Fill Valve
The fill valve receives fuel from the fill nozzle at the CNG fill station. It is located under the fill door on the top of the CNG fuel tank cover. The fill valve contains a filter element designed to trap contaminants. For 1997 vehicles, the filter is internal. For 1998 vehicles, the filter is external. This filter must be periodically inspected and cleaned. Refer to Periodic Maintenance Inspection in Maintenance and Lubrication for service intervals. An O-ring in the fill valve opening seals the connection between the valve and the fill nozzle during refueling. This O-ring must be inspected at each fuel fill and replaced if missing or damaged.
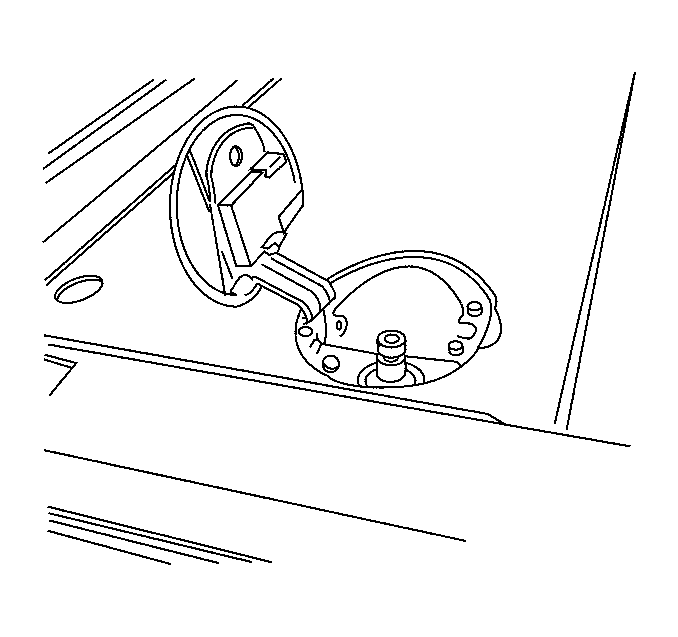
Fill Line
The fill line is constructed of 3/8 inch flexible, steel braided hose protected by a plastic cover. The line connects the fill valve to the CNG fuel tank.
CNG Fuel Tank
The CNG fuel tank is constructed of steel and wrapped in carbon fiber set in epoxy. Tank capacity is 50 L (13.2 gallons gasoline equivalent) at 24 820 kPa (3,600 psi) and 21°C (70°F). The tank is located at the front of the pickup box and is mounted in a two-piece bracket with two straps. The tank is protected by a cover in order to prevent damage from shifting cargo and ultraviolet radiation.
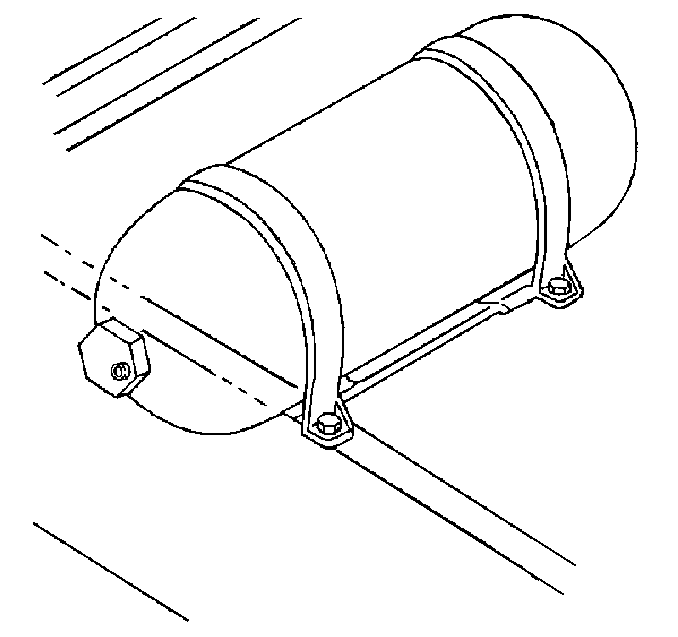
High Pressure Lock-Off (HPL)
The high pressure lock-off is a normally closed, solenoid-operated valve. It is mounted on the end of the CNG fuel tank and is not serviceable separately from the tank.
The HPL solenoid is controlled by the alternative fuel engine control unit (AF ECU). The valve opens when the solenoid is energized with 12 volts, allowing fuel to flow to the low pressure regulator (LPR). The HPL is energized only when the engine is cranking or running. Any time the engine is stopped (ignition ON or OFF), the HPL closes to shut off fuel supply.
CNG Fuel Tank Brackets
The CNG fuel tank brackets consist of a tank mounting frame, five tank support brackets, two tank straps, and two tank brackets. The tank mounting frame and tank support brackets mount in the floor of the pickup box. The tank brackets and tank straps secure the CNG fuel tank to the tank mounting frame. All of the brackets are steel.
Tank Cover
The CNG tank cover protects the tank from damage caused by shifting loads or ultraviolet radiation.
