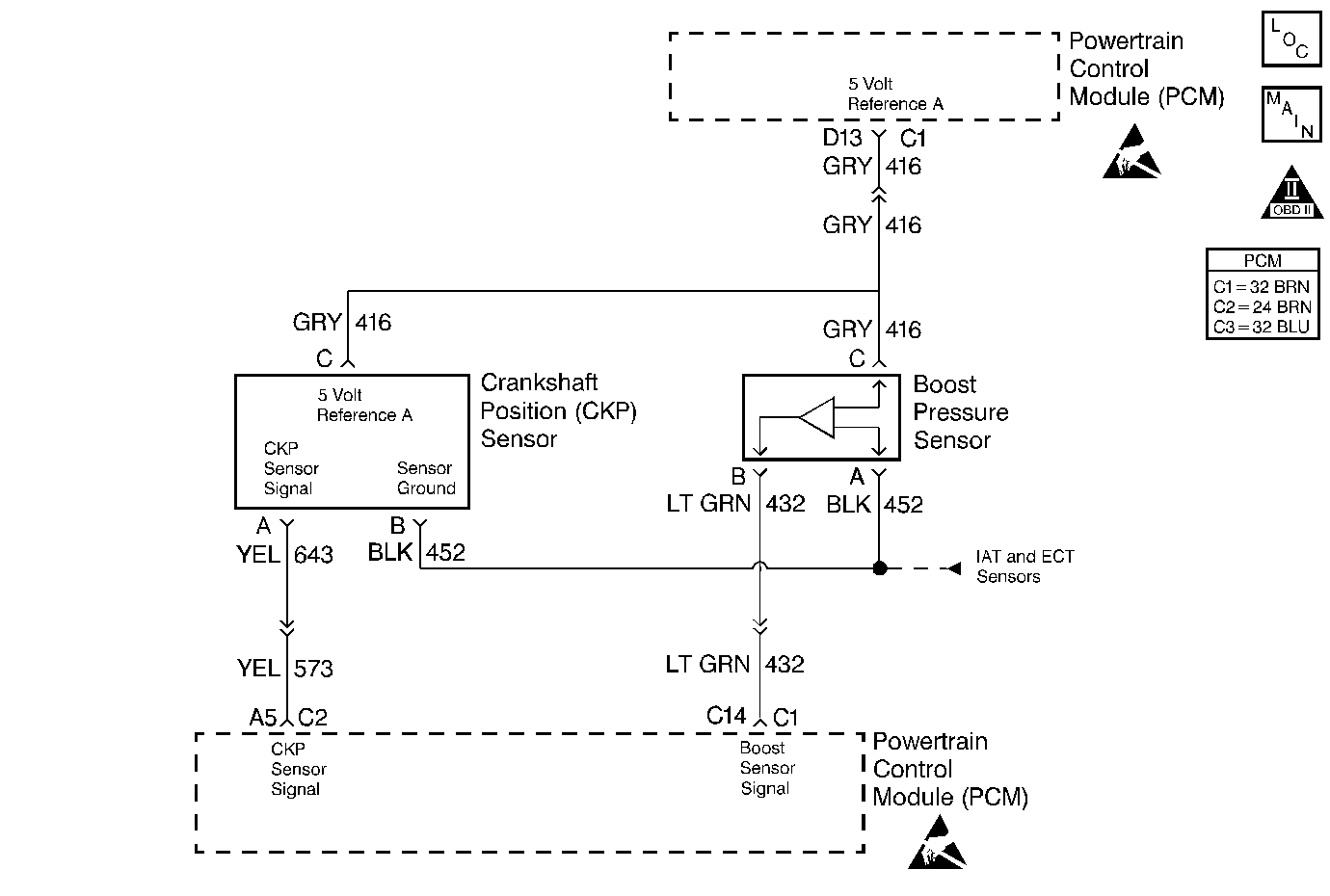
Circuit Description
The PCM operates a solenoid to the control boost. This solenoid is normally open. By providing a ground path, the PCM energizes the solenoid which then allows a vacuum to pass to the wastegate valve. During normal operation, the PCM compares the wastegate duty cycle signal with the boost signal and makes corrections in the duty cycle accordingly.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The PCM performs this diagnostic continuously. |
| • | The engine speed greater than 2400 RPM. |
| • | The fuel rate is greater than 20 mm. |
| • | The boost pressure is greater than, less than, or equal to 20 kPa from desired (internal to PCM). |
| • | All conditions were met for 10 seconds. |
or
| • | The engine speed is greater than 1800 but less than 2400 RPM. |
| • | The fuel rate is greater than 20 mm. |
| • | The conditions were met for 10 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A poor performance condition will exist. |
| • | The PCM will reduce maximum fuel. |
| • | The PCM will disable the torque converter clutch (TCC). |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after three consecutive trips without a fault condition. |
| • | A History DTC will clear when forty consecutive warm-up cycles that the diagnostic does not fail [the coolant temperature has risen 5°C (40°F) from the start up coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 71°C (160°F) during that same ignition cycle]. |
| • | The use of a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
A vacuum leak or a pinched vacuum line may cause a DTC P0236. Check all of the vacuum lines and the components connected to the hoses for any leaks or sharp bends. Check the vacuum source. A possible EGR DTC will store if there is a problem with the vacuum source. Also check for a proper vacuum line routing.
The turbocharger wastegate actuator uses a pulse width modulated vacuum solenoid that causes the vacuum to fluctuate under normal conditions. A steady vacuum reading indicates a restricted solenoid vent filter or a solenoid vent orifice.
Test Description
The number(s) below are the Step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This will check the wastegate solenoid and the filter. If the filter is plugged, the filter will not allow the solenoid to vent and this will cause an overboost condition.
-
This step checks the turbocharger wastegate actuator for vacuum leaks. The actuator must hold a vacuum.
-
This step will check for vacuum leaks at the lines.
-
This step will check for a skewed boost pressure sensor.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing any DTCs, use the Scan Tool Capture Info to save freeze frame and failure records for reference, as the Scan Tool loses data when using the Clear Info function. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | Go to A Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check | |||||||
2 | Is the DTC P1656 also set? | -- | Go to DTC P1656 Wastegate Solenoid Control Circuit | |||||||
3 |
Is the vacuum greater than or equal to the specified value (vacuum will fluctuate)? | 15 in Hg | ||||||||
Is the vacuum greater than the specified value? | 1 in Hg | |||||||||
Does the turbocharger wastegate actuator hold vacuum? | -- | |||||||||
Was a problem found? | -- | |||||||||
7 |
Does the turbocharger wastegate actuator rod move freely? | -- | ||||||||
8 | Check the vacuum pump for proper output. Refer to Vacuum Pump Diagnosis in Vacuum Pump. Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||
Does the scan tool display a change in the boost pressure? | -- | |||||||||
10 | The DTC is intermittent. If no additional DTCs are stored, refer to Diagnostic Aids. If any additional DTCs are stored, refer to those tables. Are there any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||
11 | Replace the boost sensor. Refer to Boost Sensor Replacement . Is this action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
12 | Check for a plugged wastegate solenoid filter. Is the wastegate solenoid filter plugged? | -- | ||||||||
13 | Replace the wastegate solenoid. Refer to Wastegate Solenoid Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
14 | Replace the turbocharger wastegate actuator. Refer to Wastegate Actuator in Turbocharger. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
15 | Replace the vacuum pump. Refer to Vacuum Pump Replacement in Vacuum Pump. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
16 |
Does the Scan Tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||||||||
17 | Does the Scan Tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
