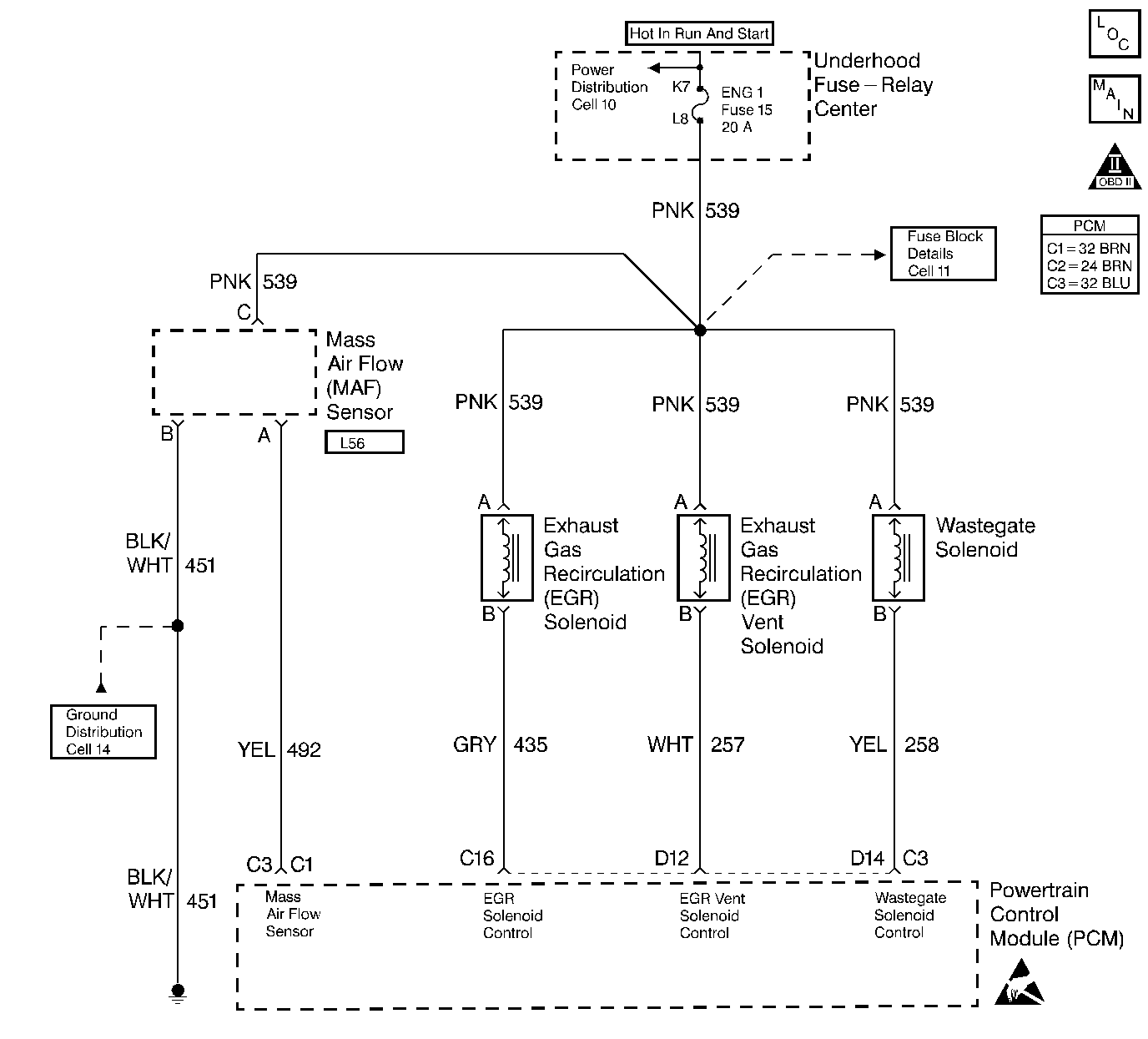
Circuit Description
The PCM operates a solenoid to control the EGR valve. This solenoid is normally open. By providing a ground path the PCM energizes the solenoid which then allows vacuum to pass to the EGR valve. During normal operation, the PCM compares its desired EGR signal with the EGR pressure signal and makes corrections in the duty cycle accordingly. If there is a difference in the PCM command and what is at the EGR valve sensed by the EGR control pressure/BARO sensor, the PCM makes minor adjustments to correct.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The PCM performs this DTC diagnostic continuously. |
| • | The DTCs P0405, P0406, P0102 and P0103 are not set. |
| • | The EGR vent solenoid ON. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The difference between ambient air pressure and EGR pressure is less than 15 kPa. |
| • | All diagnostic set conditions met for 2 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will shut down the EGR. |
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the Failure Records will store this information. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive drive trip, the Freeze Frame records the operating conditions at the time of failure and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL off after three consecutive trips without a fault condition. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if this or any other emission related diagnostic does not report any failures |
| • | The use of a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
A vacuum leak or a pinched vacuum line will cause a DTC P0404. Check all vacuum lines and components connected to the hoses for leaks or sharp bends or deformities. Check the vacuum source to the EGR solenoid assembly. Also check for a small leak in EGR valve and proper vacuum line routing.
To run the diagnostic test the engine must be at operating temperature with the vehicle in drive at idle for approximately 1 minute. Then, with vehicle in park, hold engine rpm steady between 1500 and 2100 rpm for 30 seconds. If the diagnostic test fails to run, vehicle must be driven.
The Adaptive Learn Matrix (ALM) is used to adjust the EGR vacuum control based on mass air flow (MAF). The ALM may change as a result of back pressure increases over the life of the vehicle or other engine system variations. The ALM is made up of sixteen cells (numbered from zero to fifteen) in which each cell covers a range of engine speed (RPM) and load (mm3).
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing any DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save freeze frame and failure records for reference, as the Scan tool loses data when using the Clear Info function. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Is the vacuum greater than the specified value? | 15 in. Hg | ||
Repair restriction between EGR control pressure/BARO sensor and vacuum tee (including vacuum tee). Is action complete? | -- | -- | ||
4 | Replace the EGR Control Pressure/BARO sensor. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Control Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
5 |
Important: After Repairs, the EGR ALM cells must be reset (under special functions in scan tool). Are EGR ALM cells reset? | -- | -- | |
6 |
Does the Scan Tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
7 | Does the Scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
