Coolant Test
Tools Required
| • | J 26568 Coolant Tester Centigrade |
| • | J 23688 Coolant Tester Fahrenheit |
Inspect the color, the texture and the odor of the coolant in order to detect any contamination.
The following materials may cause contamination:
| • | Fuel |
| • | Engine oil |
| • | Automatic transmission fluid |
Repair any contamination in order to prevent internal damage to the engine.
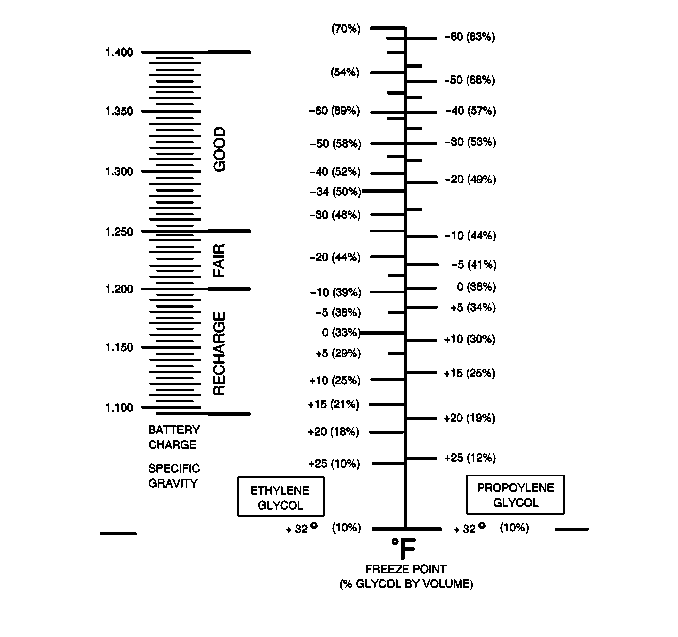
Use the J 26568 or the J 23688 in order to inspect the antifreeze protection of the coolant.
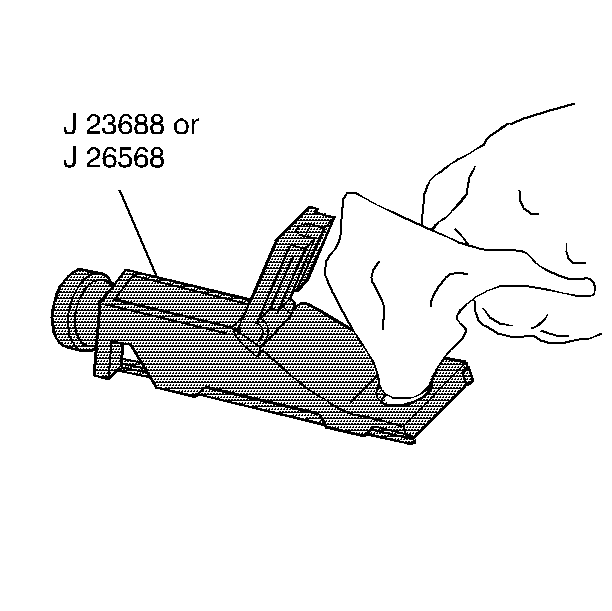
This action will expose the measuring window and the bottom of the plastic cover.
| 2. | Use a tissue or a soft clean cloth in order to wipe the surface dry. |
| 3. | Close the plastic cover. |
| • | Ensure that the hydrometer markings are correct. |
| • | Unless J 26568 or the J 23688 have the provision for temperature correction, test the coolant at the temperature at which the J 26568 or the J 23688 is calibrated. If the coolant is warmer or cooler than this temperature, the reading may be incorrect. |
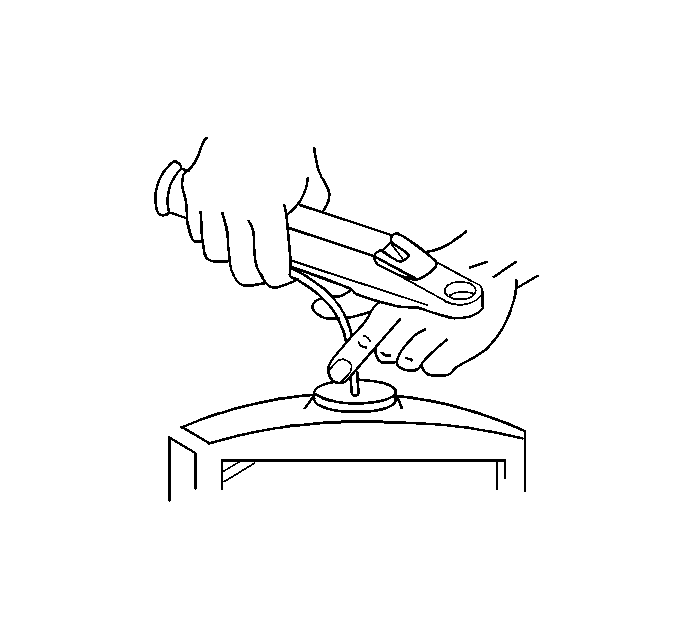
Important:
• Do not open the plastic cover during readings. Coolant evaporation
may change the readings. • If the reading is unclear, the measuring surface was not correctly
cleaned. Wipe the surface dry and test the coolant again.
Follow the manufacturer's directions in order to use the J 26568 or theJ 23688 .
Radiator Cap
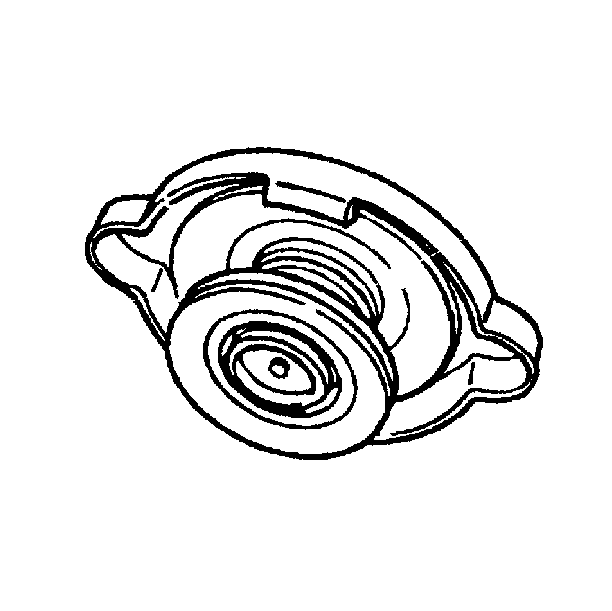
Inspect the radiator cap for proper opening and closing pressures.
This action will ensure the safe, efficient operation of the cooling system. A pressure cap that can not maintain pressure will lower the boiling point of the engine coolant. A lower engine coolant boiling point will cause the engine cooling system to operate at a higher than normal temperature.
If the cap is faulty, replace the cap. Refer to Cooling System Leak Testing .
