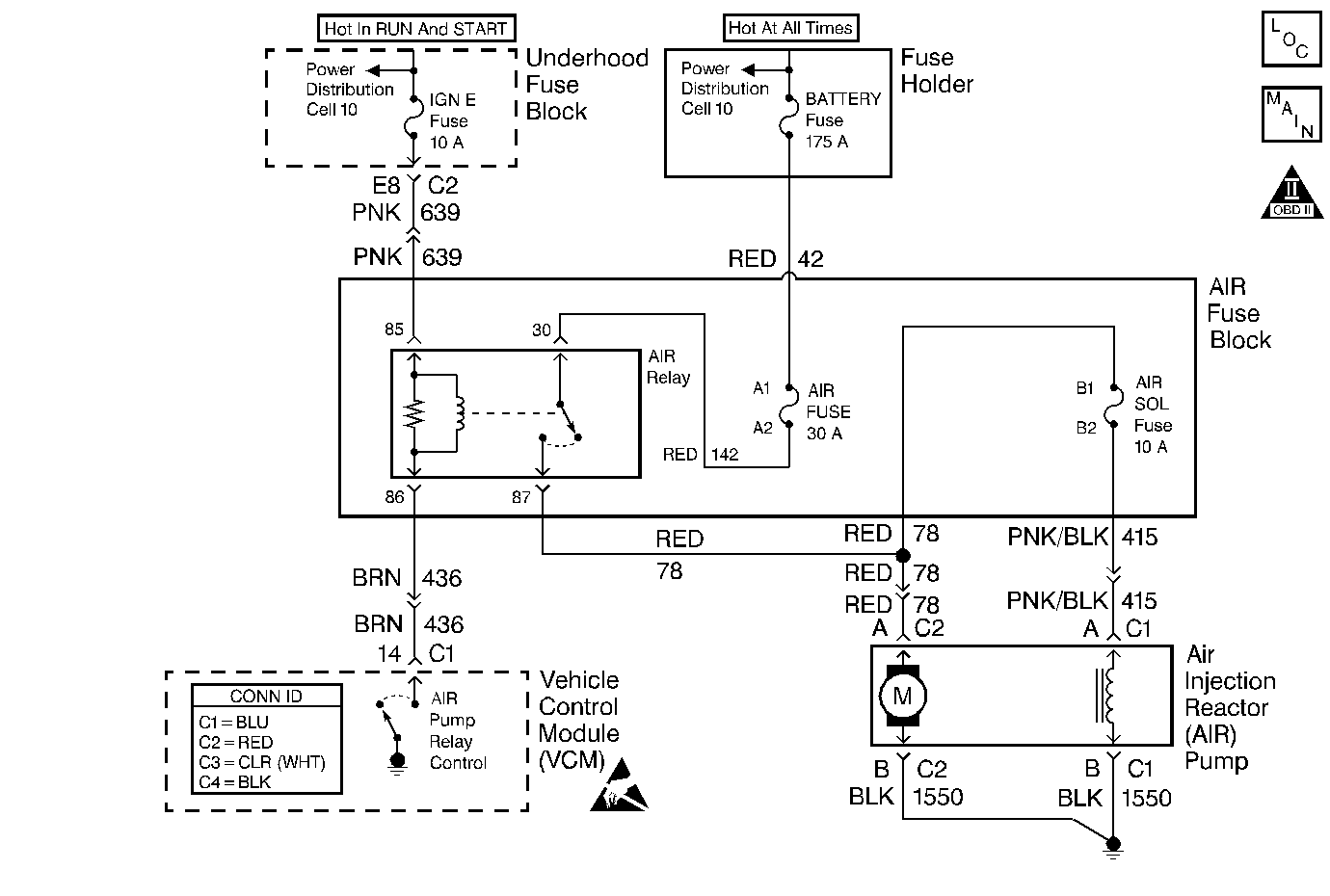
Circuit Description
An AIR Pump is used on this vehicle to lower tail pipe emissions at start-up. The VCM supplies a ground to the AIR Pump Relay, which energizes the AIR Pump and the AIR Solenoid.
When the AIR Pump is enabled, the VCM monitors the HO2S voltage. If the HO2S voltages go below a calibrated threshold value, the VCM interprets this as an indication that the AIR System is operational.
When the AIR Pump is disabled, the VCM monitors the HO2S voltages. The HO2S voltages should increase above a calibrated threshold value and switch normally.
If the VCM did not sense more than a predetermined amount of HO2S rich switches, a malfunction will be reported.
