Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis Enhanced
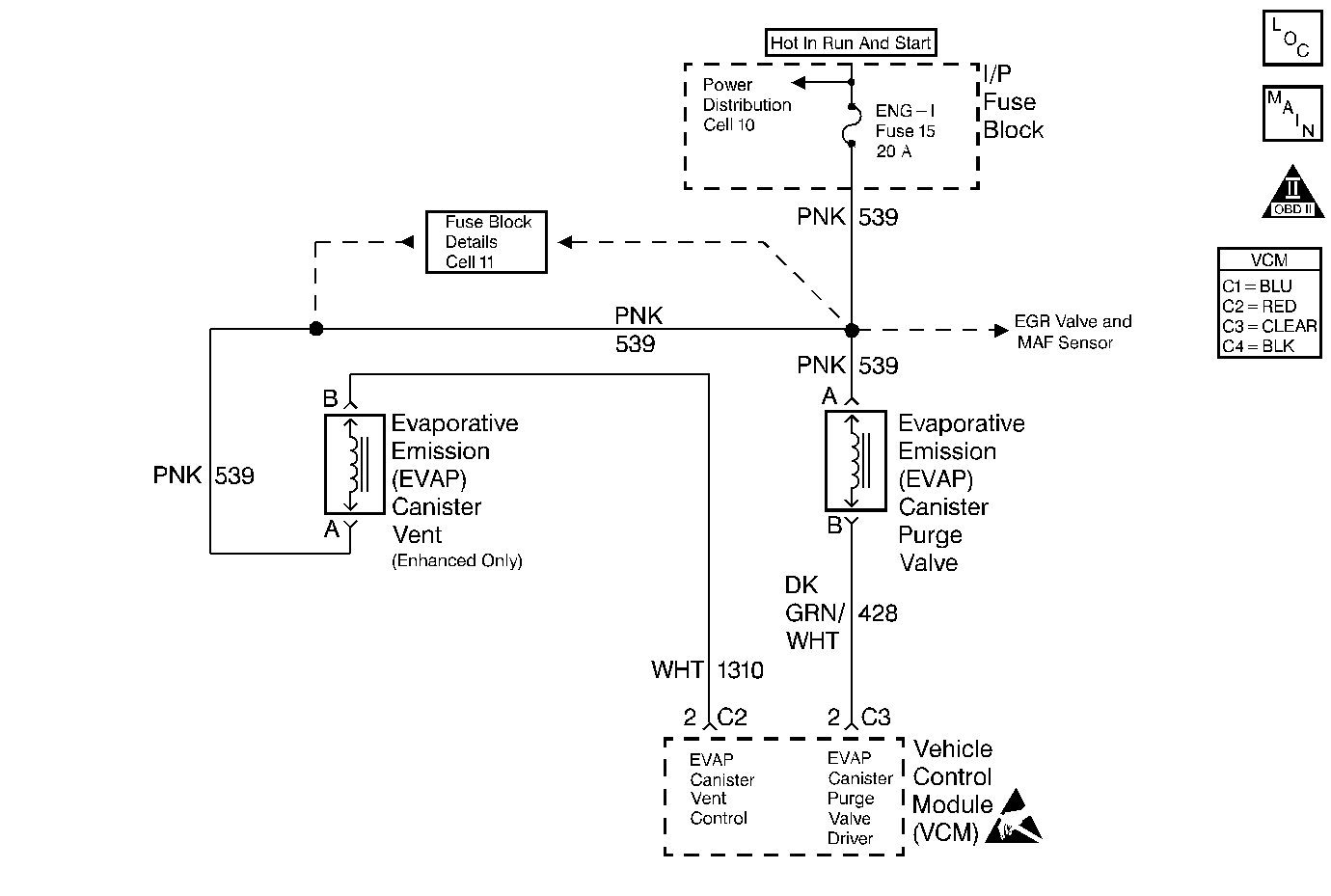
Circuit Description
The Enhanced evaporative system includes the following components:
| • | The fuel tank |
| • | The EVAP vent solenoid |
| • | The fuel tank pressure sensor |
| • | The fuel pipes and hoses |
| • | The vapor lines |
| • | The fuel cap |
| • | The evaporative emission canister |
| • | The purge lines |
| • | The EVAP purge solenoid |
The evaporative leak detection diagnostic strategy is based on applying the vacuum to the EVAP system and monitoring the vacuum decay. The VCM monitors the vacuum level via the fuel tank vacuum sensor input. At an appropriate time, the EVAP purge solenoid and the EVAP vent solenoid turn ON, allowing the engine vacuum to draw a small vacuum on the entire evaporative emission system. If a sufficient vacuum level cannot be achieved, a large leak or a malfunctioning EVAP purge solenoid is indicated. The following conditions can cause this problem:
| • | A missing, malfunctioning, improperly installed, or loose fuel cap |
| • | A disconnected or malfunctioning fuel tank pressure sensor |
| • | A disconnected, damaged, pinched, or blocked EVAP purge line |
| • | A disconnected or damaged EVAP vent hose |
| • | A disconnected, damaged, pinched, or blocked fuel tank vapor line |
| • | A disconnected or malfunctioning EVAP purge solenoid |
| • | A disconnected or malfunctioning EVAP vent solenoid |
| • | An open ignition feed circuit to the EVAP vent or purge solenoid |
| • | A damaged EVAP canister |
| • | A leaking fuel sender assembly O-ring |
| • | A leaking fuel tank or fuel filler neck |
Results of Incorrect Operation
| • | Poor idle, stalling and poor driveability can be caused by: |
| - | Damaged canister |
| - | Hoses split, cracked, or not connected to the proper tubes |
| • | Evidence of fuel loss or fuel vapor odor can be caused by: |
| - | Liquid fuel leaking from the fuel lines |
| - | Cracked or damaged EVAP canister |
| - | Disconnected, misrouted, kinked, deteriorated or damaged EVAP pipe or canister hoses |
| - | Air cleaner or air cleaner gasket improperly seated |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
