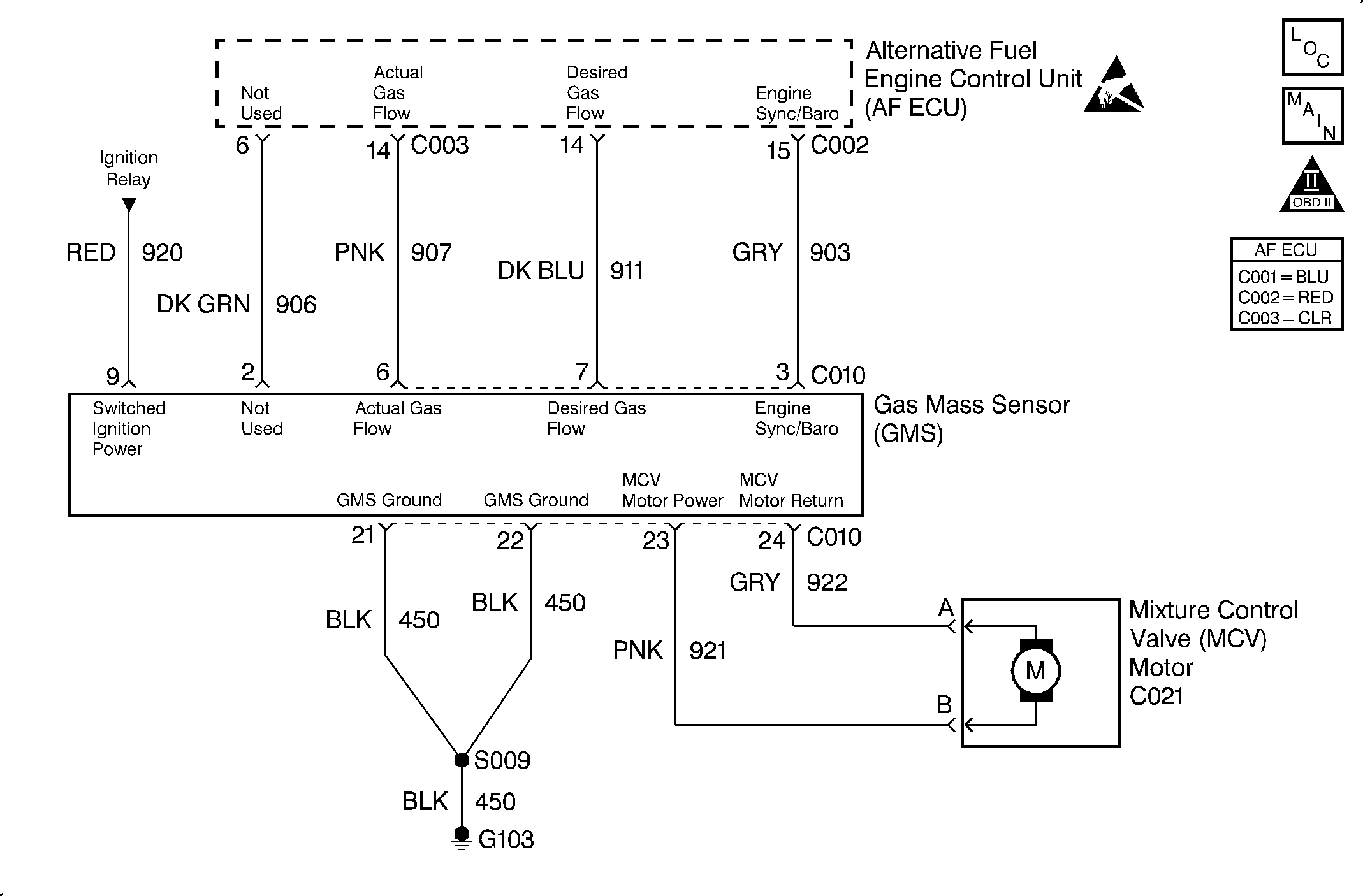
Circuit Description
The Gas Mass Sensor (GMS) provides a frequency signal proportional to the mass-flow of gaseous fuel entering the engine. The GMS actual gas signal varies from about 700 Hz at idle to about 2700 Hz at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
The GMS desired gas signal from the ECU is an input to the GMS which is a frequency ranging from about 700 Hz to 5000 Hz. This signal, when present, activates the GMS and commands a desired Mixture Control Valve (MCV) position.
The GMS actual gas signal is one of the most important inputs used by the ECU for fuel control while operating on CNG. The GMS provides fuel mass-flow feedback to the ECU which is used to precisely trim the position of the MCV for the required fuel flow rate.
