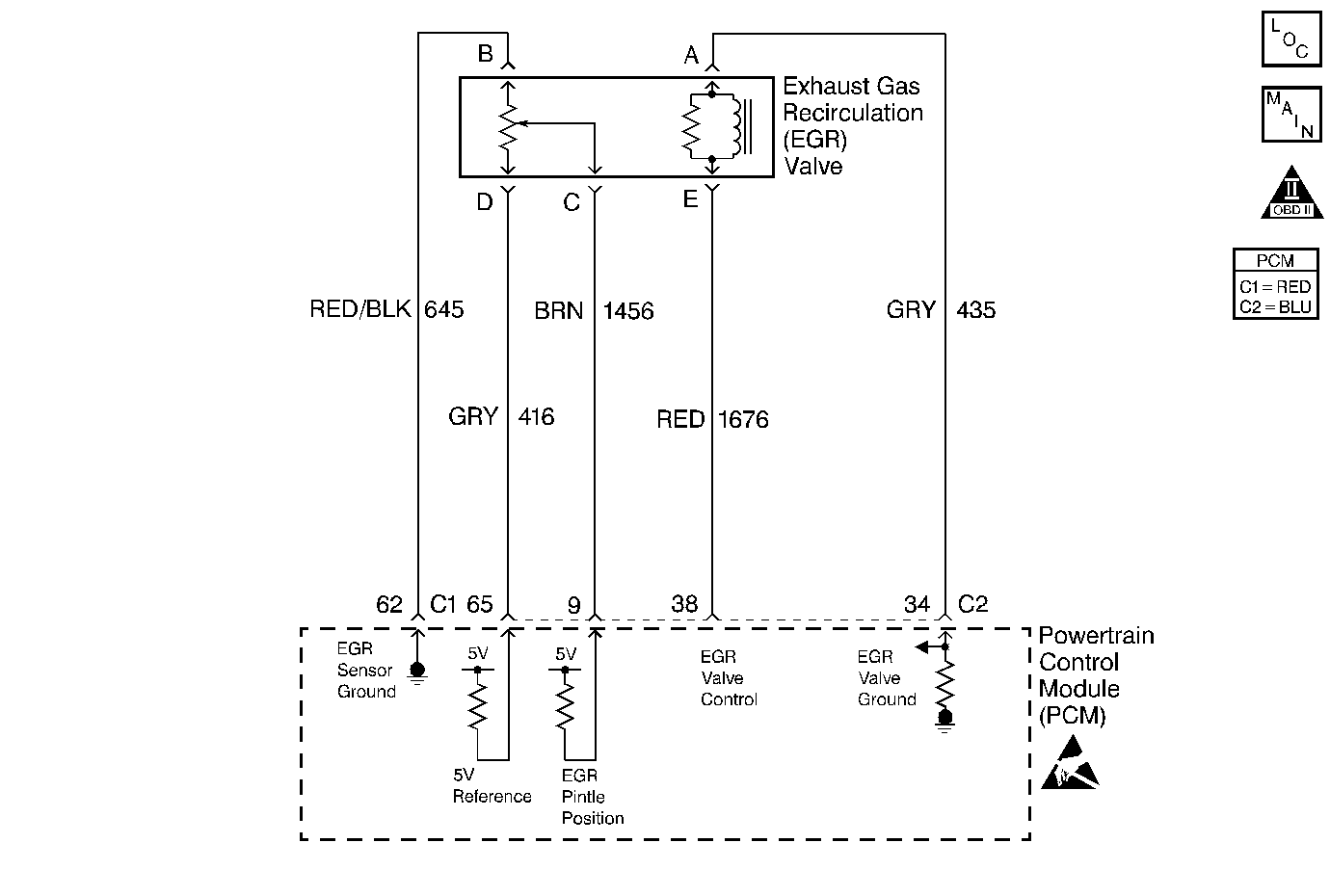
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to lower Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused by high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are reduced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with a PCM controlled pintle. The PCM controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensors. The PCM then commands the EGR valve to operate when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through the PCM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the Desired EGR Position.
