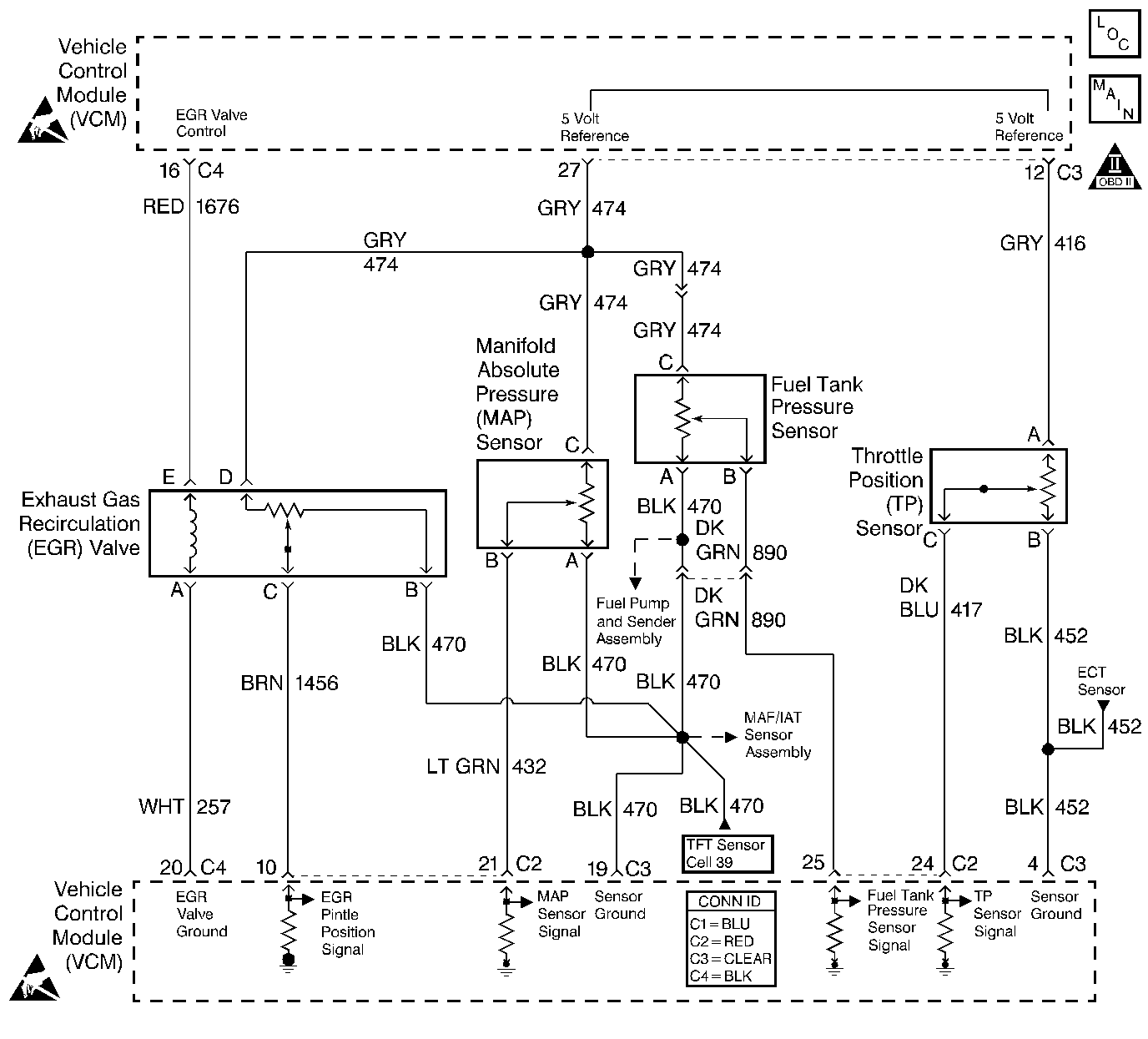
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor is a potentiometer. The control module supplies the TP sensor a reference voltage, a signal, and ground circuits. When the throttle is depressed, the TP sensor signal rises to near the reference voltage. When the throttle is released, the TP sensor signal decreases from the reference voltage. The control module monitors the TP sensor signal circuit voltage in order to determine the throttle blade angle, or opening.
This DTC is designed to detect a TP sensor signal voltage higher than the possible operating range of a normally functioning TP sensor.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The TP sensor signal voltage is more than 4.7 volts for 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
The scan tool reads the throttle position in volts. The scan tool should read about 0.45-0.85 volt with the throttle closed and the ignition switch turned ON or at idle. The voltage should increase at a steady rate as the throttle is moved toward the Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
Also, some scan tools will read the throttle angle. 0 percent equals closed throttle. 100 percent equals WOT.
Scan the TP sensor while depressing the accelerator pedal with the engine turned off and the ignition turned on. The display should vary from below the 1.25 volts (1250 mV) with the throttle closed to over 4.5 volts (4500 mV) when the throttle is held at the WOT position.
This DTC will result if the TP ground circuit is open or the TP signal circuit is shorted to the voltage.
Refer to the Symptoms .
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
If the TP signal measures more than 4.8 volts, then the condition exists.
-
With the TP sensor disconnected, and if the VCM and the wiring are okay, the TP signal should go below 0.25 volt. This test could set a DTC P0122.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool display a TP sensor voltage more than the specified value? | 4.7 V | |||
Does the scan tool display a TP sensor voltage less than the specified value? | 0.25 V | |||
4 | The DTC is intermittent. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
5 | Measure the 5 volt reference circuit at the TP sensor harness connector with a J 39200 DMM connected to a ground. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 5.2 V | ||
6 | Probe the TP sensor ground circuit at the TP sensor harness connector with a test lamp connected to B+. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | ||
7 | Replace the TP sensor. Refer to Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Check for a short to voltage in the TP sensor signal circuit. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
9 |
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 0 V | ||
10 | Measure the voltage on the MAP sensor 5 volt reference circuit at the VCM C3 connector with a J 39200 DMM connected to a ground. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 0 V | ||
11 | Repair the open in the TP sensor ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 | Repair the circuit as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Repair the short to voltage on the 5 volt reference circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
16 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