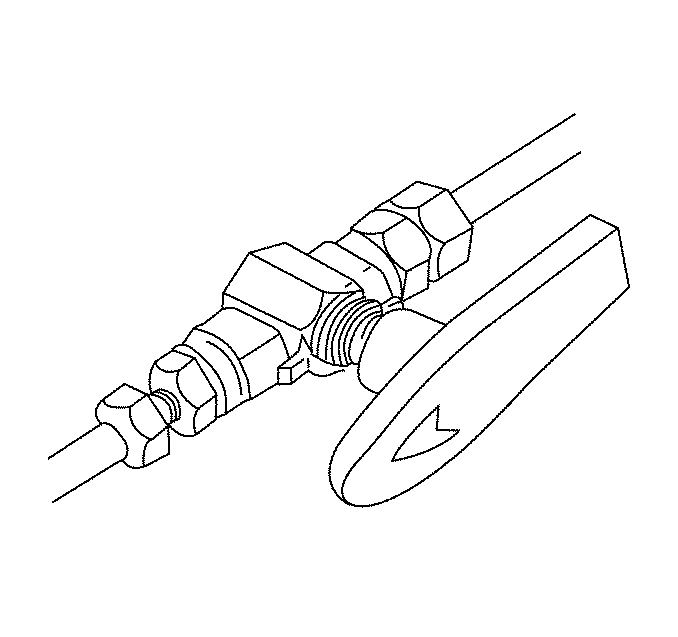
CNG Manual Shut-Off Valve (MSV)
The CNG manual shut-off valve allows fuel supply to be shut off for service during an emergency. The valve has a red handle and is mounted on the frame rail below the driver's door. Turning the handle ¼-turn clockwise closes the valve. Turning the handle ¼-turn counterclockwise opens the valve.
Fuel Sending Unit (FSU) (1997)
The fuel gauge receives a signal from the fuel sending unit (FSU) in order to display the CNG fuel level. The FSU converts tank pressure to a variable resistance. The resistance is high, and the fuel gauge pointer moves to its maximum position, which is F on the gauge face, when the CNG fuel tank is full (20 628 kPa [3,000 psi] at 21°C [70°F]). The resistance is low, and the fuel gauge pointer moves to its minimum position, which is E on the gauge face, when the CNG fuel tank is empty (less than 4 136 kPa [600 psi] at 21°C [70°F]). The FSU is mounted on the high pressure lock-off (HPL).
Remember that CNG is a gas. Its volume, therefore, is affected by changes in temperature and pressure. This will also affect the fuel gauge reading. The gauge may read past FULL (F) after refueling. The gauge may read a little less than FULL (F) after driving several miles. This "settling" of the CNG in the fuel tank is normal and does not indicate a problem with the FSU or the fuel gauge.
Fuel Pressure Sensor (FPS) and Fuel Temperature Sensor (FTS) (1998)
The fuel gauge receives a signal from the engine control unit (ECU) to display the CNG fuel level. The fuel pressure sensor (FPS) and the fuel temperature sensor (FTS) each output a voltage to the ECU. Using these voltages, the ECU calculates CNG fuel level and outputs a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal to the fuel gauge. This PWM signal corresponds to the amount of fuel in the CNG fuel tank.
The FPS is mounted on the high pressure lock-off (HPL). The FTS is part of the HPL and is mounted inside the CNG fuel tank.
Fuel Gauge Selector Switch and Fuel Indicator Lamp
The fuel indicator lamp shows the operator which fuel the vehicle is using. When the fuel indicator lamp is off, the vehicle is operating on CNG. When the fuel indicator lamp is on, the vehicle is operating on gasoline.
The fuel gauge selector switch allows the operator to check the fuel level in both the gasoline and CNG fuel tanks. If pressed while operating on CNG, the fuel gauge will indicate the amount of fuel in the gasoline fuel tank. If pressed while operating on gasoline, the fuel gauge will indicate the amount of fuel in the CNG fuel tank. During the fuel level check, the fuel gauge will display the fuel level for about ten seconds. The gauge will then return to its previous position.
CNG Fuel Lines
Caution: Natural gas is stored under high pressure. If a leak occurs, the high pressure could cause a personal injury. In order to prevent Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) fuel leaks, always replace the CNG fuel system O-rings during service.
Caution: Replace damaged Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) fuel lines. Do not repair the CNG fuel lines. Attempting to repair damaged CNG fuel lines could result in a serious personal injury.
All high and medium pressure fuel line connections are sealed with O-ring face seals (ORFS). Always replace the ORFS when a CNG fuel line union is disconnected for service. Verify that the O-ring is designed for CNG. Do not use a common automotive or plumbing O-ring. Lubricate the replacement ORFS with petroleum jelly or equivalent.
High Pressure Lines -- 6.4 mm (1/4 in) diameter, constructed of stainless steel tubing, pressure rating of 24 820 kPa (3,600 psi).
Medium Pressure Lines -- 9.5 mm (3/8 in) diameter, constructed of stainless steel tubing and flex hose, pressure rating of 1 380 kPa (200 psi).
