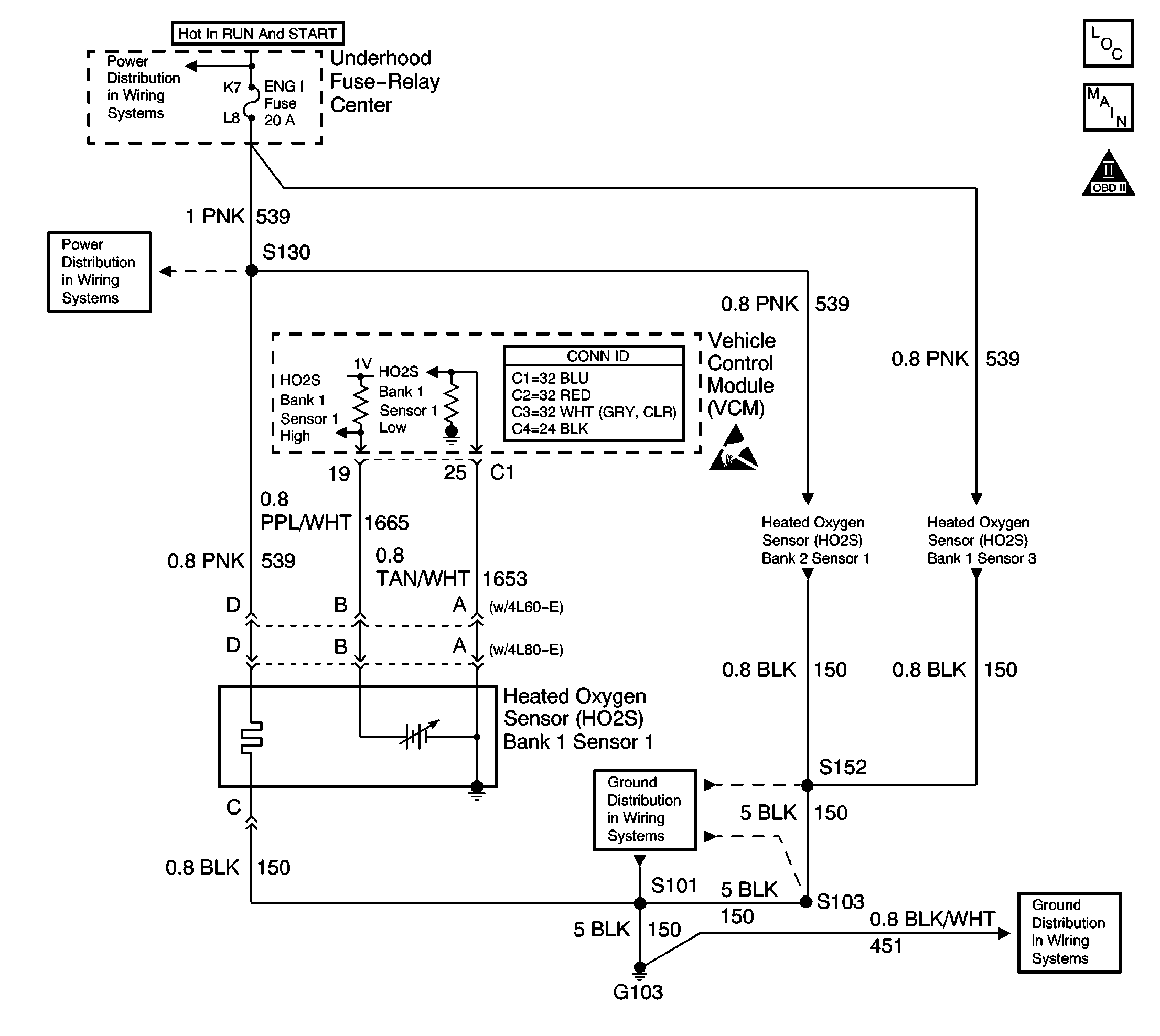
Circuit Description
In order to provide the best possible combination of driveability, fuel economy, and emission control, the vehicle uses a closed loop air and fuel metering system. While in closed loop, the VCM monitors the oxygen sensor signal voltage. The VCM adjusts the fuel delivery based on a signal voltage. The long and short term fuel values, which a scan tool can monitor, indicate a change made to the fuel delivery. Ideal fuel trim values are around 0 percent (128 counts). If the oxygen sensor signal indicates a lean condition, the VCM will add fuel. This results in fuel trim values of more than 0 percent. If the oxygen sensor detects a rich condition, the fuel trim values will read less than 0 percent. This will indicate that the VCM is reducing the amount of fuel delivered. The VCM sets this DTC when an excessively rich condition is detected.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active oxygen sensor (O2S) DTCs |
| • | No active throttle position (TP) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active EGR sensor DTCs |
| • | No active EVAP system DTCs |
| • | No active engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active mass air flow (MAF) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active intake air temperature (IAT) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active vehicle speed sensor (VSS) DTCs |
| • | No active misfire DTCs |
| • | The throttle position is less than 70 percent |
| • | Engine speed is between 575 and 4,000 RPM |
| • | The barometric pressure (BARO) is more than 70 kPa |
| • | The ECT is 75 - 114°C (167- 237°F) |
| • | The MAP is 22 - 85 kPa. |
| • | The IAT is between -8 and +76°C (46 - 169°F) |
| • | The MAF is 3 - 85 g/s |
| • | The vehicle speed is less than 85 mph |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The average of the short term fuel trim values over a period of 120 seconds indicates that a rich condition is present.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
Important: To complete a trip cycle for the fuel trim diagnostic, the fuel trim diagnostic test must enable and run according to the above enabling conditions and the conditions for setting. A trip is not considered complete until the fuel trim diagnostic has been run by the VCM.
