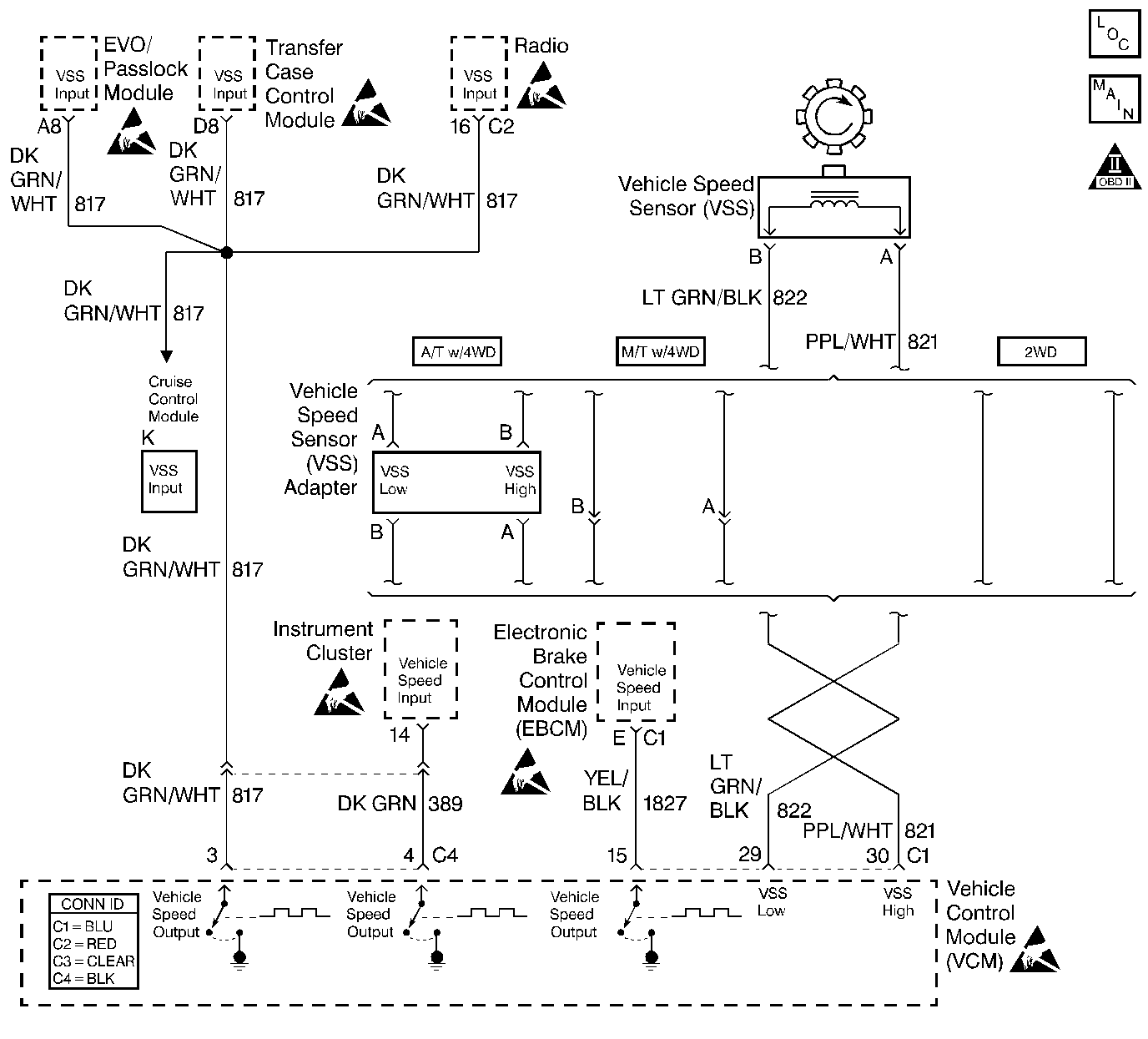
Circuit Description
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) is a magnetic induction sensor. The VSS is mounted close to the output shaft gear in the transmission. The gear teeth induce an alternating current in the sensor as the output shaft rotates. This frequency is applied to the control module at the rate of 40 cycles per output shaft revolution. The control module calculates the vehicle speed using this AC voltage signal.
If the VSS signal is not detected at any vehicle speed for 5 seconds, this diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active MAP sensor DTCs |
| • | The MAP is less than 20 kPa |
| • | The ECT is 60°C (140°F) or more |
| • | The engine speed is between 1400-4400 RPM |
| • | The throttle position is less than 3 percent |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The VCM detects a vehicle speed less than 1 mph for 5 seconds or more during decel.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Inspect the face of the vehicle speed sensor for metal shavings. This could result in an intermittent DTC. Also check for the following conditions:
| • | A chipped, cracked, or damaged rotor |
| • | Incorrect alignment of the rotor to the speed sensor |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
This test checks the AC voltage output of the vehicle speed sensor.
-
This test checks for an internal transmission problem.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Is the voltage above the specified value? | 0.5 V | |||
3 | Check for an open in the vehicle speed sensor high circuit between the sensor and the VCM. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
4 | Check for an open in the vehicle speed sensor low circuit between the sensor and the VCM. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
5 | Check for a short to ground in the VSS high circuit between the sensor and the VCM. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
Did you find a problem? | -- | |||
7 | Replace the vehicle speed sensor. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Repair or replace the vehicle speed sensor rotor as necessary. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Check for a poor connection at the vehicle speed sensor. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
10 | Check for a poor connection at the VCM harness connector. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
11 |
Important:: Special procedures are required to repair the twisted/shielded cable contained in this circuit. Repair the circuit as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
14 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
