Diagnostic Information
Use the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) tables in this section in order
to locate a faulty circuit or a component through the process of elimination.
The BCM performs a continual self-diagnosis on certain control functions.
A DTC sets when a malfunction is detected by the BCM. The BCM will not turn
the SERVICE ENGINE SOON malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) ON.
Class 2 Serial Data Communication
The Class 2 network continually monitors various subsystems (i.e.
ATC, BCM, HVAC, IPC, PCM, and VCM) and operating conditions for possible system
malfunctions. Compare the system conditions against standard operating limits
in order to detect certain circuit and component malfunctions. A 5-digit
alphanumeric diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is stored in the computer memory.
When a malfunction is detected by this self-diagnostic system, the DTC(s)
may later be retrieved by the service technician using a scan tool. The scan
tool may aid the technician in repairing various subsystems.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
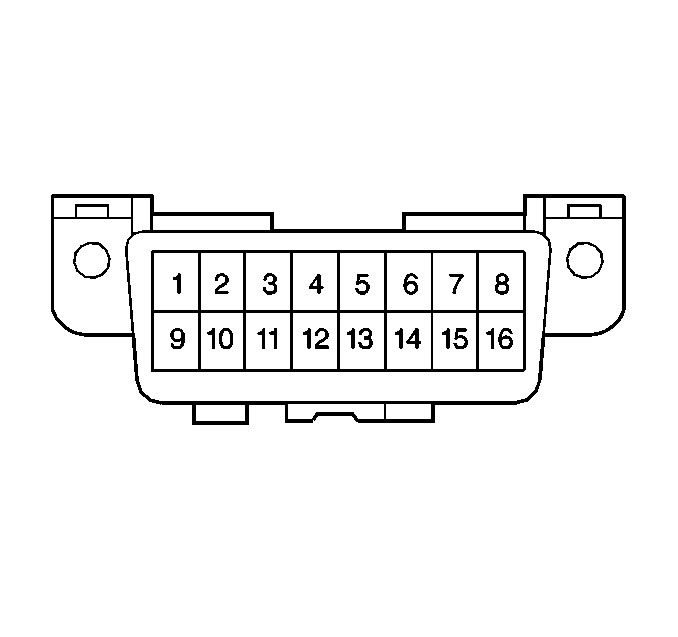
The 16-pin DLC is wired to the body control module. The 16-pin DLC is
located under the dash panel on the left side. The DLC connector has terminals
that are used in order to connect to a scan tool. The following list shows
some common uses of the scan tool:
| • | Identifying stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) |
| • | Performing output control tests |
Scan Tool Diagnosis
Use the scan tool in order to monitor the communications between the
BCM and the PCM/VCM. The scan tool also displays Passlock™ data. The
Passlock™ DATA LIST display is located under the PASSLOCK selection.
This list shows the status of the hardwired connections from the Passlock™
sensor to the BCM. These scan tool values may be very useful in diagnosing
the Passlock™ system.
The Passlock™ system is designed in order to deter theft, even
if various parts are changed. The following components may not be changed
without the possibility of going into a no-start condition:
| • | The powertrain control module (PCM) |
| • | The body control module (BCM) |
| • | The vehicle control module (VCM) |
If any of these parts are replaced, refer to the Learn Procedure in
Body Control Module (BCM) Programming/RPO Configuration
.
The BCM and the PCM/VCM require the full 10 minutes in order to complete
a lockout cycle. The ignition key MUST remain in the RUN position until the
telltale turns OFF. If the ignition key is turned from the RUN position
before the telltale turns OFF, you will have to repeat the lockout cycle.
The Passlock™ system requires 3 consecutive lockout cycles
in order to complete the 30 minute learn procedure for a changed component.
Refer to Theft Deterrent for more information on the Passlock™ system.
Scan Tool Information Modes
On the scan tool, four modes are available in the body control module
selection. Select the following items:
- Body control module
- Data display
- Data list
The following list appears on the scan tool:
The scan tool allows for the for the display of Class 2 values,
or the state of components commanded by the various systems (i.e. ATC, BCM,
HVAC, IPC, PCM and VCM). The tests available are dependent upon the system
selected, but may include the following modes:
Data (analog inputs): This test displays analog values as seen by the system.
Inputs (digital inputs): This test displays digital values as seen by the system and provides
an indication of whether the input has cycled.
Outputs (digital outputs): This test allows for digital outputs controlled by the BCM system
in order to be turned OFF/ON.
Special functions (analog outputs): This test allows for analog outputs of the BCM system to be set
at a desired value.
Clear diagnostic trouble codes: This test will erase all DTCs stored for the system currently selected.
If the malfunction is still present, the DTC may immediately reset.
Security data (content theft): This test contains information applicable to the content theft
system.
The Diagnostic Executive
The diagnostic executive is a unique segment of software that is designed
in order to perform the following functions:
| • | Coordinate and prioritize the diagnostic procedures |
| • | Define the protocol for recording and displaying the results |
| • | Receive the diagnostic test results and records the pass and the
fail status |
The following list shows the main responsibilities of the diagnostic
executive:
| • | Monitor the diagnostic test-enabling conditions |
| • | Monitor and record test status information |
| • | Record pass and fail status of test results |
A diagnostic test is a series of steps that has a beginning and an end.
The result of a diagnostic test is pass or fail, which is reported to the
diagnostic executive. When a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the
diagnostic executive records the following data:
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not currently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the diagnostic executive
records the following data:
| • | The fault identified by the diagnostic test is currently active. |
| • | The fault identified by the diagnostic test has been active since
the last 100 ignition cycles or since the codes have been cleared. |
| • | The code supported BIT is enabled. |
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Diagnosis
This section uses the following items in order to direct you in performing
specific tests in order to locate and repair the problem:
The diagnostic table is a step by step procedure used in order to determine
the circuit or the component that is the source of the problem. The following
items are located above the diagnostic table:
| • | Actions taken when a DTC is set |
When the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are set, the BCM detects a
malfunction in a particular circuit or other system. Other system malfunctions
are generally (but not exclusively) reported to the BCM via Class 2
data message. The BCM is programmed with routines for internal checks
that the BCM follows only under prescribed conditions (called test conditions).
When these conditions exist, the BCM inspects certain circuits or systems
for a malfunction. These inspections are called failure conditions or
conditions for setting the DTC. When these conditions are true, a DTC
is set. The BCM turns ON the SECURITY malfunction indicator lamp (MIL)
for the Passlock™ system-related malfunctions. Refer to the applicable
DTC table for procedures and details.

