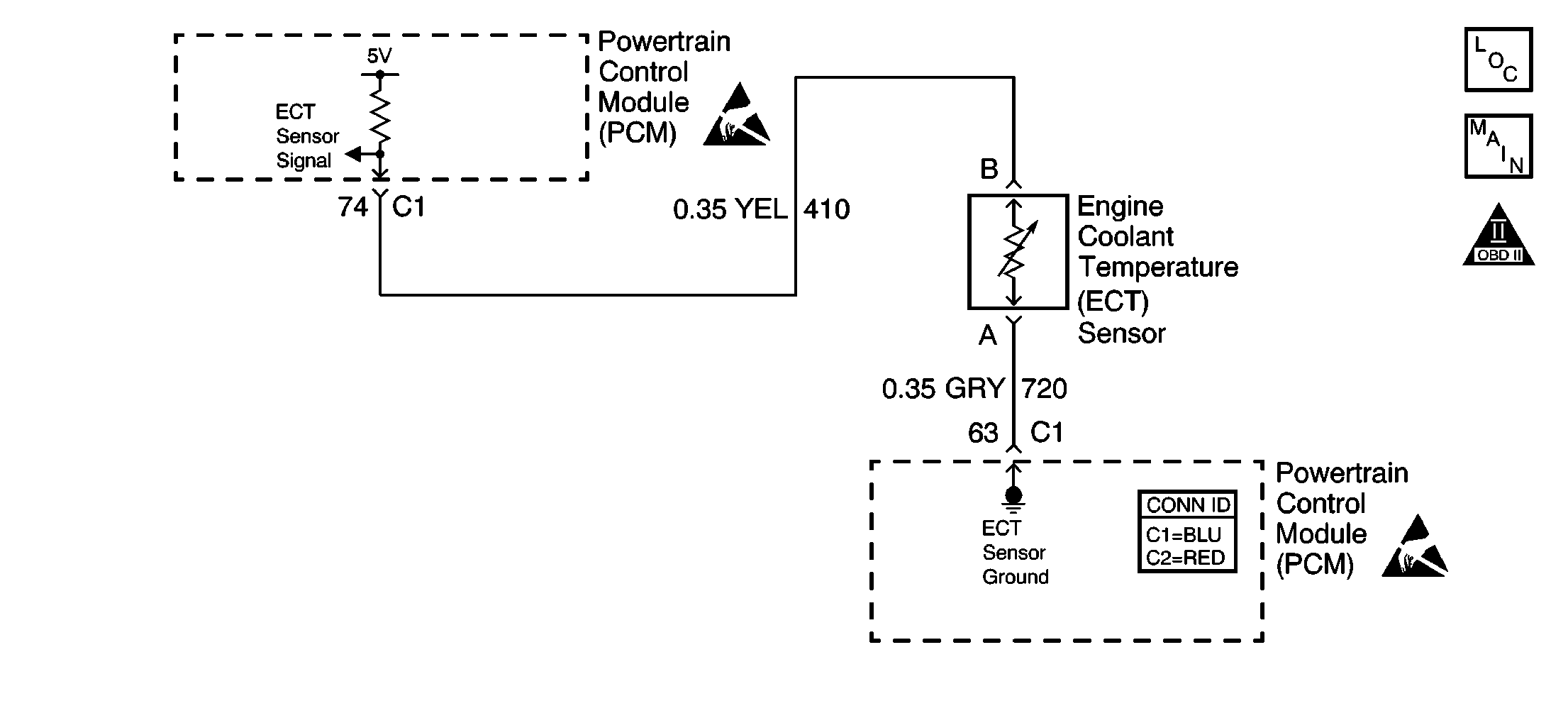
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor contains a semiconductor device, a thermistor, which changes resistance based on temperature . The ECT sensor mounts in the left bank cylinder head near the front of the engine. The ECT sensor has a signal circuit and a ground circuit. The powertrain control module (PCM) applies a voltage, about 5.0 volts, on the signal circuit to the sensor. The PCM monitors changes in this voltage caused by changes in the resistance of the sensor in order to determine the engine coolant temperature.
When the engine coolant is cold, the sensor or thermistor resistance is high, and the PCM signal voltage only pulls down a small amount through the sensor to ground. The PCM senses a high signal voltage or low temperature. When the engine coolant is warm, the sensor resistance is low, and the signal voltage pulls down a large amount. This causes the PCM to sense a low signal voltage, or high temperature.
When the PCM senses a signal voltage higher than the normal operating range of the sensor, this DTC sets.
Engine Coolant Temperature | Thermistor Resistance | Signal Voltage |
|---|---|---|
Cold | High | High |
Warm | Low | Low |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The engine operates longer than 60 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The ECT is less than -35°C (-31°F). |
| • | The intermittent condition exists for a total of 1.0 second during a 20.0 second time period. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM stores the DTC information into memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will not illuminate. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature gauge defaults to a predetermined value. |
| • | The message center will display a message. This message may only be displayed briefly. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Remove any debris from the PCM connector surfaces before servicing the PCM. Inspect the PCM connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing the PCM. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent water intrusion into the PCM.
| • | Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can cause an intermittent DTC. Inspect the related circuits for being too close to secondary ignition wires and the generator. |
| • | If the engine sat overnight, the engine coolant temperature and intake air temperature values should display within a few degrees of each other. If the temperatures are not within 3°C (5°F), refer to Temperature Versus Resistance . |
| • | When moving related connectors, visually and physically inspect connectors for the following: |
| - | Poor mating of the connector halves or a terminal not fully seated, or backed out, in the connector body |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals--Carefully reform or replace all connector terminals in the related circuits in order to insure proper terminal contact tension. |
| - | Poor terminal to wire connection--Inspect for poor crimps, crimping over wire insulation rather than the wire. |
| - | Dirt or corrosion on the terminals--Inspect the connector seals for being there and for being damaged. |
| • | For an intermittent, refer to Symptoms . |
| • | When moving the related wiring harnesses, visually and physically inspect the wiring for the following: |
| - | Wire insulation that is rubbed through, causing an intermittent short. |
| - | Wiring broken inside the insulation. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If DTC P0118 failed this ignition, this indicates a hard failure is present. When a hard failure is present, both the hard and intermittent DTCs set.
-
Inspects for proper connections.
-
Inspects the wiring harness.
-
Using the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data can help determine how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also help determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same Freeze Frame conditions, such as RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc., that you observed. This will isolate when the DTC failed. For any test that requires probing the PCM or component harness connectors, use the connector test adapter kit . Using this kit prevents any damage to the harness connector terminals.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Did DTC P0118 Fail This Ignition? | -- | Go to DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit High Voltage | ||
Does the sensor value change abruptly while a related connector is being moved? | -- | |||
Observe the affected sensor value on the scan tool while moving the related wiring harnesses. Does the sensor value change abruptly while moving the related electrical harnesses? | -- | |||
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Go Diagnostic Aids | ||
6 | Repair the damaged connectors and terminals. Refer to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Repair the circuit as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
10 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
