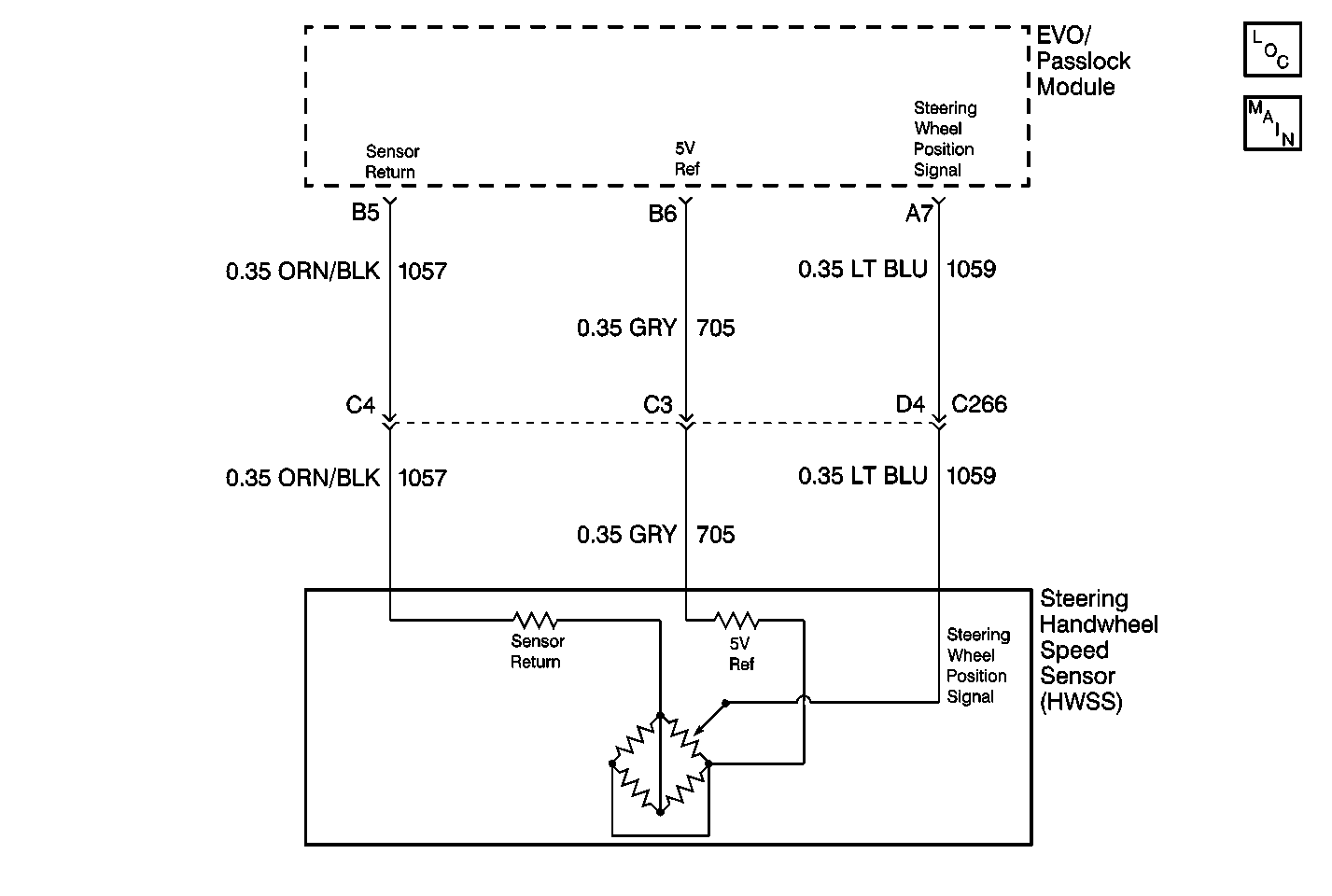
Circuit Description
The EVO/Passlock™ module receives the vehicle speed information through the vehicle control module (VCM) of the gasoline engines, or the powertrain control module (PCM) of the diesel engines, and the class 2 data line. With the vehicle speed information, the EVO/Passlock™ module compares the vehicle speed signal received from the VSS with the vehicle speed data received from the class 2 data line. The VSS is a permanent magnet sensor producing an AC signal with varying frequency. The VSS is mounted in the transmission, or the transfer case in selectable four wheel drive models, and is driven off the output shaft. The VSS produces a pulsing AC voltage and the number of pulses increase with the vehicle speed. The VCM/PCM supplies the vehicle speed signal to the instrument cluster and to the EVO/Passlock™ module.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The steering wheel rotation sensor voltage is greater than 4.9 volts for one second or longer.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The EVO/Passlock™ module does not send any current to the PS solenoid actuator. This causes the retraction of the EVO valve. This provides the maximum fluid flow and full power steering assist at all times.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
| • | A history DTC will clear after 100 consecutive ignition cycles have occurred without a fault. |
| • | The history and the current DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
The scan tool will read the steering wheel position in volts. With the ignition switch in the ON position, and as the steering handwheel speed sensor is rotated, the voltage reading should be 0.2-4.9 volts. The voltage should increase at a steady rate up to 4.9 volts when the wheel is turned, one quarter revolution (90 degrees) in either direction.
| • | Above 0.2 volts. |
| • | Below 4.9 volts when the steering wheel is rotated one quarter revolution (90 degrees). |
Using the scan tool, scan the handwheel speed sensor.
| • | Above 0.2 volts. |
| • | Turn the steering wheel. |
| • | The scan tool display should increase from above 0.2 volts and below 4.9 volts as the steering wheel is turned one quarter revolution (90 degrees). |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This step prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and to store the Snapshot data. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. Refer to this stored information as necessary. When the voltage is 0.2-4.9 volts, the electronic variable orifice (EVO)/Passlock™ module uses this voltage to detect changes in the position of the steering wheel and the rate of steering. The system voltage increase and decreases proportionately to the steering wheel rotational speed. If the voltage is not within the specifications, a DTC sets.
