High Pressure Regulator (HPR)
The high pressure regulator (HPR) is supplied with fuel from the CNG fuel tank. The HPR reduces CNG fuel pressure from 24 820 kPa (3,600 psi) to approximately 1 172 kPa (170 psi). It is mounted on a bracket inside the driver's side frame rail. To prevent freezing during pressure reduction, the HPR is heated with engine coolant supplied through hoses. The HPR has an internal 40 micron filter that must be serviced at specified intervals. Refer to Periodic Maintenance Inspection for service intervals.
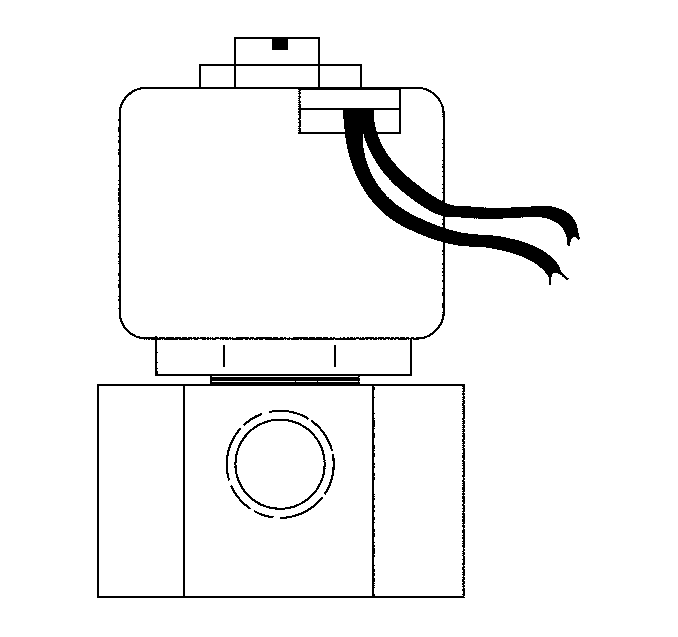
Low Pressure Lock-Off (LPL) Solenoid
The low pressure lock-off (LPL) solenoid is an electrically operated valve that allows gaseous fuel to flow to the low pressure regulator (LPR). The LPL solenoid is located in line between the high pressure regulator (HPR) and the LPR.
The LPL solenoid is controlled by the alternative fuel engine control unit (AF ECU). When the solenoid is energized with 12 volts, the valve opens, allowing fuel to flow to the LPR. The LPL is energized only when the engine is cranking or running. Any time the engine is stopped (ignition ON or OFF), the LPL closes to shut-off fuel supply.
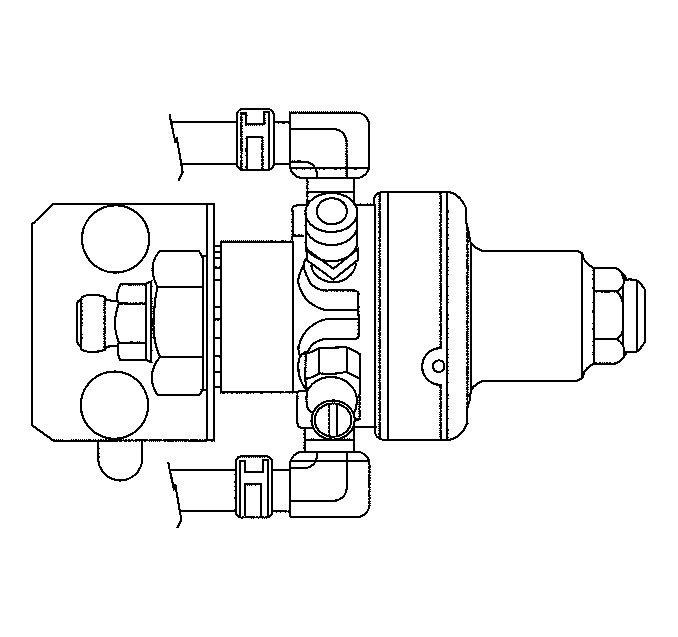
Low Pressure Regulator (LPR)
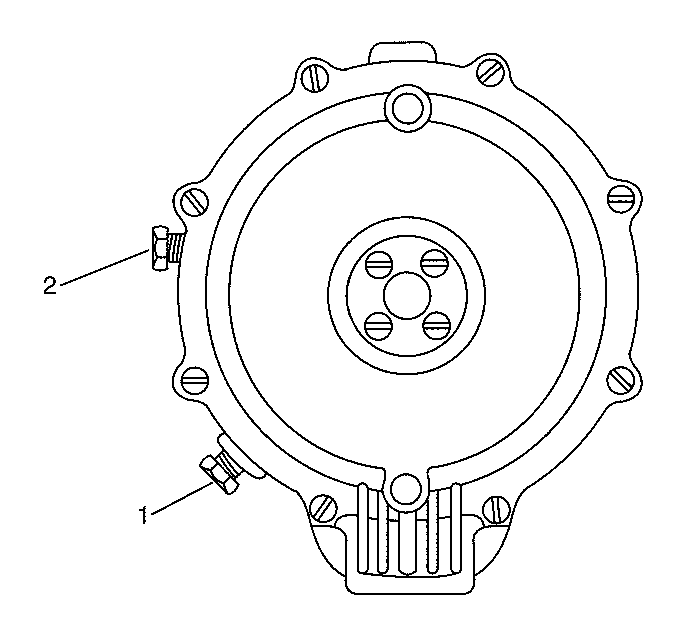
When the low pressure lock-off (LPL) solenoid is open, the low pressure regulator (LPR) receives CNG at an inlet pressure regulated by the HPR. The LPR is a two-stage pressure regulator which reduces the CNG fuel pressure from 1 172 kPa (170 psi) to approximately 1.5 kPa (0.21 psi). The LPR is located in line between LPL and the gas mass sensor/mixture control valve (GMS/MCV). The regulator has two 3.175 mm (1/8 in) NPT test ports. One test port monitors primary pressure (1), and the other test port monitors secondary pressure (2).