The PCM monitors the results of its command through a feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the EGR valve pintle position is sent to the PCM. This feedback signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR Position. The PCM monitors the EGR valve pintle position input to ensure that the valve responds properly to commands from the PCM and to detect a fault if the pintle position sensor circuit is open. If the PCM detects an open pintle this DTC will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0506, P0507, and P1404 not set. |
| • | Ignition voltage is greater than 11.7V. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
EGR commanded ON (Desired EGR Position is greater than 0 percent).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, this information will be stored in Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive drive trip, the operating conditions at the time of failure will be written to Freeze Frame and the Failure record will be updated. |
| • | The EGR Valve is disabled. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has Run and Passed and not Failed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles (coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 70°C (160°F) during the same ignition cycle). |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear Information function. |
| • | A last test failed (Current DTC) will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | Disconnect the PCM battery feed for 30 seconds. |
Diagnostic Aids
Due to the moisture associated with exhaust systems, the EGR valve may freeze and stick in colder weather at times. After the vehicle is brought into a warm shop for repairs, the valve warms and the problem disappears. By watching the Actual EGR and Desired EGR Positions on a cold vehicle with a scan tool, the fault can be verified easily. Inspect the Freeze Frame data to determine if the DTC set when the vehicle was cold by viewing the engine coolant temperature (ECT).
Test Description
Numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
Commanding the EGR valve open determines whether the PCM can control the EGR valve accurately and if the malfunction is present.
-
A test light, when connected to ground, will glow dimly when the EGR valve is commanded to 20 percent, and brighter as the EGR valve is commanded to 100 percent.
-
The test light will have glowed brightly in the previous step if the EGR control circuit was shorted to B+ and the Actual EGR Position on the scan tool will display 100 percent. A test light that did not illuminate, indicates that the circuit may be open or shorted to ground.
-
If the EGR valve 5 volt reference is shorted to voltage, the DVM will read battery voltage and additional DTCs may be set.
-
The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to the latest Techline procedures for PCM reprogramming.
-
Although the circuitry acted correctly when checked, a problem may still lie within the terminals which would not show up in probe type testing. Be sure to check the terminals for being backed out, improperly formed, or damaged.
-
Check the terminals for being backed out, improperly formed or damaged, and for poor tension.
-
Clearing the DTCs is a very important step for this diagnostic. The clearing function allows the EGR valve to relearn a new pintle position. The DTC must be cleared with the ignition switch ON, with the engine OFF or when the engine is idling.
-
If no malfunctions have been found at this point and no additional DTCs were set, refer to Diagnostic Aids for additional checks and information.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the Desired EGR Position? | 20%, 50%, 70%, 100% | |||
3 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
As the command is raised, does the test light glow brighter, flash or maintain a steady dim glow? | 20%, 50%, 70%, 100% | |||
5 | Repair the open or poor connection in the EGR ground circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
6 | With the test light connected to ground, probe the signal circuit. Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
With the test light still connected to ground, again probe the EGR ignition feed circuit without commanding the EGR valve with the scan tool. Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
8 | Check the signal circuit for a short to voltage and repair as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
With a DVM connected to ground, probe the 5 V reference circuit. Is the voltage measured near the specified value? | 5 V | |||
10 | Check the EGR ignition feed circuit for a short to voltage and repair as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
11 | Connect the test light to B+ and again probe the EGR ignition feed circuit. Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
Check the EGR ground circuit for a poor connection or proper terminal tension at the EGR and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
14 | Check the 5 V reference circuit for a short to voltage and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
15 | Check the control circuit for a short to ground and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
16 | Check the EGR ignition feed circuit for an open or poor connection at the EGR valve electrical connector and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
17 | Replace the EGR valve. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Check the PCM electrical connector for a poor connection and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | |||
Check if any additional DTCs are set. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