This is a type A DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The following conditions will set the DTC:
| • | The vehicle is in the CNG operation mode. |
| • | The ECT is between 80°C (176°F) and 105°C (221°F). |
| • | The CNG fuel sending unit voltage is greater than 1.95 volts (fuel level above 1/8 tank). |
| • | The battery voltage is greater than 10 volts. |
| • | The engine speed is higher than 500 RPM. |
| • | None of the following DTCs are active: 14, 15, 16, 35, 36, 37, 42, 43, 44, 45, 51, 52, 62, 63, 64, 65. |
| • | There is an out of range signal. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECU will set DTC 53 and illuminate the MIL lamp after one fault has occurred if a low frequency failure is detected. The ECU will simultaneously initiate a fuel mode switch-over to gasoline. The vehicle will not attempt to operate on CNG again until the next key cycle.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
The ECU turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive driving trips without a fault condition present. A DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles (coolant temperature has risen 40°C (72°F) from the start-up coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 70°C (160°F) during that same ignition cycle) or the code clearing procedure has been used.
Diagnostic Aids
Always diagnose ANY VCM codes that are present before beginning this diagnostic procedure.
Diagnose and correct any ECU DTCs that are present pertaining to the O2 sensors, the MAF sensor and GMS DTC 51 and DTC 52 before attempting to diagnose DTC 53.
Any condition that results in incorrect fueling can cause DTC 53 to set. Check for the following conditions:
| • | Improper wire harness routing near secondary ignition components and other high voltage sources. |
| • | MAF sensor DTCs and wiring problems. |
| • | O2 sensor DTCs and wiring problems. |
| • | Malfunctioning EVAP system. |
| • | Incorrect CNG fuel system pressure. |
| • | Inspect the harness for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal to wire connection |
| - | A damaged harness |
Important: The GMS actual gas flow and desired gas flow frequencies cannot be monitored in the gasoline mode at any time. These frequencies cannot be monitored in the CNG mode with the Key On/Engine Off. The signals will only be present while operating on CNG and only with the engine in the crank or run modes.
Since DTC 53 causes a switch-over to gasoline when it sets, the conditions that cause it may be monitored before the switch-over by using a Tech 2 scan tool to monitor MAF and a DVOM to monitor GMS actual gas circuit frequency. Compare the readings according to the diagnostic high/low limits in the following table:
MAF g/sec | GMS Ideal Hz* | High Limit Hz | Low Limit Hz |
|---|---|---|---|
10 | 955 | 1067 | 795 |
20 | 1172 | 1317 | 985 |
30 | 1325 | 1473 | 1112 |
40 | 1438 | 1600 | 1212 |
50 | 1526 | 1724 | 1290 |
75 | 1733 | 1965 | 1455 |
100 | 1919 | 2188 | 1582 |
150 | 2207 | 2463 | 1792 |
200 | 2415 | 2754 | 1984 |
*Actual gas circuit frequency output. | |||
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This step visually and physically inspects the items that can cause a lean condition in order to determine the cause of the mis-fueling.
-
This step inspects for HO2 sensor faults by operating the vehicle on gasoline and interrogating the VCM for DTCs.
-
This step inspects for a fault in the EVAP system which can cause DTC 53 to set.
-
This step inspects for HO2 sensor wiring problems.
-
This step inspects for correct fuel system pressures.
-
This step inspects the GMS ground connection.
-
This step inspects for improper routing of the wire harness.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Alternative Fuels (AF) Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Alternative Fuels (AF) Powertrain On Board (OBD) System Check | ||||||||||||||||||||
Visually and physically verify the following items:
Was a repair made? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
The fuel indicator light will remain OFF due to the removal of the CNG system fuse. Was a problem found? | -- | Go to the applicable VCM DTC table in Engine Controls - 5.0, 5.7L in the C/K Truck Service Manual | Go to Step 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Perform the AF Fuel System Diagnosis. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . Was a problem found and repaired? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Perform the EVAP Control System Diagnosis. Refer to EVAP Control System Diagnosis in Engine Controls - 5.0, 5.7L in the C/K Truck Service Manual. Was a problem found and repaired? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Was a problem found? | 0.5 ohms | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
Was a problem found? | 0.5 ohms | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Does the DVOM read within the specified range? | 11-13 V | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Is there continuity? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||
11 | Make the necessary wiring repairs. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis in the C/K Truck Service Manual. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
12 | Replace the GMS/MCV. Refer to Gas Mass Sensor/Mixture Control Valve and Mounting Bracket Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
13 |
Did the MIL illuminate and the DTC set? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||
14 | Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
