Refer to
Ignition System
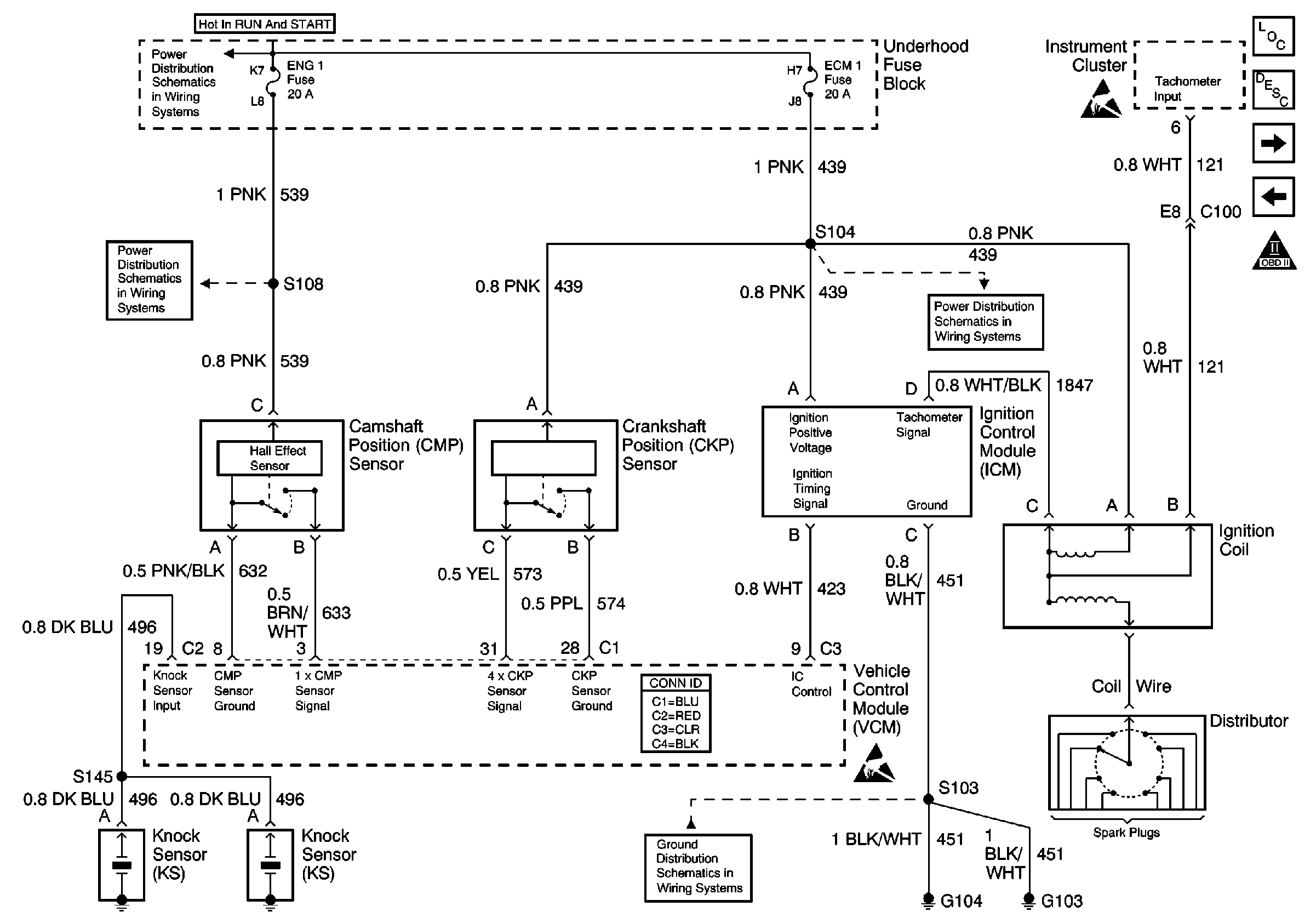
.
Circuit Description
The diagnosis for an engine that cranks but does not run must have three elements present before proceeding with the diagnostic table. The following conditions must exist:
| • | The battery must be adequately charged. |
| • | The engine cranking speed must be sufficient. |
| • | There must be an adequate amount of fuel in the fuel tank. |
Diagnostic Aids
If the fuel pump circuit and the ignition system are OK, perform the following procedures:
| • | Inspect for the following conditions: |
| - | An after-market vehicle theft deterrent system could cause a start then stall or a no start condition |
| - | Fouled spark plugs |
| - | An EGR valve stuck open |
| - | Water or foreign material in the fuel system |
| - | A grounded ignition control (IC) signal circuit may cause a No Start or a Start then Stall condition |
| - | Restricted exhaust system |
| • | Inspect the following ignition components: |
| - | A grounded tach circuit |
| - | Worn distributor cap |
| - | Worn distributor rotor |
| • | Inspect ignition wires by lightly spraying them with water in order to identify intermittant no starts |
Inspect the following base engine components if no fault was found in this diagnostic table:
| • | Cylinder valve timing |
| • | Loose or broken timing chain |
| • | Low compression |
| • | Worn camshaft lobes |
| • | Bent or burned intake or exhaust valves |
The VCM has integrated circuits that are fault protected, therefore if a circuit has failed, the integrated circuit may not be damaged. If that is the case, then the system will keep the circuit open until the condition in the circuit has been corrected.
Afterwards reinstall the VCM and check the circuit. Replace the VCM only if the circuit is still inoperative.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic tables.
-
If the engine starts, the problem could be intermittent. Basic engine mechanical problems, the vehicle theft deterrent (VTD) system, if equipped, and poor connections could cause a no start condition.
-
This step will determine if the cause of the no start or start and stall is related to the VTD.
-
If the signal is over 2.5 volts, the engine may be in the clear flood mode which will cause starting problems.
-
If the engine coolant sensor is below -30°C (-22°F), the VCM provides fuel for this extremely cold temperature which will severely flood the engine.
-
Voltage at the spark plug is checked using theJ 26792 spark plug tester tool. No spark indicates a basic ignition problem.
-
This test will determine if there is fuel pressure at the fuel injection unit and holding steady.
-
Use the J 34730-375 injector test lamp in order to test the injector circuits. A blinking lamp indicates that the VCM is controlling the injector.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Attempt to start the engine. Does the engine start and continue to run? | -- | Go to Symptoms | ||
Does the VTD fuel disabled parameter display active while you crank the engine? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Theft Deterrent in Theft Deterrent | ||
Monitor the TP sensor on the scan tool. With the throttle closed, is the TP sensor over the specified value? | 2.5 V | |||
Monitor the ECT sensor on the scan tool. Is the ECT sensor below the specified value? | -30°C (-22°F) | Go to DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit High Voltage | ||
Inspect for spark at two spark plug wires using the J 26792 spark plug tester. Is spark present at both spark plug wires? | -- | |||
Is the fuel pressure within the specified range? | 379-413 kPa (55-60 psi) | |||
Does the injector test lamp flash for each injector circuit? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
