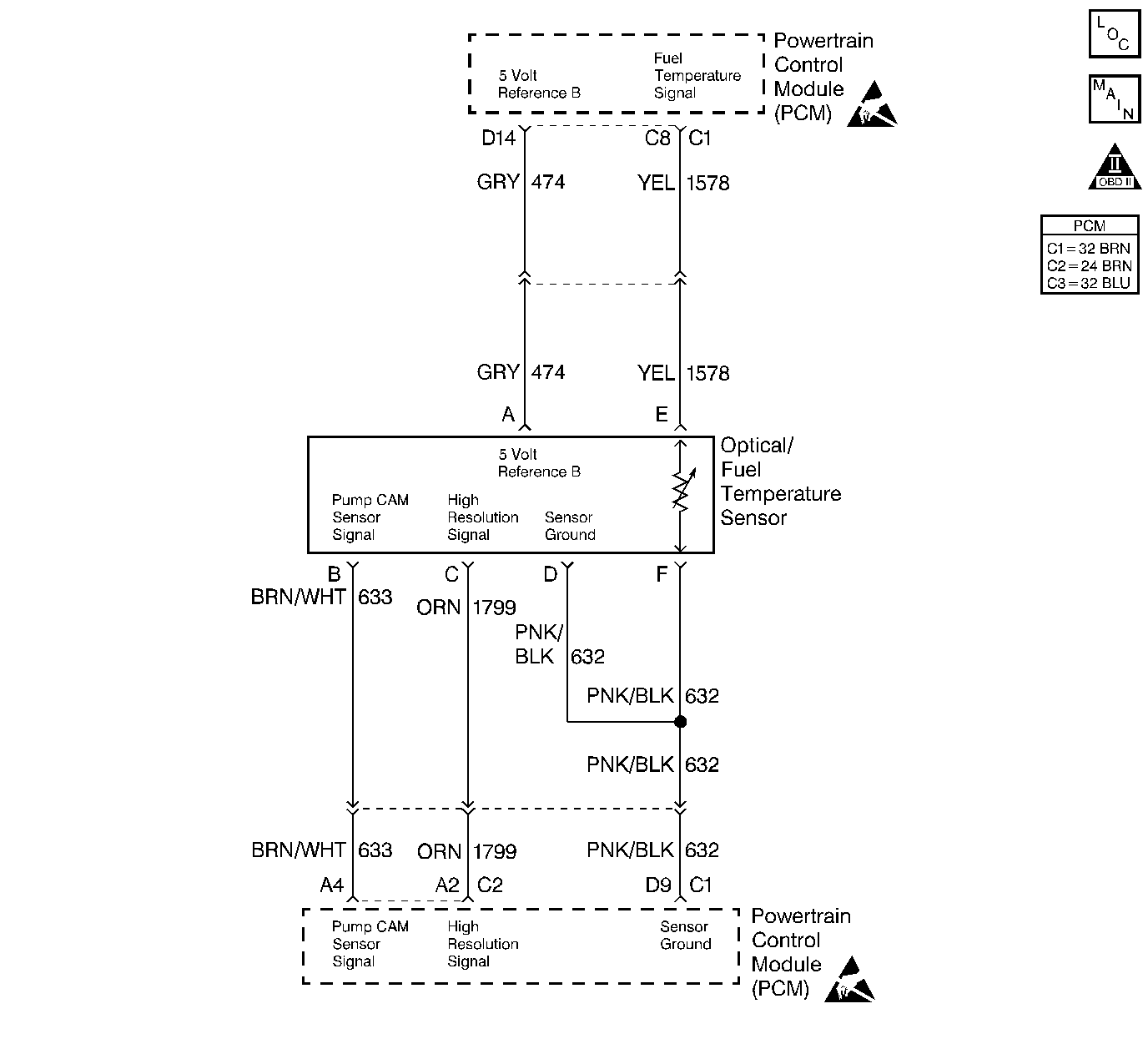
Circuit Description
The optical sensor provides a pump cam signal to the PCM by counting the pulses on the sensor which is disk located inside of the injection pump. The pump cam is one of the most important inputs by the PCM for fuel control and timing. This test monitors the number of crankshaft position pulses that have occurred since the last cam pulse. The physical one to one correspondence between the pump cam and the crankshaft implies that if more crank pulses are detected than cam pulses, the cam pulses have been missed.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Eight consecutive cam pulses are missing.
