VCM Outputs Diagnosis IAC System Check
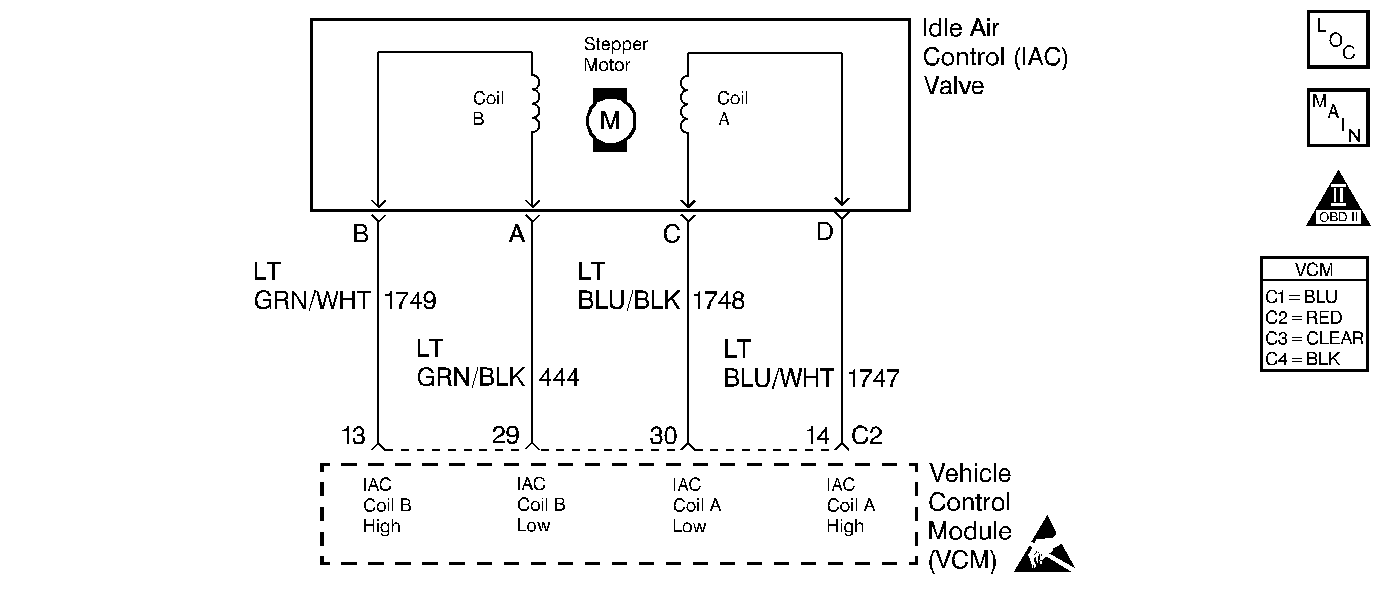
Circuit Description
The VCM controls idle RPM with the IAC valve. To increase idle RPM, the VCM retracts the IAC pintle from the seat, allowing more air to bypass the throttle plate. To decrease RPM, it extends the IAC pintle valve in towards the seat, reducing air flow through the IAC valve port in the throttle body. A scan tool will read the VCM commands to the IAC valve in counts. The higher the counts, the more air allowed (higher idle). The lower the counts, the less air allowed (lower idle).
IAC Valve Reset Procedure Without A Scan Tool
- Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF for 5 seconds.
- Turn OFF the ignition for 10 seconds.
- Start the engine and check for proper operation.
IAC Valve Reset Procedure With Scan Tool
- Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
- Install a scan tool.
- Select F4 Misc. Tests.
- Select F3 IAC System.
- Select F1 IAC Reset.
- Use up arrow to reset IAC.
Diagnostic Aids
A slow, unstable, or fast idle may be caused by a non-IAC system problem that cannot be overcome by the IAC valve. The following checks should be made to repair a non-IAC system problem.
Important: If for some reason the air intake to the engine is restricted, the VCM will attempt to compensate by backing out the IAC pintle to maintain desired idle. If the engine has another source of air to the intake, the VCM will compensate by extending the IAC pintle, scan IAC counts may reach zero as the VCM tries to maintain desired idle.
| • | Vacuum Leak (High Idle) - If idle is too high, stop the engine. Fully extend (low) IAC with tester. |
| Start engine. If idle speed is above 800 RPM, locate and correct vacuum leak including crankcase ventilation system. Also, check for binding of throttle blade or linkage. |
| • | System lean (high air/fuel ratio) - Idle speed may be too high or too low. Engine speed may vary up and down, disconnecting IAC does not help. May set DTC P0171. The scan tool will read Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) output less than 300 mV (0.3 volt). Check for low regulated fuel pressure or water in fuel. |
| • | System rich (low air/fuel ratio) - Idle speed too low. Scan IAC counts are usually above 80. System obviously rich and may exhibit black smoke exhaust. May set DTC P0172. The scan tool will read Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) signal fixed above 800 mV (0.8 volt). |
| Check for high fuel pressure, leaking or sticking injector. Silicone contaminated HO2S scan voltage will be slow to respond. |
| • | Throttle body - Remove IAC valve and inspect bore for foreign material. |
| • | IAC Valve Electrical Connections - IAC valve connections should be carefully checked for proper contact. |
| • | Crankcase Ventilation Valve - An incorrect or faulty crankcase ventilation valve may result in an incorrect idle speed. |
| • | A/C Compressor - Refer to Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor Clutch Control Diagnosis if circuit is shorted to ground. If the relay is faulty, an idle problem may exist. |
| • | If intermittent poor driveability or idle symptoms are resolved by disconnecting the IAC, carefully recheck connections, valve terminal resistance or replace IAC. |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The IAC tester is used to extend and retract the IAC valve. Valve movement is verified by an engine speed change. If no change in engine speed occurs, the valve can be retested when removed from the throttle body.
-
This step checks the quality of the IAC movement in Step 1. Between 700 RPM and about 1500 RPM the engine speed should change smoothly with each flash of the tester light in both extend and retract. If the IAC valve is retracted beyond the control range (about 1500 RPM), it may take many flashes in the extend position before engine speed will begin to drop. This is normal on certain engines, fully extending IAC may cause engine stall. This may be normal.
-
Steps 1 and 2 verified proper IAC valve operation while this step checks the IAC circuits. Each lamp on the node light should flash red and green while the IAC valve is cycled. While the sequence of color is not important if either light is OFF or does not flash red and green, check the circuits for faults beginning with poor terminal contacts.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Does the RPM change? | -- | |||
Does the RPM change smoothly with each flash of the IAC driver within the specified range? | 700-1500 RPM | |||
Do the lights flash red and green but never OFF? | -- | |||
5 | Using the other connector on the IAC driver pigtail, check the resistance across the IAC coils. Are the readings within the specified value between terminal A to B and C to D? | 40-80 ohms | ||
6 | Check the resistance between IAC terminals B to C and A to D. Are the resistances at the specified value? | ∞ | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
7 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
8 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
9 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
10 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
11 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
12 | Replace the IAC valve. Refer to IAC Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Replace the VCM. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 |
Does the component now operate properly? | -- | System OK |
