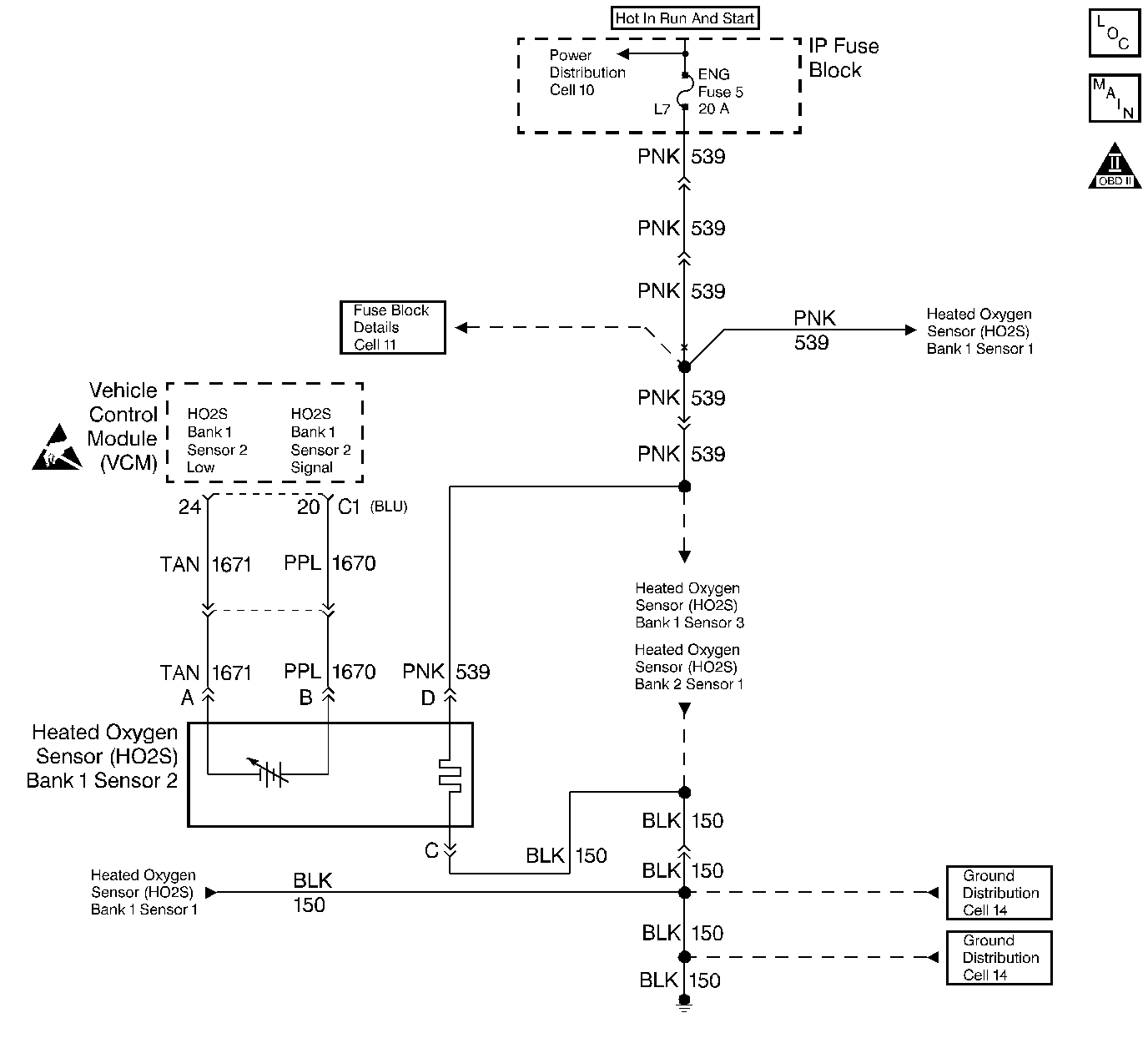
Circuit Description
The VCM supplies a voltage of approximately 0.45 volt (450 mV) between the HO2S High and HO2S Low circuits.
