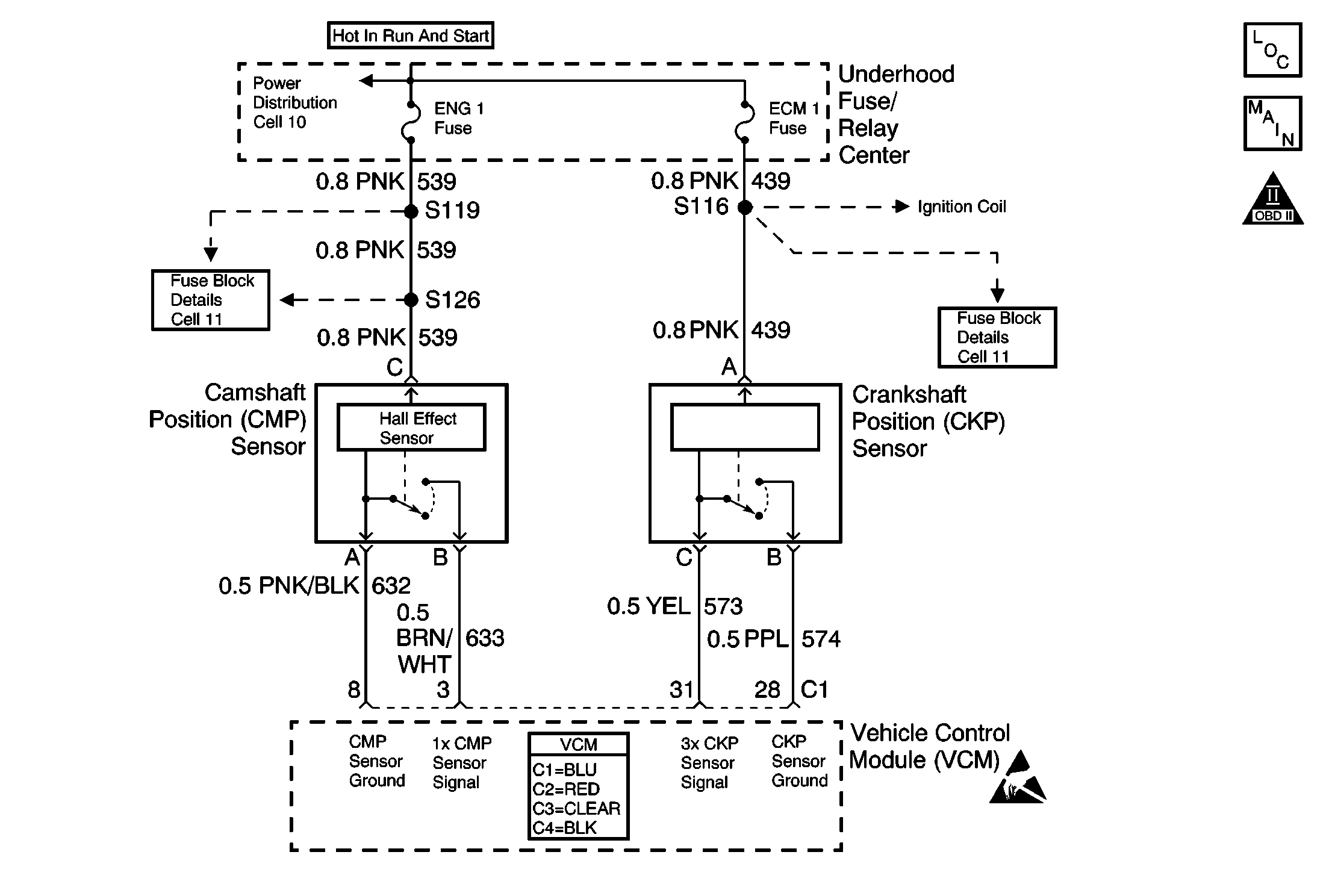
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is mounted in the front of the engine behind the harmonic balancer. The CKP sensor works in conjunction with a 3X (4X on V8 applications) reluctor wheel mounted on the front of the crankshaft. The CKP sensor has a B+ power supply, a ground, and a signal circuit.