Inspect the service port. Make sure that the dust cap and valve core is not loose or damaged (the valve core may have left hand threads). If the service port is suspect of leakage use the following procedure:
Disconnect the purge line from the EVAP Purge solenoid valve.
Connect a hand vacuum pump to the service port by placing the hose/adaptor over the unthreaded end portion of the service port.
Apply vacuum to 5 in. Hg. If the vacuum does not hold replace the service port (may require line replacement).
-
If the vehicle passes the Service Bay Test then an intermittent leak or restriction had occurred. Check the fuel tank cap for a possible loose or off condition that may have caused this DTC to set.
If the Service Bay Test can not be run, proceed to Step 5. If a fault is not currently present the diagnostic table steps will return you to Step 3.
-
Refer to the information supplied with the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic cart on proper setup and adjustment procedures.
-
With pressure applied it may be necessary to disconnect the EVAP lines at the components to verify that a line or component is not restricted. A restriction would prevent a vacuum (or the Step 9 test pressure) from forming in the fuel tank.
-
An EVAP Pressure sensor that does not correctly respond to vacuum (or pressure) will cause this DTC to set.
The EVAP Pressure Sensor monitors a range from 7.5 in. H2O of pressure to -17.5 in. H2O of pressure (vacuum).
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-board Diagnostic (OBD) System check? | -- | ||||||||||
2 | Check for DTC's P0442, P0446, P0452, P0453, P0461, P0462, P0463 and P1441. Are any of the above EVAP system DTC's stored in HISTORY? | -- | Go to the DTCs that are set | |||||||||
Inspect the EVAP system for the following conditions:
Repair the EVAP system if needed. Was a repair made to the EVAP system? | -- | |||||||||||
|
Important: : Before proceeding with the Service Bay Test the vehicle must meet the
following operating criteria:
If any of the above conditions are not met the scan tool will display Test Aborted upon activating the Service Bay Test.
