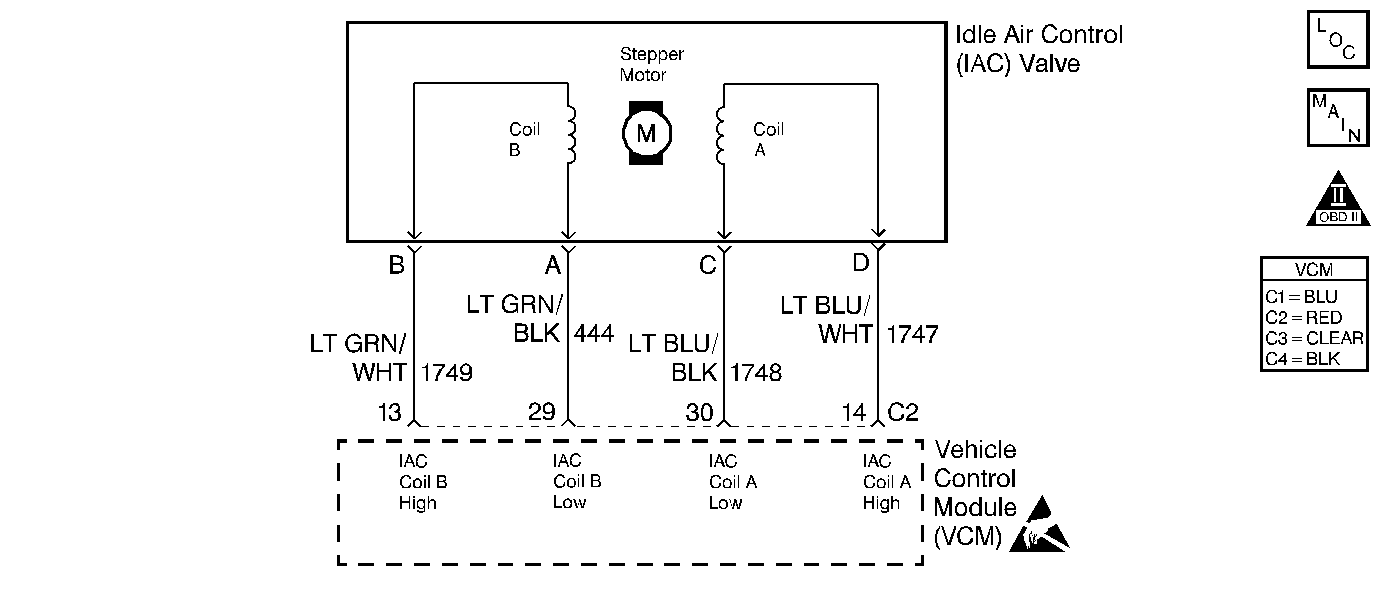
Circuit Description
The VCM controls the idle speed with an Idle Air Control (IAC) valve to a calculated desired RPM based on the sensor inputs and the actual engine RPM. The VCM uses 4 circuits to move an Idle Air Control (IAC) valve, allowing varying amounts of air flow into the intake manifold. In order to increase the idle RPM, the VCM moves the IAC valve out, allowing more air to bypass the throttle plate. In order to decrease the RPM, the VCM will move the IAC valve in, reducing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate. A scan tool reads the VCM commands to the IAC valve in counts. The higher the counts, the more air that is allowed to bypass the throttle plate (higher idle). The lower the counts, the less air that is allowed to bypass the throttle plates (lower idle). This is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Test Enable (Non-Intrusive)
| • | No TP sensor DTCs. |
| • | No ECT sensorDTCs. |
| • | No VS sensor DTCs. |
| • | No MAP sensor DTCs. |
| • | ECT is greater than 50°C. |
| • | IAT is greater than -25°C. |
| • | BARO is greater than 70 kPa. |
| • | Vehicle Speed is less than 2 mph. |
| • | System voltage is between 10 volts and 16 volts. |
| • | Engine run time is greater than 30 seconds. |
| • | TP is less than 1%. |
| • | Above met for a time greater than 3 seconds. |
| • | Change in Calculated MAF is greater than 3 grams per second. |
Run Test (Intrusive)
| • | Calculated MAF is between 17.5 grams per second and 50.0 grams per second. |
| • | Vehicle Speed is between 25 MPH and 85 MPH. |
| • | Change in TP Sensor is less than 1%. |
| • | Change in engine speed is less than 50 RPM. |
| • | IAC motor commanded to 10% for 100 ms. |
| • | Change in Calculated MAF is greater than 3 grams per second. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The VCM turns the MIL ON after 2 consecutive driving cycles with the fault active.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
The VCM turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive driving trips without a fault condition present. A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles (the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the start-up coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 71°C (160°F) during that same ignition cycle) or the scan tool clearing feature has been used.
Diagnostic Aids
An IAC valve which is stopped and cannot respond to the VCM, a throttle stop screw which has been tampered with, or a damaged throttle or linkage could cause this DTC. A slow, unstable, or fast idle may be caused by a non - IAC valve system problem that cannot be overcome by the IAC valve. Out of range control IAC scan tool counts will be above 60 if idle is too low and zero if idle is too high. Check for the following conditions:
| • | Fuel system too lean and rich. |
| • | Throttle body - inspect bore for foreign material. |
| • | Refer to Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle and Stalling . |
| • | IAC reset is done with scan tool misc functions mode. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The IAC tester is used to extend and retract the IAC valve. Valve movement is verified by an engine speed change. If no change in engine speed occurs, the valve can be retested when removed from the throttle body.
-
This step checks the quality of the IAC movement in Step 2. Between 700 RPM and about 1200 RPM, the engine speed should change smoothly with each flash of the tester lamp in both extend and retract. If the IAC valve is retracted beyond the control range (about 1500 RPM), it may take many flashes in the extend position before engine speed will begin to drop. This is normal on certain engines, fully extending IAC may cause engine stall. This may be normal.
-
Steps 2 and 3 verified proper IAC valve operation while this Step checks the IAC circuits. Each lamp on the node lamp should flash red and green while the IAC valve is cycled. While the sequence of color is not important if either lamp is OFF or does not flash red and green, check the circuits for faults beginning with poor terminal contacts.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool to record the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records for reference. This data will be lost when the Clear Info function is used. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||||||||||
Did the Engine RPM decrease and increase as the IAC is cycled? | -- | |||||||||||
Observe the RPM. The RPM should change smoothly with each flash of the IAC Driver lamp. Does the RPM change smoothly within the specified value? | 700-1500 RPM | |||||||||||
4 | Check the IAC passages. If OK, replace the IAC. Important: If a repair has been made refer to IAC Reset Procedure before resetting. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
Do both Green and Red lamps flash on and off? | -- | |||||||||||
6 | Check for the following conditions:
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||
7 | Repair the connections and terminal contacts as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Engine Electrical. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
8 |
Is the resistance within the specified value? | -- | ||||||||||
9 |
Is the resistance at the specified value? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||
10 | Replace the IAC valve. Refer to IAC Valve Replacement . Important:: If a repair has been made refer to IAC Reset Procedure before resetting. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
11 | Replace the VCM. Important: If the VCM is faulty, program the new VCM. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
12 |
Does scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||||
13 | Using the scan tool, select the Capture Info and the Review Info. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to The Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