As the crankshaft rotates, the reluctor wheel teeth interrupt a magnetic field produced by a magnet located in the sensor. The sensors internal circuitry detects this field and produces a frequency which the control module monitors on the signal circuit. The control module uses this signal in order to accurately measure crankshaft velocity, which is important to ignition control spark timing, fuel injector timing, and for misfire detection.
The control module can detect small variations in the CKP sensor and reluctor wheel. These part tolerances must be learned by the control module before an accurate CKP signal can be determined. At high engine speeds, slight variations in the following components make misfire detection difficult:
| • | Crankshaft |
| • | Reluctor wheel |
| • | CKP sensor |
The control module learns variations during the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learning Procedure, and compensates for these variations when performing misfire calculations. Only a scan tool can command the control module to perform the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learning Procedure.
Perform the learning procedure after the following actions:
| • | A control module replacement |
| • | Any operation or repair involving the crankshaft, the CKP sensor, or the CKP sensor to reluctor wheel gap relationship |
| • | An engine replacement |
Important: A control module power disconnect with the ignition ON may erase the stored pulse value and set the DTC P1336.
Disconnecting the control module will not erase the learned crankshaft position system variation as long as the ignition switch is in the OFF position.
Important: Reprogramming the control module does not require running the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn Procedure unless the module is new or from another vehicle.
If the crankshaft position system variation is not within an acceptable range, or can not be learned, DTC P1336 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine is running |
| • | No active camshaft position (CMP) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active CKP sensor DTCs |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The vehicle control module (VCM) has not learned the crankshaft position system variation.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) the first time the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module will set the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The control module stores the failure information in the scan tools Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect for the following conditions if the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn Procedure cannot be completed:
| • | A chipped or damaged reluctor wheel |
| • | An incorrect alignment of the CKP sensor with the reluctor wheel |
| • | An excessive crankshaft run-out |
| • | Interference in the signal circuit to the CKP sensor |
| Important: The VCM does not allow the scan tool to enable the learn procedure when an incorrect crankshaft-to-camshaft ratio is received. |
| • | An incorrect ratio of crankshaft-to-camshaft pulses. |
The engine misfire diagnostic is disabled when the engine speed is more than 1,000 RPM and this DTC is active.
When the learn procedure is in progress and the engine speed is at 4,000 RPM, a decrease in engine speed will occur. During the engine coast-down, the VCM monitors the CKP sensor signal and stores the pattern. This pattern is used to determine if the crankshaft speed variations are due to an engine misfire.
Inspect for intermittents.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly inspect any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The VCM enables the learn process after 65°C (150°F) is reached. Engine deceleration occurs when the learn procedure is in progress. The VCM monitors and records the CKP sensor signal during engine coast down conditions.
-
TEST IN PROGRESS on the scan tool indicates the VCM is performing the learn procedure. If the VCM receives an incorrect crankshaft to camshaft pulse ratio, an incorrect transmission range signal input, corrupted communication, or no change in the brake switch input, the learn procedure will not be allowed.
-
If a repair is necessary due to a condition which prevented the learn procedure from enabling, the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learning Procedure must be performed.
-
The ignition must be in the OFF position for at least 10 seconds after the learn procedure is complete and the engine RPM has returned to idle. The VCM saves the signal data after these conditions are met.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Perform the CKP System Variation Learn Procedure. Refer to Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn . Does the scan tool indicate the procedure is completed? | -- | |||
Attempt the CKP System Variation Learn Procedure as many times as the specified value. Refer to Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn . Does the scan tool indicate the procedure is completed? | 3 | |||
Check the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and the crankshaft reluctor wheel for damage. Refer to Diagnostic Aids. Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Turn OFF the ignition for 15 seconds. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
6 | Replace the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and/or the crankshaft reluctor wheel. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Reluctor Ring Replacement in Engine Mechanical and to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Perform the CKP System Variation Learn Procedure. Refer to Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
9 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
