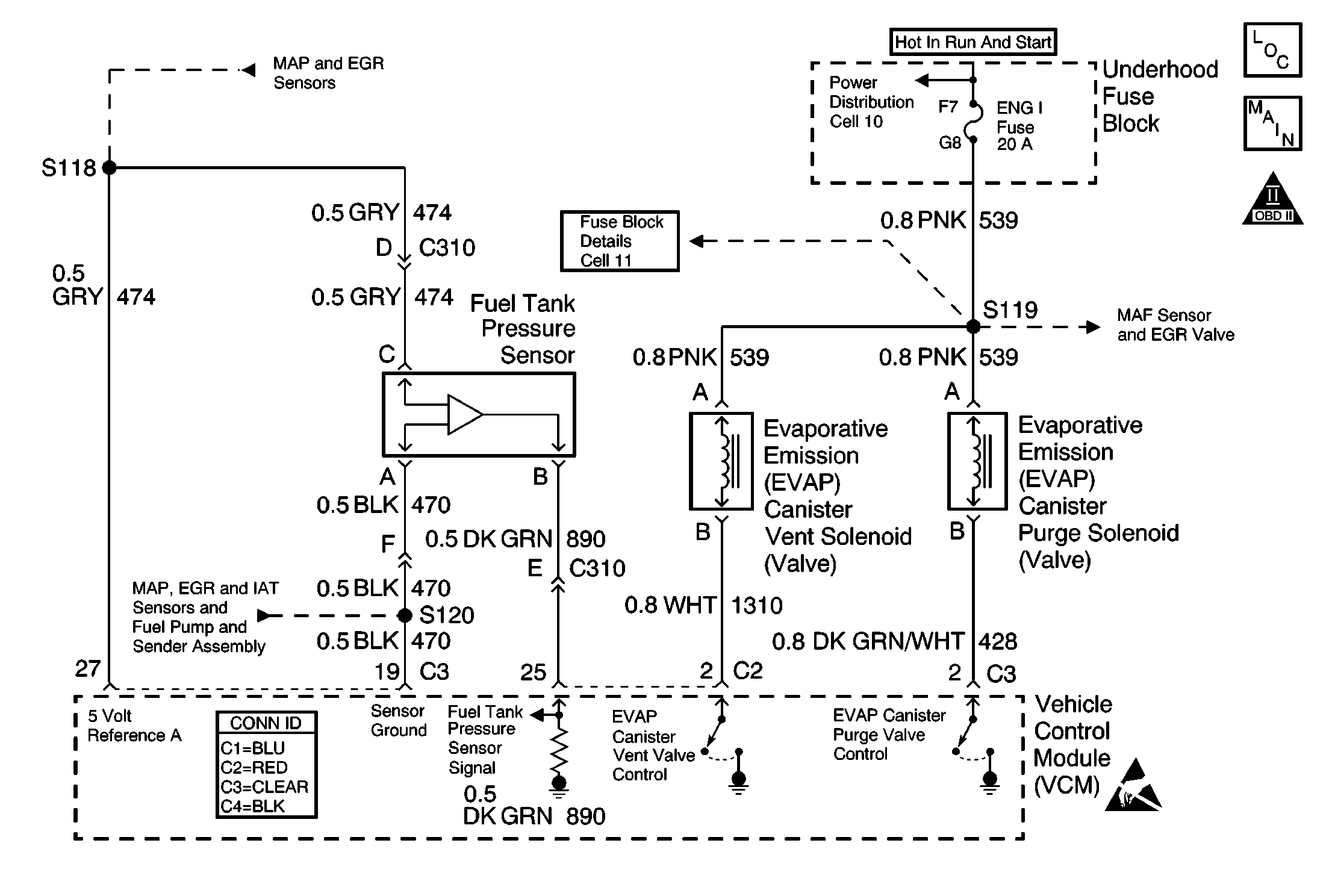
Circuit Description
The fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor responds to changes in the fuel tank pressure or vacuum. This information is used in order to detect vacuum decay or an excessive vacuum during the EVAP diagnostic routing. The FTP sensor signal voltage to the vehicle control module (VCM) varies from a minimum of about 0.1 volts with pressure in the fuel tank to more than 4.0 volts with a high vacuum in the fuel tank.
The FTP sensor display on the scan tool has an auto-zero feature which occurs at each ignition cycle and is corrected according to the barometric pressure. Because of this, the FTP sensor display may not accurately reflect the actual output of the sensor or the conditions within the fuel tank.
The FTP sensor diagnosis table is intended to isolate and diagnose the electrical problems in the sensor wiring or in the sensor.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The ignition switch is in the RUN position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The FTP sensor voltage is more than 4.98 volts for more than 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The VCM turns ON the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 2 consecutive driving cycles with the fault active.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
- Inspect the control module harness connectors for the following conditions:
- Inspect the wiring harness for damage--If the harness appears to be OK, observe the FTP sensor display on the scan tool while moving the connectors and the wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
| • | Backed-out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Faulty terminal-to-wire connection |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If the FTP sensor value is less than -16.50 inches H2O, an FTP sensor circuit problem or an internally shorted FTP sensor may be present . Note that -17.32 inches H20 is less than -16.50 inches H20.
-
If the FTP sensor value is more than 7.4 inches H2O, the fault is the FTP sensor, or the reference voltage is more than 5.00 volts. With good circuits, a disconnected FTP sensor should indicate 7.4 inches H2O.
-
A high voltage reading on the 5 volt reference circuit could be caused by a short to voltage on another 5 volt reference circuit, some 5 volt reference circuits are shared inside and outside the VCM. A defective linear exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve may bleed battery voltage onto the 5 volt reference circuit.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Is the fuel tank pressure more than the specified value? | -16.50 in. H2O | Fault not present, go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Disconnect the FTP sensor connector. Is the fuel tank pressure more than the specified value? | 7.0 in. H2O | |||
4 | Using a DMM, measure the voltage between the 5 volt reference circuit and ground at the FTP sensor connector. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 5.20 V | ||
5 | Using a DMM, measure the voltage between the FTP sensor signal circuit and ground. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 0.5 V | ||
6 | Repair the short to voltage on the EVAP fuel tank pressure sensor signal circuit. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
Repair the short to voltage on the 5 volt reference circuit. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | ||
8 |
Was the terminal contact repaired? | -- | ||
9 | Replace the fuel tank pressure sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
Was the terminal contact repaired? | -- | ||
11 |
Important: The replacement VCM must be programmed. Replace the VCM. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
13 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