Does the vehicle pass the Service Bay Test? | -- | Condition not present. Go to Test Descriptions and Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||
5 |
Is the vacuum at or above the specified value? | 12 in. Hg. | ||||||||||
6 |
Can the specified value be obtained and held? | 5 in. Hg. | ||||||||||
7 |
Can the specified value be obtained and held? | 5 in. Hg. | ||||||||||
8 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||
|
Important: The following steps require the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic station J 41413 and the ultrasonic leak detector J 41416. Always zero the EVAP Pressure and Vacuum (in. H2O) gauges on the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic station before proceeding with diagnosis.
Important: Do Not apply more than 15 in. H2O of pressure to the EVAP system. Was a leak found? | -- | |||||||||||
Was a problem found? | -- | |||||||||||
11 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||||||||||
12 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||||||||||
13 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
14 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||
15 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||||||||||
16 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||||||||||
17 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
18 |
Was problem found? | -- | ||||||||||
19 |
Important: : Inspect the EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve and the purge line for carbon contamination. Refer to Diagnostic Aids. Replace the EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
20 | Replace the EVAP Vent Valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Vent Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
21 | Replace the EVAP Vapor Canister. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Replacement Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
Do the values indicate the same amount of vacuum in the EVAP system to within the range specified? | 2 in. H2O | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||
23 | Replace the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
24 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
25 |
Does the Scan Tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | -- | |||||||||
26 | Does the Scan Tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis Non-Enhanced

Circuit Description
The Evaporative System (EVAP) includes the following components:
| • | Fuel Tank |
| • | Fuel Pipes and Hoses |
| • | Vapor Lines |
| • | Evaporative Canister |
| • | Purge Lines |
| • | EVAP Purge Solenoid |
The EVAP Purge Solenoid valve allows manifold vacuum to purge the canister. The Vehicle Control Module (VCM) supplies a ground to energize the solenoid valve (purge "ON"). The EVAP Purge Solenoid control is Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) or turned ON and OFF several times a second. The duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by the engine operating conditions which include engine load, throttle position, engine coolant temperature, and ambient air temperature. The duty cycle is calculated by the VCM and the output is commanded when the appropriate conditions have been met.
There are no EVAP system DTCs.
Diagnostic Aids
When there is continuous purge of the EVAP canister containing fuel vapors, a rich condition with a higher IAC Position value and a lower than normal Long Term Fuel Trim value may be seen. This is similar to a leaking fuel injector.
When there is continuous purge of the EVAP canister not containing fuel vapors (new canister, disconnected purge line, or disconnected vapor lines), a lean condition with a low IAC Position value and a higher than normal Long Term Fuel Trim value may be seen. This is similar to a vacuum leak.
Check for the following:
| • | EVAP lines for charcoal contamination |
| • | Damaged EVAP canister purge solenoid O-ring |
| • | Cracked or punctured EVAP Canister |
| • | Blocked air separator |
| • | Damaged vacuum line, purge line, vent line, or fuel tank vapor lines |
| • | Poor connection at VCM |
| • | Damaged harness or connectors |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table
-
Checks to see if a vacuum source is present, along with certain conditions before the purge solenoid is commanded ON. Also shows a change of vacuum as the purge solenoid is being cycled
-
Checks for power to the solenoid, the ground circuit, the connections at the purge solenoid and the solenoid itself.
-
Checks for an open or grounded ignition feed circuit.
-
Checks for an open EVAP canister purge control circuit or faulty control module.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Is vacuum present when the solenoid is energized? | 45°C (113°F) 2000 RPM | |||
Is the test light ON? | -- | |||
Is the test light ON? | -- | |||
Is the test light ON? | -- | |||
6 | Check the purge line to the EVAP canister and repair if necessary. Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
7 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
8 | Repair the open in the ignition feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Repair the open in the EVAP canister purge control circuit to the EVAP canister purge solenoid. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
11 | Replace the EVAP canister purge solenoid. Refer to the Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 |
Does the EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid operate properly? | -- | System OK |