When the current DTC initially sets, a software flag indicating an emissions related fault sets for 3 trips. The flag will clear provided the lean condition is no longer present. However, if the VCM detects the conditions for setting the current DTC during a trip while the flag is still set, the VCM turns on the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). The MIL remains on during all of the subsequent trips until the DTC has been cleared by service or the lean condition has not been detected and the conditions for checking the fuel trim have been met for 3 consecutive trips.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
If using the diagnostic tables does not isolate the problem, try monitoring the LT fuel trim and fuel trim cell while operating the vehicle under various loads. This may isolate the condition which caused the setting of the current DTC.
A condition that causes DTC P0300 Engine Misfire Detected may also set the current DTC. Conversely, an extremely rich condition which sets the current DTC can cause a misfire at idle and DTC P0300 to set. If the cause of the current DTC cannot be determined and DTC P0300 is also set, refer to DTC P0300 Engine Misfire Detected .
Typical Fuel Trim Values
Control Module Leaning Fuel | No Adj. | Control Module Enriching Fuel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Lean | DTC sets | -- | DTC sets | Max. Rich |
-25% | -14% | 0% | +20% | +25% |
The fuel trim values table indicates the typical fuel adjustment values as displayed on a scan tool. Negative values, or a rich condition, indicates that the injector pulse width is being decreased in order to lean out the fuel mixture. Positive values, or a lean condition, indicates that the injector pulse width is being increased in order to richen the fuel mixture.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
A more negative value indicates the VCM is leaning the fuel mixture, and a more positive value indicates the VCM is richening the fuel mixture.
-
This step checks the fuel system for problems.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: : Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records for reference. The control module data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Important: : If any DTCs are set other than P0172 or P0175, refer to those DTCs before proceeding with this diagnostic.
Is the Long Term FT Bn 1 value closer to 0% than the specified value? | -14 % Long Term FT | |||||||||||||||||||
3 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Refer to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||||||||
4 | Visually and physically check the following items:
Did any of the above checks isolate a condition requiring repair? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
Caution: Wrap a shop towel around the fuel pressure connection in order to reduce the risk of fire and personal injury. The towel will absorb any fuel leakage that occurs during the connection of the fuel pressure gage. Place the towel in an approved container when the connection of the fuel pressure gage is complete. Caution: The fuel pump will operate for 2 seconds after you have turned off the ignition. Make sure that all the fuel pipes and fittings are securely fastened in order to prevent personal injury. Does fuel pressure hold within the specified range? | 379-413 kPa (55-60 psi) | |||||||||||||||||||
6 | Perform the Fuel Injector Balance Test with Tech 2 . Was an injector problem found? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
7 | Perform the DTC P1441 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Flow During Non-Purge . Was a problem found? | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||||||||
8 |
Is the Long Term FT Bn 1 value closer to 0% than the specified value? | -14 % Long Term FT | ||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Is the Long Term FT Bn 1 value closer to 0% than the specified value? | -14 % Long Term FT | ||||||||||||||||||
10 |
Is the Long Term FT Bn 1 value closer to 0% than the specified value? | -14 % Long Term FT | ||||||||||||||||||
11 | A rich condition is not present. Does a driveability symptom still exist? | -- | Go to Driveability Symptoms | |||||||||||||||||
12 | Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
13 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic passed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
14 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
