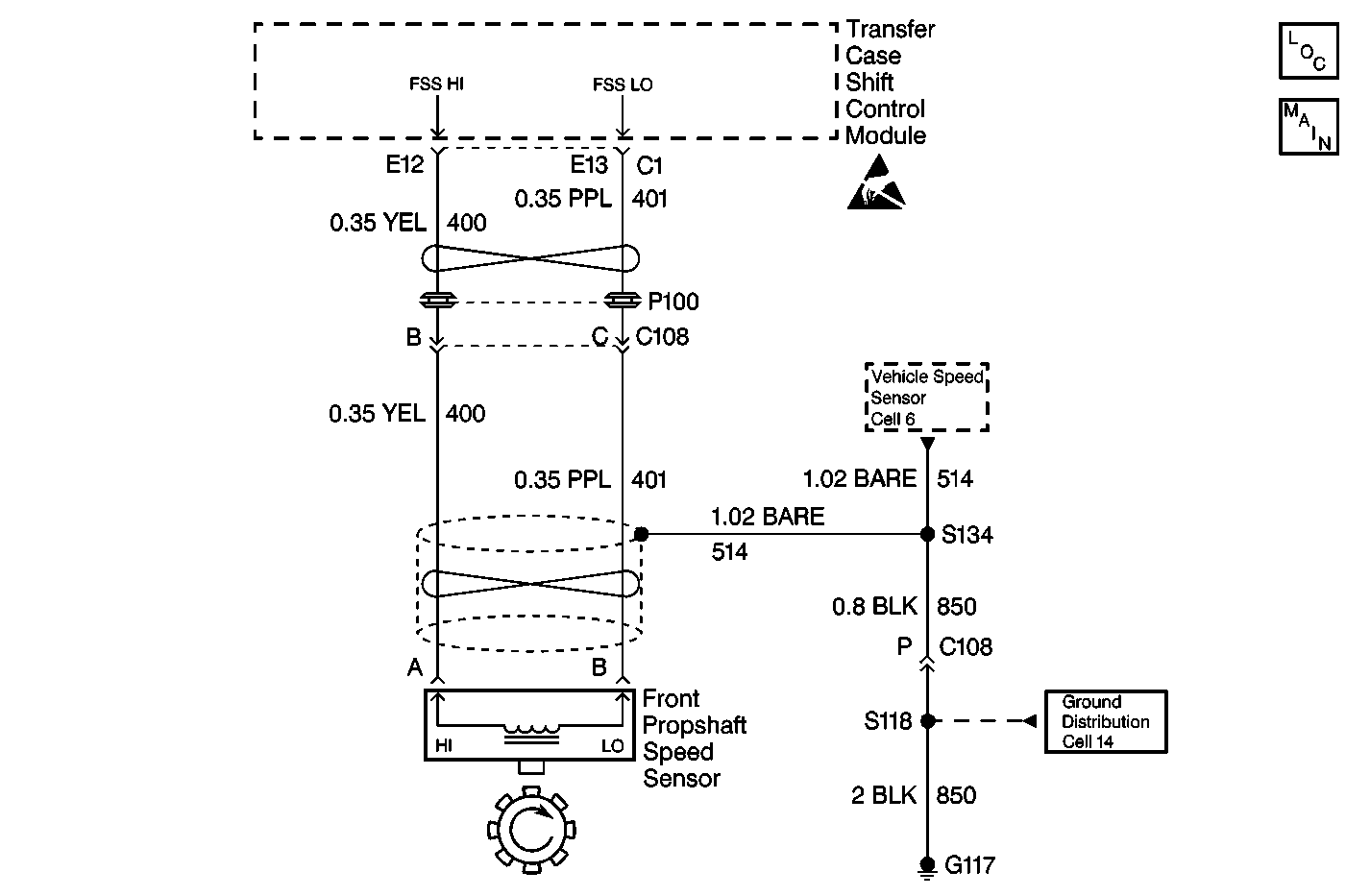
Circuit Description
The Front Propshaft Speed Sensor is a permanent magnet (PM) generator. The PM generator produces a pulsing AC voltage. The AC voltage level and number of pulses increases as speed increases. The module converts the pulsating AC voltage to a propshaft RPM which is used for calculations, and to monitor the difference between the front and rear propshaft speed. It is also used in the AUTO (Adapt) mode of operation to determine the amount of slip and the percent of torque to apply to the front axle. The module only looks at this input when the vehicle is in AUTO (Adapt) mode, 4H, and 4L ranges. The propshaft RPM can be displayed with a scan tool. The module only monitors this input when the vehicle is AUTO, 4H, or 4L.