The VCM will activate the AIR Pump during closed loop operation. When the AIR System is activated, the VCM will monitor the HO2S voltages and short term fuel trim values for both banks of the engine. If the AIR System is operating properly, the HO2S voltages should go low and the short term fuel trim should go high.
The VCM checks that the HO2S voltages return to above a rich threshold when the AIR Pump is disabled.
If the VCM determines that the HO2S voltages for both banks did not respond as expected during the tests, DTC P0410 will set. If only one sensor responded, the VCM will set either a DTC P1415 or P1416 to indicate on which bank the AIR System is inoperative.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active ECT sensor DTCs |
| • | No active IAC sensor DTCs |
| • | No active HO2S DTCs |
| • | No active misfire DTCs |
| • | No active MAP DTCs. |
| • | No active Fuel Trim DTCs |
| • | No active EVAP DTCs |
| • | No active TP Sensor DTCs |
| • | No active IAT DTCs |
| • | No active MAF DTCs |
| • | The MAF is less than 25 g/s |
| • | The commanded air/fuel ratio is 14.7:1 |
| • | The engine load is less than 34 percent |
| • | Power enrichment mode is not active |
| • | DFCO (Decel Fuel Cutoff Mode) is not active |
| • | Catalyst overtemp protection is not active |
| • | The system has been in closed loop mode for more than 20 seconds |
| • | The short term fuel trim is between 124-132 counts |
| • | The engine speed is more than 550 RPM |
| • | The ECT is between 80-110°C (176-230° F) |
| • | The system voltage is 11.7 volts or more |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The O2 sensor voltage is less than 222 mv for more than 1.3 seconds, or |
| • | The short term fuel trim value changes more than 20 percent when the secondary air injection pump is turned on and the system is in closed loop operation. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The VCM illuminates the MIL during the second consecutive drive cycle in which the diagnostic reports a fail. |
| • | The VCM will set the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The VCM stores the failure information in the scan tools Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Low AIR System volume may cause a DTC P1415, P1416 or an intermittent complaint. Also check for the following conditions:
| • | Pinched, kinked or restricted AIR pipes, hoses or fittings |
| • | Leaks, holes, loose fittings or hoses |
| • | Restricted or obstructed AIR pump inlet |
| • | Leaks or restrictions in the vacuum hoses for the AIR Shut Off Valve. |
An AIR supply hose that is melted before the check valve could indicate exhaust gas back-flow past the check valve.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step will determine if the AIR system is functioning correctly.
-
This step determines if there is a short to voltage on the AIR pump supply voltage circuit. Allowing the AIR pump to operate continuously.
-
This step is to test for a short to voltage on the AIR solenoid supply voltage circuit keeping the AIR solenoid ON at all times.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||
2 |
Does the secondary air injection (AIR) pump run constantly? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||
3 |
Does the AIR pump turn ON and OFF when commanded with a scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||||||
Do the HO2S 1 bank 1 and HO2S 1 bank 2 voltage parameters decrease to the specified value within six seconds? | 100 mV | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||||
5 |
Does the AIR shut-off valve hold vacuum for the specified amount? | 30 seconds. | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 53 | ||||||||||
6 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF when commanded with a scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||||
7 |
Is the fuse open? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||||||
8 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 47 | ||||||||||
9 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 33 | ||||||||||
10 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF when commanded with a scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 40 | Go to Step 31 | ||||||||||
11 |
Important: The DMM and test leads must be calibrated to 0 ohms in order to prevent misdiagnosis. Refer to the DMM User Manual for calibration procedure. Measure the resistance of the AIR pump ground circuit with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-3 ohms. | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 50 | ||||||||||
12 |
Important: Ensure that the fuse rating does not exceed the load rating of the jumper wire.