Important: If the voltage is measured with a 10 megaohm digital voltmeter, the voltage may read as low as 0.32 volt. The Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) varies the voltage from approximately 1.0 volt (1000 mV) during rich conditions to 0.10 volt (100 mV) during lean conditions.
When the HO2S temperature measures below 360°C (600°F) the sensor will not produce any voltage. The sensor will behave like an open circuit. This will result in an open loop operation.
The HO2S heater provides for a faster sensor warm-up which allows the sensor to become active in a shorter period of time. The sensor will also remain active during a long extended idle. The DTC P0137 determines if the HO2S or circuit is shorted low by checking for a lean condition during a steady throttle and power enrichment (PE). This DTC is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No TP sensor DTCs |
| • | No EVAP DTCs |
| • | No IAT sensor DTCs |
| • | No MAP sensor DTCs |
| • | No ECT sensor DTCs |
| • | No MAF sensor DTCs |
| • | No intrusive test in progress |
| • | No device controls active |
| • | The system voltage measures at least 9.0 volts. |
Test Enable Lean Test
| • | Closed Loop |
| • | Closed loop low MAP is not active. |
| • | Air to fuel ratio is at least 14.5 but less than 14.8 |
| • | The TP is greater than 5% but less than 99%. |
| • | The above met for 5 seconds. |
| • | The HO2S voltage is less than 0.086 volts (86 mV). |
Test Enable PE Lean Test
| • | A Closed Loop |
| • | The Power Enrichment mode active |
| • | The high speed fuel cutoff not active |
| • | No related HO2S DTCs since code clear |
| • | Time elapse since test enable is at least 1 second |
| • | The HO2S voltage measures less than 0.598 volts (598 mV). |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The VCM turns on the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) after 2 consecutive failures.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Never solder the HO2S wires. For proper wire and connector repair refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis.
Using the scan tool, observe the L.T. fuel trim values at the different RPM and the air flow conditions. The scan tool also displays the fuel trim cells, so the scan tool can check the L.T. fuel trim values in each of the cells in order to determine when the DTC may have set. If the conditions for this DTC exist, the L.T. fuel trim values measure around 158 or greater.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | A sensor pigtail may be mispositioned and contacting the exhaust system. |
| • | An intermittent short to ground in the Signal circuit between the VCM connector and HO2S.. |
| • | A poor VCM ground |
| • | Lean injectors: Refer to Fuel Injector Balance Test . |
| • | Fuel Contamination: Water, even in small amounts, near the in-tank fuel pump inlet can be delivered to the injectors. The water causes a lean exhaust and can also set this DTC. |
| • | Fuel pressure: If the pressure is too low, the system will be lean. In order to confirm, monitor the fuel pressure while driving the vehicle at various speeds and loads. Refer to Fuel System Pressure Test . |
| • | Exhaust leaks: If there is an exhaust leak, the engine may pull the outside air into the exhaust. and past the sensor. |
| • | Vacuum or the Crankcase leaks can cause a lean condition or a possibly a high idle. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Running the engine at 1200 RPM keeps the HO2S temperature hot in order to ensure the HO2S remains active. Running the engine at 1200 RPM can indicate the exhaust oxygen content accurately.
-
Opening the HO2S circuit should result in a displayed voltage between 350 and 550 mV. If the display is still fixed below the 350 mV, the fault is a short to a ground in the HO2S high signal circuit or a faulty VCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records for reference. This data will be lost when the clear DTC Information function is used. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool data display indicate a HO2S voltage fixed less than the specified value? | 1200 RPM 0.086 V (86 mV) | |||
Does the scan tool data display indicate a HO2S voltage that is within the specified range? | 0.35-0.55 V (350-550 mV) | |||
4 | The DTC is intermittent. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
5 | Check for a short to ground in the HO2S signal circuit. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
6 | Repair the circuit as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Refer to the Diagnostic Aids. Was a problem found and repaired? | -- | ||
8 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Replace the VCM. Important: When replacing the VCM, the new VCM will need to be programmed. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||
11 | Use the scan tool in order to display the Capture Info and the Review Capture Info functions. Are there any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
