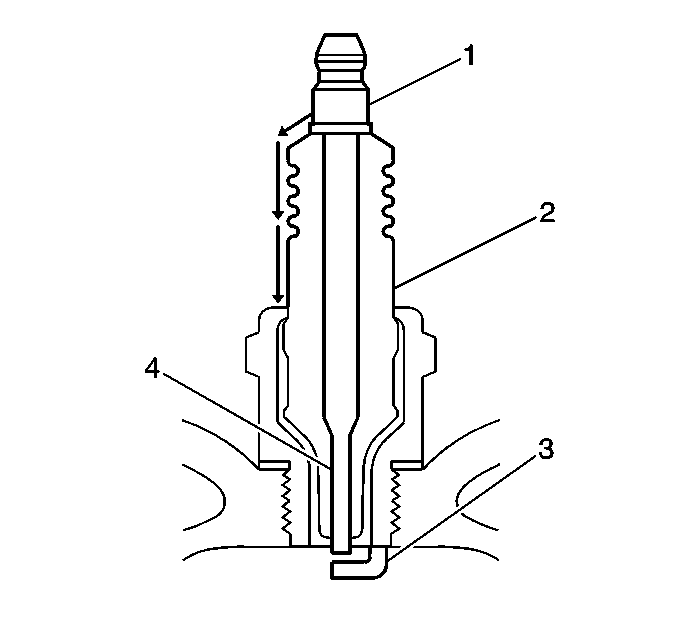
| - | Inspect the spark plug boot for damage. |
| - | Inspect the spark plug recess are of the cylinder head for moisture, such as oil, coolant, or water. A spark plug boot that is saturated will cause arcing to ground. |
| • |
|
| • |
|
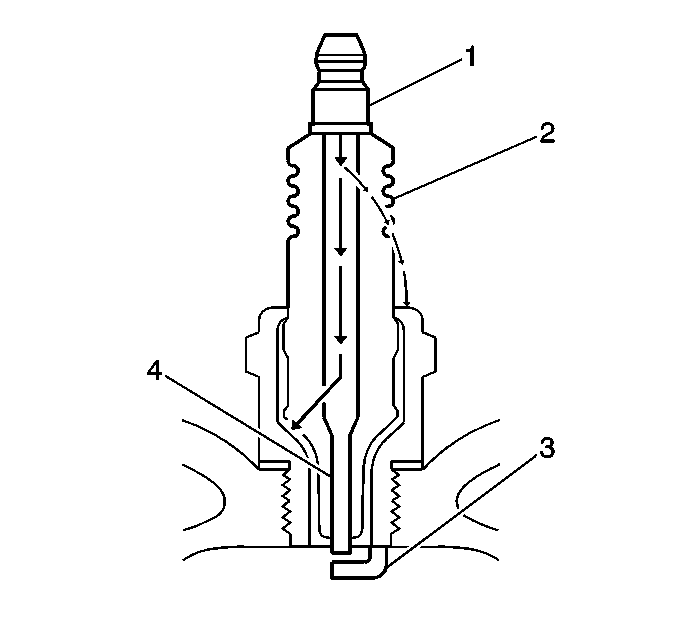
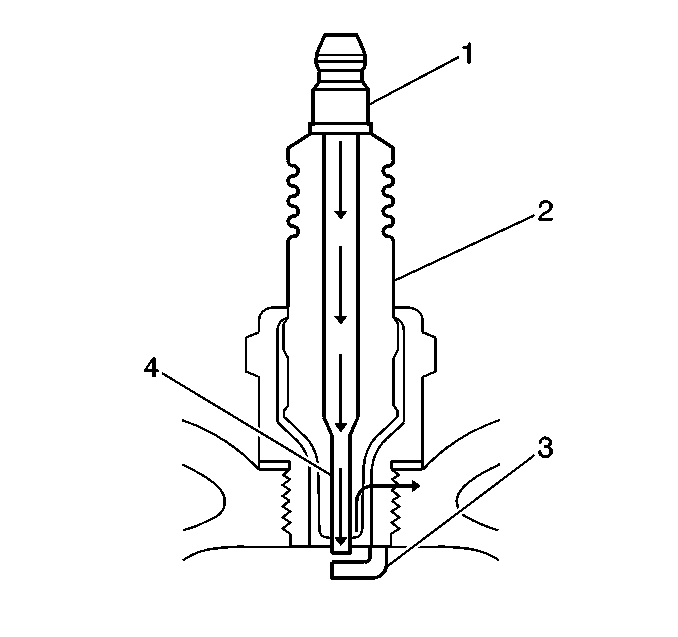
| - | Measure the gap between the center electrode (4) and the side electrode (3). Refer to Ignition System Specifications . An excessively wide electrode gap can prevent correct spark plug operation. |
| - | Inspect for the correct spark plug torque. Refer to Ignition System Specifications . Insufficient torque can prevent correct spark plug operation. An over torqued spark plug, causes the insulator (2) to crack. |
| - | Inspect for signs of tracking that occurred near the insulator tip instead of the center electrode (4). |
| - | Inspect for a broken or worn side electrode (3). |
| - | Inspect for a broken, worn, or loose center electrode (4) by shaking the spark plug. |
| • | A rattling sound indicates internal damage. |
| • | A looses center electrode (4) reduces the spark intensity. |
| - | Inspect for bridged electrodes (3,4). Deposits on the electrodes (3,4) reduce or eliminates the gap. |
| - | Inspect for worn or missing platinum pads on the electrodes (3,4), if equipped. |
| - | Inspect for excessive fouling. |
| • |
Visual Inspection
| • | Normal operation - Brown to grayish-tan with small amounts of white powdery deposits are normal combustion by-products from fuels with additives. |
| • | Carbon fouled - Dry, fluffy black carbon, or soot caused by the following conditions: |
| - | Rich fuel mixtures |
| • | Leaking fuel injectors |
| • | Excessive fuel pressure |
| • | Restricted air filter element |
| • | Incorrect combustion |
| - | Reduced ignition system voltage output |
| • | Weak ignition coils |
| • | Worn ignition wires |
| • | Incorrect spark plug gap |
| - | Excessive idling or slow speeds under light loads can keep spark plug temperatures so low that normal combustion deposits may not burn off. |
| • | Deposit fouling - Oil, coolant, or additives that include substances such as silicone, very white coating, reduces the spark plug intensity. Most powdery deposits will not affect spark plug intensity unless they form into a glazing over the electrode. |