-
This step probes the ground circuit and checks the circuit for high resistance, which sets DTC C0473.
-
This step verifies a shorted 5.0 volt reference circuit, which may also set additional DTCs.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Variable Effort Steering System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Slowly return the steering wheel to the center position. Does the steering wheel rotation sensor value increase steadily to the specified value when the steering wheel is rotated? | 0.2-4.9 V | Go to Step 3 | ||
3 | Operate the vehicle within the Snapshot conditions for setting the DTC as noted. Is the steering wheel rotation sensor voltage greater than the specified value? | 4.9 V | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 13 |
4 |
Is the voltage of the steering wheel rotation sensor greater than the specified value? | 0.2 V | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 6 |
Using a digital multimeter (DMM), connect the negative lead to ground and with the positive lead probe the sensor signal LT BLU (1059) wire of the harness connector of the rotation sensor. Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 5 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 7 | |
Locate and repair the short to the voltage in the signal LT BLU (1059) wire of the steering wheel rotation sensor. Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 | |
7 | Using a DMM, connect the negative lead to ground and with the positive lead probe the sensor return ORN/BLK (1057) wire of the harness connector of the rotation sensor. Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 5 V | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 8 |
8 | Using a DMM, connect the negative lead to ground and with the positive lead probe the sensor return GRY (705) wire of the harness connector of the rotation sensor. Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 5 V | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 9 |
9 | Check for a short to the voltage in the GRY (705) wire of the steering wheel rotation sensor. Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 |
10 | Check for a short to the voltage in the ORN/BLK (1057) wire of the steering wheel rotation sensor. Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Replace the steering wheel rotation sensor. Refer to Steering Wheel Position Sensor or Steering Shaft Lower Bearing Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
12 | Replace the EVO/Passlock™ module. Refer to Theft Deterrent Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
13 |
Drive the vehicle until normal operating temperature is reached. Does the scan tool display DTC C0473? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 14 |
14 | Does the scan tool display any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the appropriate DTC table |