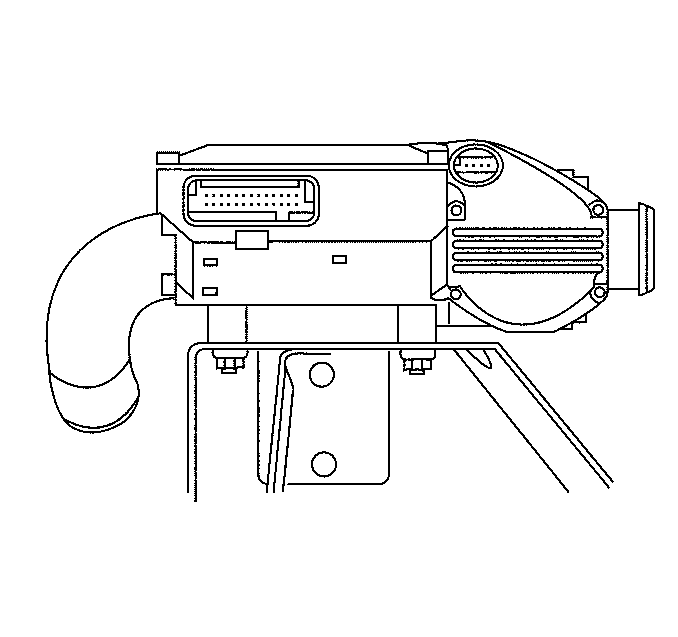
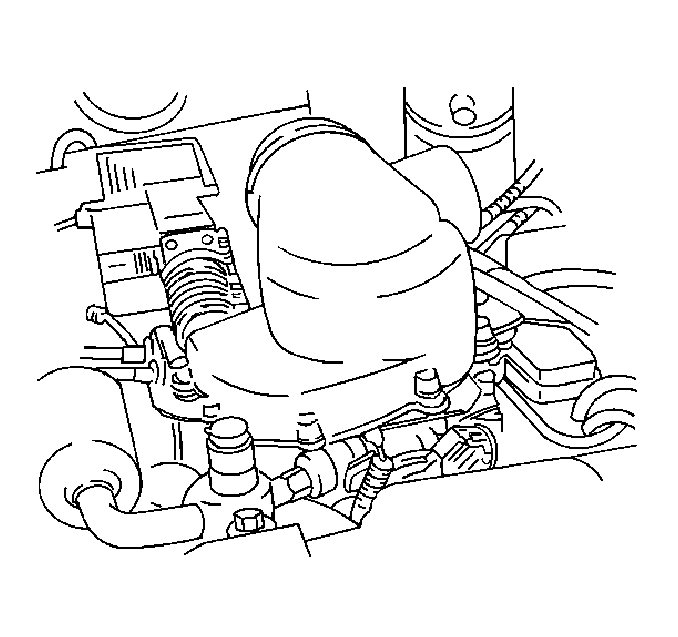
Gas Mass Sensor/Mixture Control Valve (GMS/MCV)
The gas mass sensor/mixture control valve (GMS/MCV) combines a hot wire anemometer and a magnetic rotary valve. The GMS/MCV is located in line between the low pressure regulator (LPR) and the gas distribution adapter (GDA).
The GMS measures the mass fuel flow and outputs a frequency to the AF ECU. The AF ECU processes this signal and determines the amount of fuel entering the engine. Comparing this with the optimum fuel flow rate required to obtain stoichiometry and using feedback from various engine sensors, the AF ECU modulates the MCV to maintain a stoichiometric air/fuel ratio.
Gas Distribution Adapter (GDA)
The gas distribution adapter (GDA) replaces the air inlet duct and is mounted to the throttle body. The GDA houses the gas ring which has machined slots in order to introduce the CNG into the intake air stream.
Fuel Hoses
The fuel hoses are low pressure, wire reinforced hoses. One fuel hose delivers CNG from the LPR to the GMS. The other fuel hose delivers CNG from the MCV to the GDA.