or
An average of eight cam pulses are missing.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on the first drive trip the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, this information stores in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL off after three consecutive trips without a fault condition. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up cycles during which the diagnostic does not fail (the coolant temperature has risen 5°C (40°F) from the start up coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 71°C (160°F) during that same ignition cycle). |
| • | Use of a scan tool will clear the DTC codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Intermittent DTCs (P0251, P0370 and P1216) may be caused by air entering the fuel system when fuel levels get below 1/8 of a tank while performing hard acceleration or turning maneuvers. Its also possible that a P0251, P0370 and P1216 will set if vehicle has run out of fuel. Customer driving habits should be checked to determine if vehicle has been performing in these manners. If it has been determine that the vehicle has been performing in these conditions, bleed fuel system of all air and test drive vehicle.
When the PCM is in backup fuel, fast idle and poor performance problems will exist.
An intermittent condition may be caused by the following:
| • | Poor connections. |
| • | A rubbed through wire insulation. |
| • | A broken wire inside of the insulation. |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This step will determine if this is a hard or intermittent DTC.
-
This step will determine if there is a 5 volt reference.
-
This step will check to see if the sensor is sending a signal back to the PCM.
-
The PCM supplies 5 volts on the signal circuit. This step determines if that voltage is present, not present, or too much voltage is present.
-
This step determines if the signal circuit is shorted to 5V. A normal CAM signal circuit will have 3-5mA. Any reading over 50mA indicates a short to 5V.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing any DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save freeze frame and failure records for reference, as the scan tool loses data when using the Clear Info function. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 | Is the DTC P0370 set also? | -- | Go to DTC P0370 Timing Reference High Resolution System Performance | |
Does scan tool display the specified value? | 8 Counts | |||
4 | The DTC is intermittent. If no additional DTCs are stored, refer to Diagnostic Aids. If additional DTCs were stored refer to the applicable DTC table(s) first. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
Is the voltage within the specified value? | 4.8-5.2 V | |||
6 | Probe the sensor ground circuit with a test light connected to B+ at the harness connector. Is the test light ON? | -- | ||
Is the Hertz reading at the specified value? | 60 Hz (± 3 Hz) | |||
8 |
Was the Optical sensor 5 volt reference circuit open or shorted to ground? | -- | ||
9 |
Was a repair performed? | -- | ||
10 | Check the Optical/Fuel temperature 5 volt reference circuit for a poor connection at the PCM and replace terminal if necessary. Did the terminal require replacement? | -- | ||
Is the voltage within the specified value? | 4.8-5.2 V | |||
12 | Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 4.8-5.2 V | ||
13 | Repair the short to battery/ignition voltage on the CAM signal circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 |
Was the CAM signal circuit open or shorted to ground? | -- | ||
15 | Check for a proper connection at the PCM harness terminal and replace the terminal if necessary. Did the terminal require replacement? | -- | ||
With a DMM J 39200 set to the mA scale, measure the current between the CAM signal circuit and the ground circuit at the Optical/Fuel temperature sensor electrical connector. Is the current less than the specified value? | 50 mA | |||
17 | Repair the short to reference voltage on the CAM signal circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
18 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
19 |
Important: The new injection pump must be timed. Refer to Fuel Injection Pump Timing Adjustment . Replace the injection pump. Refer to Fuel Injection Pump Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
20 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
21 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
22 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
