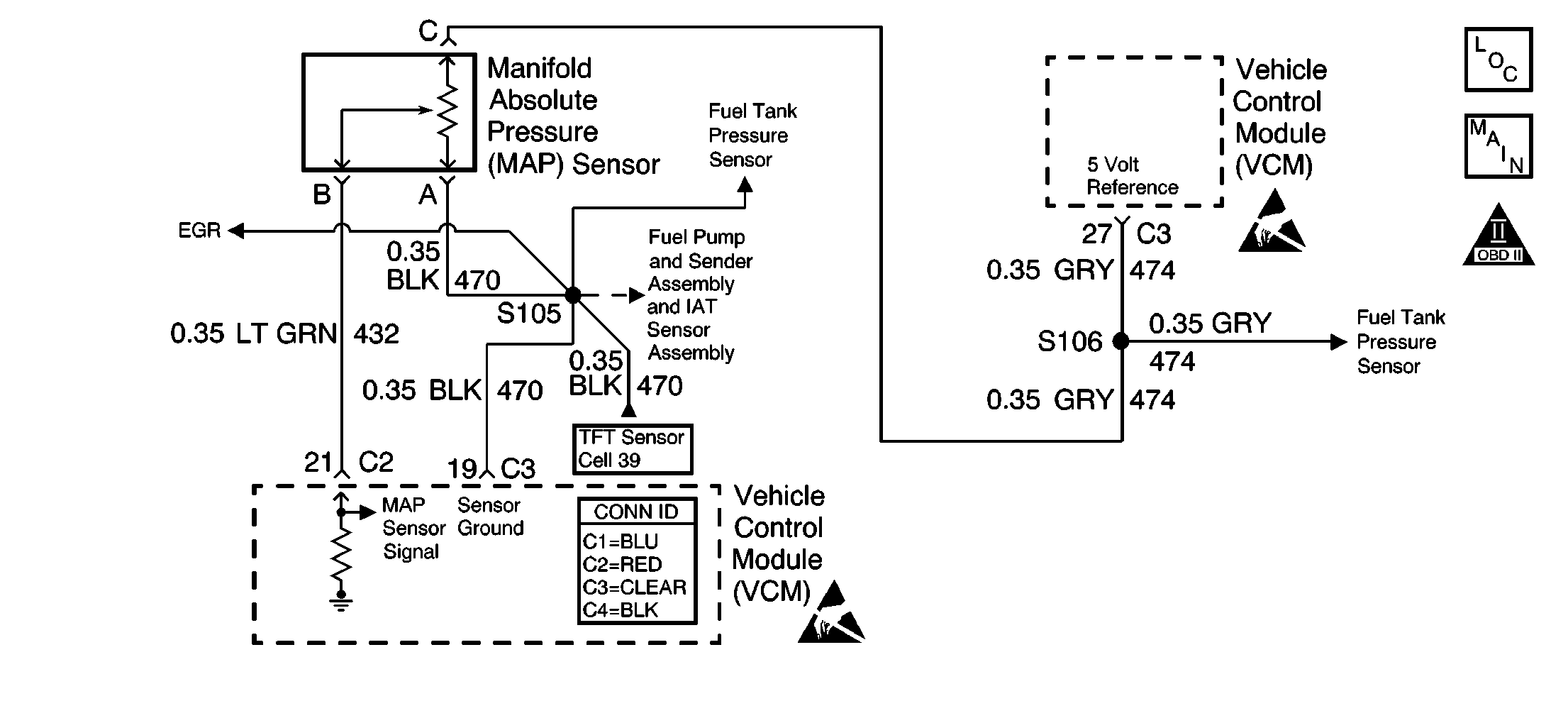
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is a pressure sensor. The control module supplies the MAP sensor a reference voltage, signal, and ground circuits. When manifold vacuum is low, the MAP sensor signal voltage rises to a value near the reference voltage, and the MAP sensor signal voltage decreases when the manifold vacuum increases. The control module monitors the MAP sensor signal circuit voltage in order to calculate the vacuum within the intake manifold.
Certain vehicle models will also use the MAP sensor in order to calculate the barometric pressure (BARO) when the ignition switch is turned ON and the engine is NOT cranked. This BARO reading may also be updated whenever the engine is operated at wide open throttle (WOT).
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is designed to detect intermittent high voltage signals on the MAP sensor circuit.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active throttle position (TP) sensor DTCs |
| • | The throttle position is less than 0.4 percent with an engine speed less than 1,200 RPM |
| OR |
| The throttle position is less than 20 percent with an engine speed more than 1,200 RPM. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The VCM detects an intermittent high MAP sensor voltage after a calibrated number of seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module stores the DTC in history after the first failure but will not illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The control module stores the failure information in the scan tools Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. |
| • | A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 70°C (160°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine OFF, the manifold pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure with the signal voltage high. The VCM uses this information as an indication of the vehicle altitude. Comparison of this reading with a known good vehicle using the same sensor is a good way to check the accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be within 0.4 volts. This DTC could set if the sensor ground circuit is intermittently open or the MAP sensor signal circuit is intermittently shorted to voltage. If the high MAP voltage reading is present, additional sensor circuit voltage codes could be set. Refer to any non-intermittent DTCs that are set.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly inspect any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If the MAP sensor signal is more than 4.6 volts then the condition is present.
-
If any other non-intermittent DTCs are set, go there first.
-
The engine must be running in order to observe the MAP sensor signal voltage activity.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool display a MAP sensor voltage more than the second specified value? | 15 in. Hg 4.6 V | |||
Are any non-intermittent DTCs set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | ||
4 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
5 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
Did the voltage fluctuate more than the specified value? | 0.5 V | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
7 | Repair the circuit as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
9 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