This DTC detects an open, short to ground, or faulty sensor.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The system will log the DTC if the front propshaft input indicates a speed of less than 16 RPM for 10 seconds while all of the following are true:
| • | Transmission NOT in PARK/NEUTRAL |
| • | Engine is running |
| • | Front axle is engaged |
| • | Rear Propshaft speed exceeds 512 RPM |
| • | Vehicle speed on Class 2 Data bus exceeds 10 mph |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | All Shifts to AUTO (Adapt) mode will be disabled. If the current mode is AUTO, the system will not allow any further adaptive events (correct slip). |
| • | The SERVICE indicator (AWD/4WD) lamp will be latched on for the remainder of the current ignition cycle. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The transfer case shift control module will clear the DTC if the condition for setting the DTC no longer exists. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 100 consecutive ignition cycles without a fault present. |
| • | History DTCs can be cleared using a scan tool. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This step determines if the front speed sensor is able to generate AC current and indicates that both the sensor and wiring to the transfer case shift control module is good.
-
This step measures the internal resistance of the front speed sensor and whether or not it is within acceptable limits.
-
This step determines if CKT 401 has a short to voltage.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Transfer Case Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 |
Were there any DTCs found? | -- | Go to Powertrain OBD System Check | Go to Step 3 |
3 |
Are the RPM values within 10 percent of each other at the same speeds? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 4 |
Does the voltage vary between the specified values? | 0-0.5 V AC | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 5 | |
Is the resistance reading within the specified values? | 1300-2700 ohms | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 21 | |
6 | Measure the resistance between transfer case shift control module connector C1 terminals E12 and E13. Is the resistance reading less than the specified value? | OL | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 7 |
Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 0 V | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 8 | |
8 | Measure the resistance between the transfer case shift control module connector C1 terminal E12 and ground. Is the resistance reading less than the specified value? | OL | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 9 |
9 | Measure voltage between the transfer case shift control module connector C1 terminal E13 and ground. Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 0 V | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 10 |
10 | Measure the resistance between the transfer case shift control module connector C1 terminal E13 and ground. Is the resistance reading less than the specified value? | OL | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Measure the resistance between the transfer case shift control module connector C1 terminal E12 and front vehicle speed sensor terminal A. Is the resistance reading with in the specified value? | 0-2 ohms | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 13 |
12 | Measure the resistance between the transfer case shift control module connector C1 terminal E13 and front vehicle speed sensor terminal B. Is the resistance reading with in the specified value? | 0-2 ohms | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 14 |
13 | Repair an open in CKT 400 between the vehicle speed sensor and the transfer case shift control module. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Are the repairs complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
14 | Repair an open in CKT 401 between the vehicle speed sensor and the transfer case shift control module. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Are the repairs complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
15 | Repair a short between CKT 400 and CKT 401. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
16 | Repair a short to voltage condition in CKT 400. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Are the repairs complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
17 | Repair a short to ground condition in CKT 400. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Are the repairs complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
18 | Repair a short to voltage condition in CKT 401. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Are the repairs complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
19 | Repair a short to ground condition in CKT 401. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Are the repairs complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
20 | Replace the transfer case shift control module. Refer to Transfer Case Shift Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
21 | Replace the front speed sensor. Refer to Speed Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- |
22 | Reconnect all ATC system components, ensure that all the components are properly mounted. Have all the ATC components been reconnected and properly mounted? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
23 | Clear all the ATC DTCs. Are all the ATC DTCs cleared? | -- | -- |
