Notice: Operating an engine without an effective crankcase ventilation system
may damage the engine. Replace the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve
at regular intervals. Use the correct PCV valve for the engine
and equipment type. Wrong or substandard parts may damage the engine components.
Use the following procedure to check the function of the
crankcase ventilation system:
- Start the engine.
- Run the engine at idle.
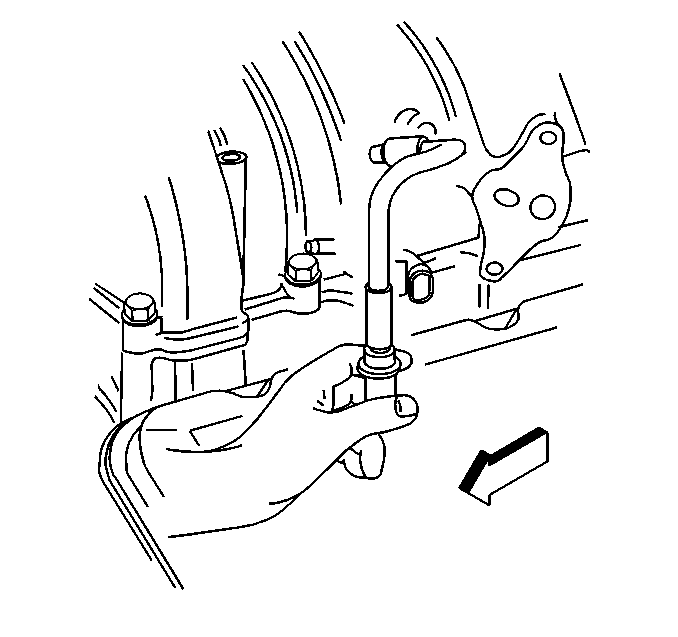
- Place your thumb over
the end of the crankcase ventilation valve to check for vacuum. Check
for a plugged intake manifold port, crankcase ventilation valve or vacuum
hoses, if there is no vacuum at the crankcase ventilation valve. Replace
or repair as necessary.
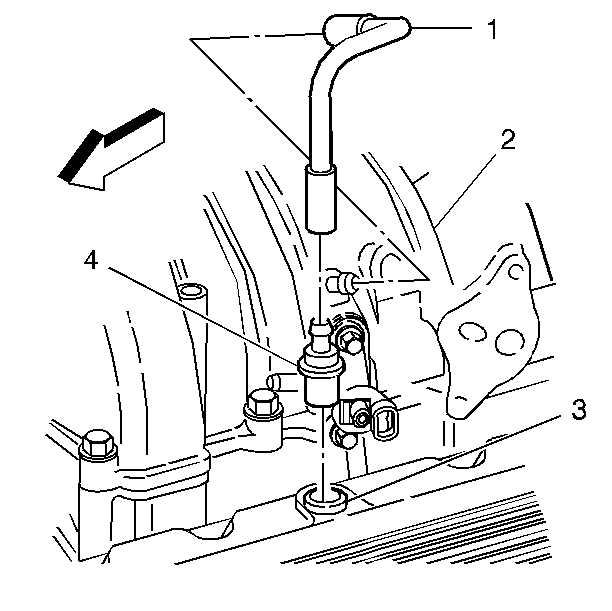
- Remove the crankcase ventilation
valve (4).
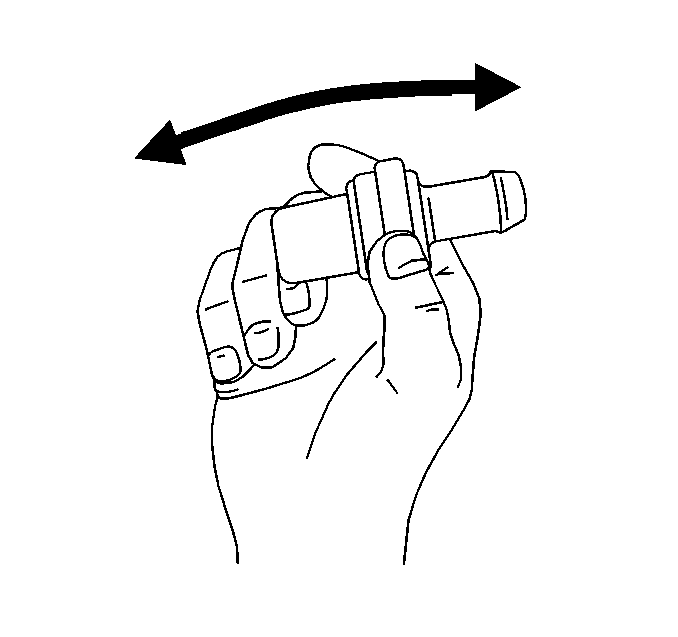
- Shake the crankcase ventilation
valve while listening for the rattle of the needle inside. Replace the crankcase
ventilation valve if the valve does not rattle.
| • | Proper operation of the crankcase ventilation system is dependent
upon a sealed engine. Check that the crankcase ventilation system is functioning
properly, if the build up of oil sludge or oil dilution is found.
Check the engine for possible causes and correct, in order to ensure
that the system will function as intended. |
| • | Periodically inspect the hoses and clamps in the crankcase ventilation
system. Replace any components showing signs of damage or deterioration. Check
for a clogged crankcase ventilation valve or a plugged hose if the
engine is idling rough. |
Results of Incorrect Operation
| • | A plugged crankcase ventilation valve or hose may cause: |
| - | Stalling or slow idle speed |
| - | High crankcase pressure |
| - | Oil in the air induction system |
| - | Excessive exhaust emissions |
| • | A leaking valve or hose may cause any of the following conditions: |
| - | Incorrect crankcase pressure |
| - | Excessive exhaust emissions |



