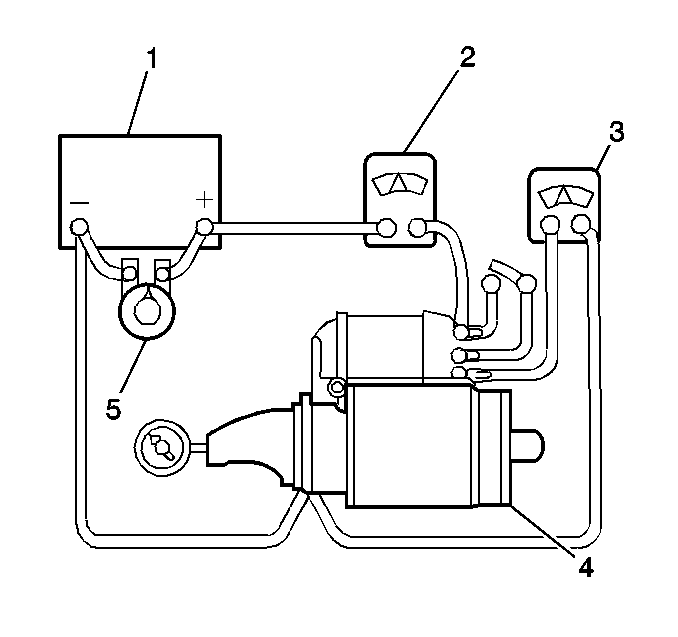
- Connect a voltmeter from the motor terminal to the motor frame.
On starter motors with ground terminals, connect the voltmeter to the
ground terminals rather than the frame.
- Use an RPM indicator in order to measure pinion speed.
- Connect the motor and an ammeter in series with the following
components:
| • | A fully charged battery of the specified voltage |
| • | A switch in the open position from the solenoid battery terminal
to the solenoid switch terminal. |
- Close the switch.
- Compare the following measurements with the no load test specified
values for the 28-MT and 37-MT Starter Motors in
Starter Motor Usage
:
- Evaluate the measurements by understanding that it is not necessary
to obtain the exact voltage specified. A good reading can be made by understanding
that if the voltage is slightly higher, the RPM will be slightly higher
and the current will remain basically unchanged
- Use the following procedure in order to obtain the exact specified
voltage (if desired):
| 7.1. | Connect a carbon pile across the battery. |
| 7.2. | Compare the reduced voltage with the no load test specified values
for the 28-MT and 37-MT Starter Motors in
Starter Motor Usage
: |
- Disconnect the circuit only with the switch open.
- Use the following information in order to interpret the test results:
| 9.1. | Rated current draw and no-load speed indicate normal condition
of the starter motor. |
| 9.2. | Low free speed and high current draw indicate the following conditions: |
| • | Tight, dirty, or worn bearings, a bent armature shaft or loose pole
shoes allow the armature to drag. |
| • | Inspect a shorted armature on a growler after disassembly. |
| • | Grounded armature fields |
| • | Verify the grounded armature after disassembly. |
| 9.3. | Failure to operate with no current draw indicates the following
conditions: |
| • | A direct ground exists in the terminal or fields. |
| • | Seized bearings should have been noted by hand turning the armature
by hand. |
| 9.4. | Failure to operate with no current draw indicates the following
conditions: |
| • | An open field circuit can be checked after disassembly by inspecting
the internal connections and tracing the circuit with a self-powered test
lamp. |
| • | Inspect the commutator for badly burned bars. |
| • | Broken brush springs, worn brushes |
| • | High insulation between the commutator bars or other causes which would
prevent proper contact between the brushes and the commutator. |
| 9.5. | Low no-load speed and low current draw indicate a higher internal
resistance due to the following conditions: |
| • | Broken brush springs, worn brushes |
| 9.6. | High free speed and high current draw indicate shorted fields.
If shorted fields are suspected, replace the field coil assembly and inspect
for improved performance. |