Does the AIR pump turn ON? | -- | Go to Step 40 | Go to Step 13 | ||||||||||
13 |
Important: The DMM and test leads must be calibrated to 0 ohms in order to prevent misdiagnosis. Refer to the DMM User Manual for calibration procedure. Measure the resistance of the AIR pump supply voltage circuit with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-3 ohms. | Go to Step 41 | Go to Step 48 | ||||||||||
14 |
Is the vacuum equal to the specified value? | 0 in Hg/0 mm Hg | Go to Step 39 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||
15 |
Does the vacuum increase to more than the specified value? | 10 in Hg/254 mm Hg | Go to Step 32 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||||||
Does the AIR pump operate constantly? | -- | Go to Step 49 | Go to Step 17 | |||||||||||
17 | Probe the AIR pump relay control circuit at the AIR connector with a test lamp that is connected to battery voltage. Refer to Probing Electrical Connectors in Wiring Systems. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 24 | Go to Step 52 | ||||||||||
18 |
Does the vacuum displayed on the gage increase to more than the specified amount when commanded ON and drop back to zero inches of Hg when commanded OFF? | 10 in Hg/254 MM of Hg | Go to Step 36 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||
19 |
Is the vacuum more than the specified value? | 10 in Hg/254 MM Hg | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||||||
20 |
Is the vacuum more than the specified value? | 10 in Hg/254 MM Hg | Go to Step 36 | Go to Intake Manifold Cleaning and Inspection In Unit Repair | ||||||||||
21 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF when commanded with a scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 23 | ||||||||||
22 | Probe the AIR solenoid ground circuit with a test lamp that is connected to battery voltage. Refer to Probing Electrical Connectors . Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 42 | Go to Step 49 | ||||||||||
23 | Inspect the AIR solenoid fuse at the AIR Fuse block. Refer to Engine Controls Component Views . Is the AIR solenoid fuse open? | -- | Go to Step 34 | Go to Step 44 | ||||||||||
24 | Test the AIR pump relay control circuit for a short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 43 | ||||||||||
25 |
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 54 | ||||||||||
26 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 27 | ||||||||||
27 |
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 57 | Go to Step 28 | ||||||||||
28 |
Is water contamination found on the inlet side of the AIR pump? | -- | Go to Step 46 | Go to Step 29 | ||||||||||
29 |
Is water contamination found on the outlet side of the AIR pump? | -- | Go to Step 35 | Go to Step 30 | ||||||||||
30 |
Does the AIR pump operate? | -- | Go to Intermittent Conditions | Go to Step 56 | ||||||||||
31 | Test the AIR pump relay control circuit for an open or short to voltage Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 43 | ||||||||||
32 |
Is a pressurize airflow present at the crossover hose? | -- | Go to Step 38 | Go to Step 37 | ||||||||||
33 |
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||
34 |
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 54 | ||||||||||
35 | Inspect the water sample taken from the outlet side of the AIR pump. Does the water sample have a yellow tint and an exhaust odor? | -- | Go to Step 51 | Go to Step 45 | ||||||||||
36 | Inspect the following components for a leak or restriction.
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||
37 | Inspect the following components for a leak or restriction.
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 56 | ||||||||||
38 | Inspect the following components for a leak or restriction.
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||
39 | Connect a vacuum pump to the AIR shut-off valve and apply 10 inches of vacuum to the AIR shut- off valve. Does the AIR shut-off valve hold vacuum for the specified amount? | 30 seconds | System OK | Go to Step 53 | ||||||||||
40 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the AIR pump relay. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 52 | ||||||||||
41 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the AIR pump connector. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 56 | ||||||||||
42 | Test for and intermittent and for a poor connection at the AIR solenoid. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 54 | ||||||||||
43 | Test for shorted terminals and poor connections at the control module. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 57 | ||||||||||
44 | Test the AIR solenoid supply voltage circuit for an open or high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||
45 |
Is water contamination found on the outlet side of the AIR solenoid? | -- | Go to Step 55 | Go to Step 51 | ||||||||||
46 | Inspect the AIR inlet hose for the following conditions.
Did you find a condition? | -- | Go to Step 56 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||
47 | Repair the open or high resistance in the battery positive voltage circuit to the AIR pump relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
48 | Repair the high resistance in the AIR pump supply voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
49 | Repair the short to voltage in the AIR pump supply voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
50 |
Important: The AIR pump and AIR solenoid have a shared ground circuit. Repair the open or high resistance in the AIR pump ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
51 | Replace the AIR Exhaust Check valves. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Check Valve and Check Valve Pipe Replacement - Bank 1 and Secondary Air Injection Check Valve and Check Valve Pipe Replacement - Bank 2 . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 56 | -- | ||||||||||
52 | Replace the AIR pump relay. Refer to Electrical Center Identification Views in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
53 | Replace the AIR shut off valve. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Shutoff Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 59 | -- | ||||||||||
54 | Replace the AIR solenoid. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Solenoid Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
55 |
Important: Ensure the correct routing of the AIR hoses. The inlet side of the AIR pump is marked IN.
Did you complete the replacements? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
56 |
Important: Ensure the correct routing of the AIR hoses. The inlet side of the AIR pump is marked IN. Replace the AIR pump. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Pump Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
57 |
Important: The replacement control module must be programmed. Replace the control module. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 58 | -- | ||||||||||
58 |
Does the AIR pump turn ON and OFF? | -- | Go to Step 59 | Go to Step 2 | ||||||||||
59 |
Does the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 60 | ||||||||||
60 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK |
