A first order tire and wheel vibration is usually the result
of one of the following five conditions:
| • | Excessive radial runout |
| • | Excessive lateral runout |
| • | Excessive radial force variation |
| • | Excessive lateral force variation |
These conditions must be eliminated one at a time in order to attain
a set of tires that are free from vibration causing elements. Substitute a
set of tires from another vehicle only as a last resort, and only after the
tires have been tested on a similar vehicle under the same conditions. Correcting
the existing tire and wheel assemblies is the most accurate and least time
consuming approach. This is due to vehicle-to-vehicle sensitivities and the
differences between the hubs of any two vehicles.
Methods of Measuring Tire/Wheel Assembly Runout
The tire and wheel assembly runout will directly affect the amount of
the imbalance and the radial force variation. Therefore, correct the runout
first before further diagnosis. The less runout, the less imbalance and radial
force variation. Radial and lateral runout can be corrected at the same
time. There are two methods for correcting the tire and wheel assembly runout:
| • | The on-vehicle method, with the tire and wheel assembly mounted
on the hub. The wheel bearing must be in good condition. |
| • | The off-vehicle method, with the tire and wheel assembly mounted
on a spin-type tire balancer. |
Perform the following initial on-vehicle inspections prior to the off-vehicle
runout checks:
- Inspect the tires for any uneven bead seatings. The distance
from the edge of the ring to the concentric rim locating ring should be equal
around the entire circumference.
- Properly mount the tires if the beads are not seated properly
in order to avoid excessive runout and imbalance.
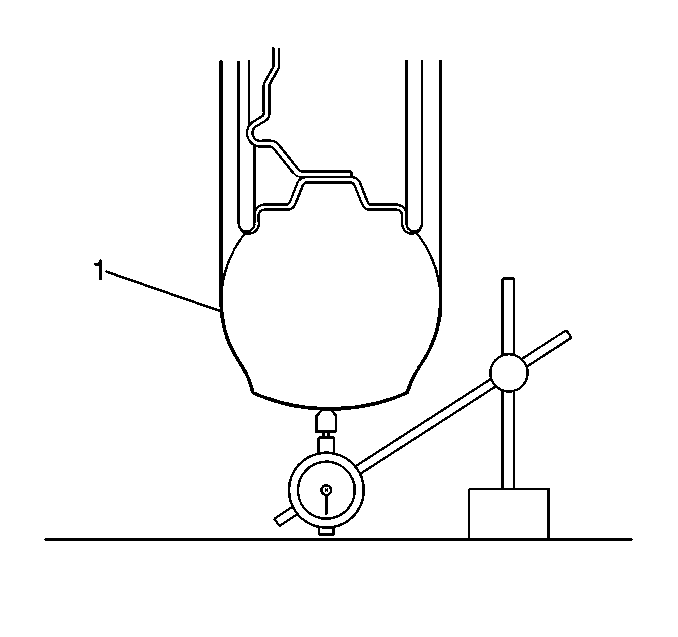
The off-vehicle method
is the easiest way of measuring the tire and wheel runout. Properly mounting
the dial indicator in the correct location in relation to the tire (1) is
easier. The dial indicator is less likely to be subjected to water, snow,
dirt, or other elements. After measuring the correct runout off-vehicle,
inspect the runout with the tire and wheel assembly mounted on the vehicle.
The runout measurement may vary greatly between these two methods. If so,
the runout is due to one of the following conditions:
| • | A mounting problem between the wheel and the vehicle |
Measuring Tire/Wheel Assembly Runout
If the vehicle has been sitting in one place for an extended period
of time, the tires may develop flat spots at the point where the tires were
resting on the ground. These flat spots will affect the runout readings.
In order to eliminate these flat spots, drive the vehicle long enough to
warm up the tires. The flat spots must be eliminated prior to taking any
runout measurements.
Measurement Procedure
- Raise and suitably support the vehicle. Refer to
Lifting and Jacking the Vehicle
in General Information.
- Obtain an initial indication of how much runout exists:
| 2.1. | Spin each tire and wheel assembly on the vehicle by hand (or at
a slow speed using the engine to run the drive wheels). |
| 2.2. | Visually inspect the amount of runout from the front or rear of
the tire. |
- Matchmark each of the tire and wheel assemblies in relation to
the wheel studs and to their position on the vehicle (LF, LR, RF, RR) for
future reference.
- Remove the tire and wheel assemblies one at a time and mount on
a spin-type wheel balancer. Refer to
Wheel Removal
in Tires and Wheels.
Locate the tire and wheel assembly on the balancer with a cone through
the back side of the center pilot hole.
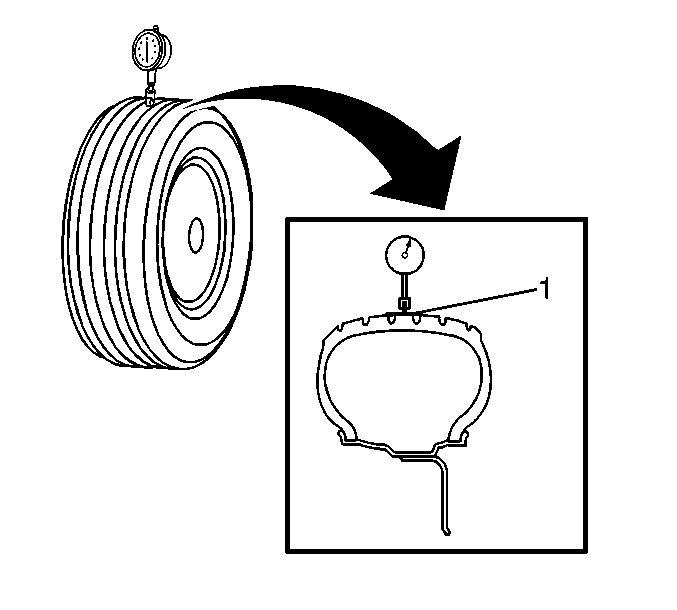
- Wrap the outer circumference
of tires that use an all-season or aggressive tread pattern with tape (1),
in order to accurately measure the radial runout.
- Measure the tire and wheel assembly radial runout.
| 6.1. | Slowly rotate the tire and wheel assembly one complete revolution
and ZERO the dial indicator on the low spot. |
| 6.2. | Rotate the assembly one more complete revolution and note the
total amount of runout indicated. |
Maximum Radial Runout
| • | Measured off-vehicle: 1.27 mm (0.050 in) |
| • | Measured on-vehicle: 1.52 mm (0.060 in) |
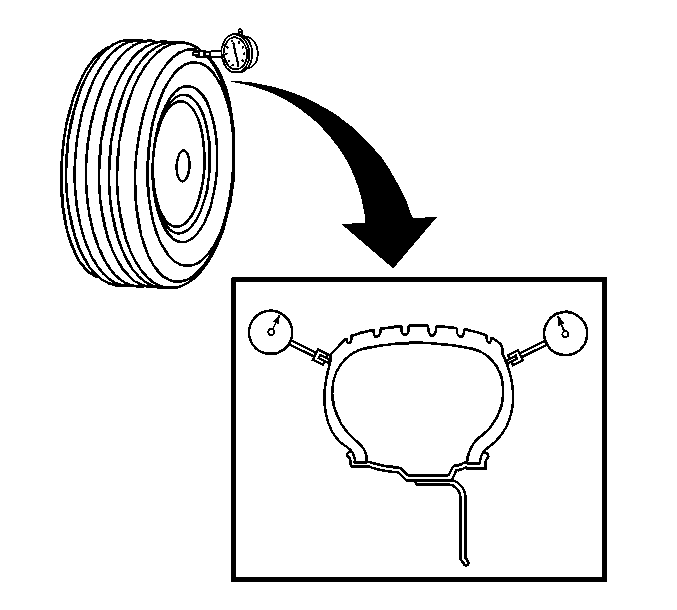
- Measure the tire and wheel
assembly lateral runout.
Lateral runout should be measured on a smooth area of the sidewall as
close to the tread as possible. Ignore any jumps or dips due to sidewall splices
and attain an average amount of runout.
| 7.1. | Slowly rotate the tire and wheel assembly one complete revolution
and ZERO the dial indicator on the low spot. |
| 7.2. | Rotate the assembly one more complete revolution and note the
total amount of runout indicated. |
Maximum Lateral Runout
| • | Measured off-vehicle: 1.27 mm (0.050 in) |
| • | Measured on-vehicle: 1.52 mm (0.060 in) |
- Make the necessary repairs to the tire and wheel assembly.
- Install the tire and wheel assembly to the vehicle. Refer to
Wheel Installation
in Tires and
Wheels.
- Repeat the procedure until all the wheel runouts have been measured.
- Lower the vehicle.
Measuring Wheel Runout
If tire and wheel assembly runout cannot be brought within tolerance,
measure the wheel runout.
If any runout measurement of a wheel exceeds specifications, the wheel
should be replaced. (ALWAYS measure the runout of a new wheel.)
If the runout of the wheel is within tolerance, and the tire and wheel
assembly runout cannot be reduced to an acceptable level, the tire should
be replaced. (ALWAYS measure the tire and wheel assembly runout after replacing
the tire.)
Measurement Procedure
- Raise and suitably support the vehicle. Refer to
Lifting and Jacking the Vehicle
in General Information.
- Matchmark each of the tire and wheel assemblies in relation to
the wheel studs and to their position on the vehicle (LF, LR, RF, RR) for
future reference.
- Remove the tire and wheel assemblies one at a time and mount on
a spin-type wheel balancer. Refer to
Wheel Removal
in Tires and Wheels.
Locate the tire and wheel assembly on the balancer with a cone through
the back side of the center pilot hole.
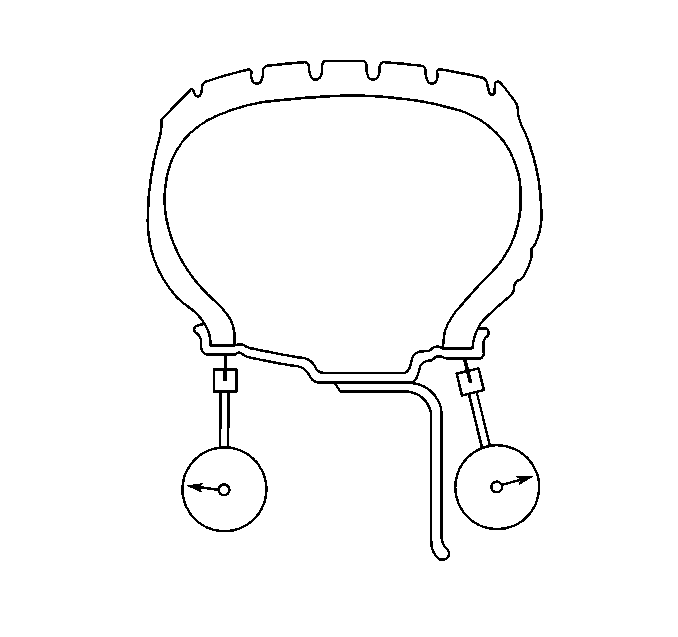
- Measure the wheel radial
runout on the outside of the wheel (with the tire mounted), if the wheel design
allows.
Wheel runout should be measured on both the inboard and outboard rim
flanges. Ignore any jumps or dips due to paint drips, chips, or welds.
| 4.1. | Slowly rotate the tire and wheel assembly one complete revolution
and ZERO the dial indicator on the low spot. |
| 4.2. | Rotate the assembly one more complete revolution and note the
total amount of runout indicated. |
Maximum Radial Runout
| • | Steel Wheel -- 1.015 mm (0.040 in) |
| • | Aluminum Wheel -- 0.762 mm (0.030 in) |
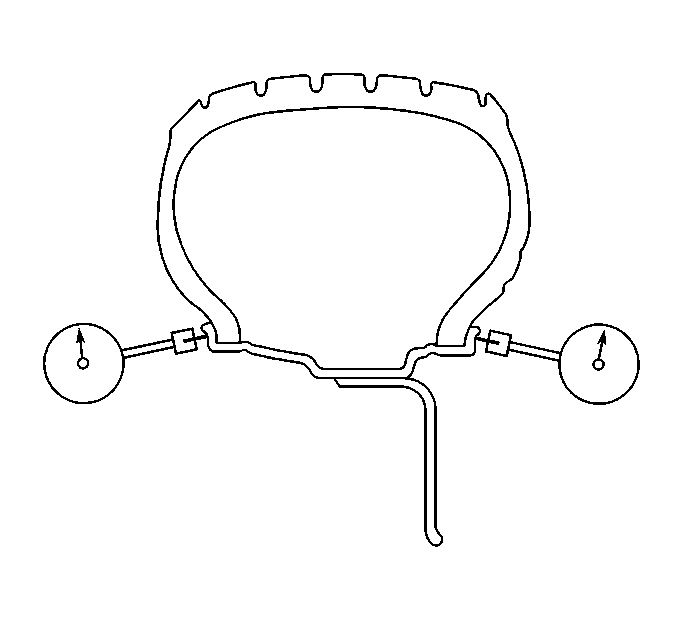
- Measure the wheel lateral
runout on the outside of the wheel (with the tire mounted), if the wheel design
allows.
Wheel runout should be measured on both the inboard and outboard rim
flanges. Ignore any jumps or dips due to paint drips, chips, or welds.
| 5.1. | Slowly rotate the tire and wheel assembly one complete revolution
and ZERO the dial indicator on the low spot. |
| 5.2. | Rotate the assembly one more complete revolution and note the
total amount of runout indicated. |
Maximum Lateral Runout
| • | Steel Wheel -- 1.143 mm (0.045 in) |
| • | Aluminum Wheel -- 0.762 mm (0.030 in) |
- If the wheel design does not allow runout measurements to be made
with the tire mounted, dismount the tire from the wheel. Refer to
Tire Mounting and Dismounting
in Tires and Wheels.
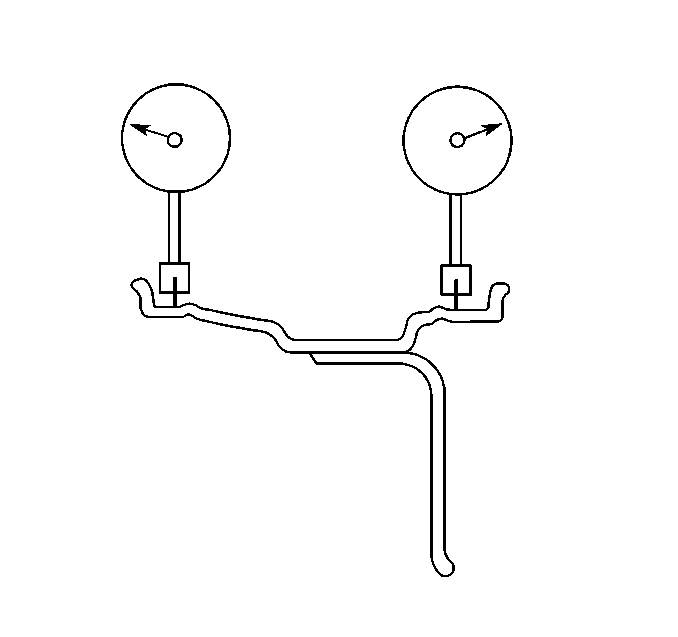
- Measure the wheel radial
runout on the inside of the wheel.
Wheel runout should be measured on both the inboard and outboard rim
flanges. Ignore any jumps or dips due to paint drips, chips, or welds.
| 7.1. | Slowly rotate the wheel one complete revolution and ZERO the dial
indicator on the low spot. |
| 7.2. | Rotate the wheel one more complete revolution and note the total
amount of runout indicated. |
Maximum Radial Runout
| • | Steel Wheel -- 1.015 mm (0.040 in) |
| • | Aluminum Wheel -- 0.762 mm (0.030 in) |
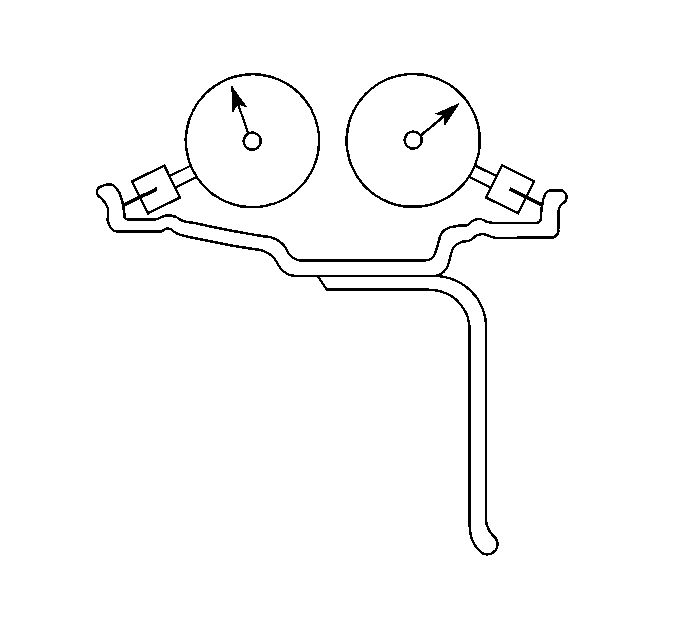
- Measure the wheel lateral
runout on the inside of the wheel.
Wheel runout should be measured on both the inboard and outboard rim
flanges. Ignore any jumps or dips due to paint drips, chips, or welds.
| 8.1. | Slowly rotate the wheel one complete revolution and ZERO the dial
indicator on the low spot. |
| 8.2. | Rotate the wheel one more complete revolution and note the total
amount of runout indicated. |
Maximum Lateral Runout
| • | Steel Wheel -- 1.143 mm (0.045 in) |
| • | Aluminum Wheel -- 0.762 mm (0.030 in) |
- Make the necessary repairs to the tire and wheel assembly.
- Install the tire and wheel assembly to the vehicle. Refer to
Wheel Installation
in Tires and
Wheels.
- Repeat the procedure until all the wheel runouts have been measured.
- Lower the vehicle.
Vectoring
Vectoring is a technique used to reduce radial or lateral runout --
and to even dynamic balance on the tire and wheel assemblies. Vectoring can
be accomplished by the positioning of the tire on the wheel and the positioning
of the tire and wheel assembly on the hub/rotor.
Tire To Wheel Vectoring (Excessive Wheel Runout)
Do the following to reduce radial/lateral runout (wheel is major contributor):
Important: Always rebalance the tire and wheel assembly after vectoring.
- Determine visually which runout needs to be minimized.
- If the radial runout is the problem, take a measurement on the
center tread rib.
- If the tread is uneven, wrap tape tightly around the tire, record
the runout magnitude, and mark the high spot location (4).
- If the lateral runout is the problem, take a measurement on the
sidewall just below the edge of the tread shoulder.
- Record the runout magnitude and mark the high spot location (4).
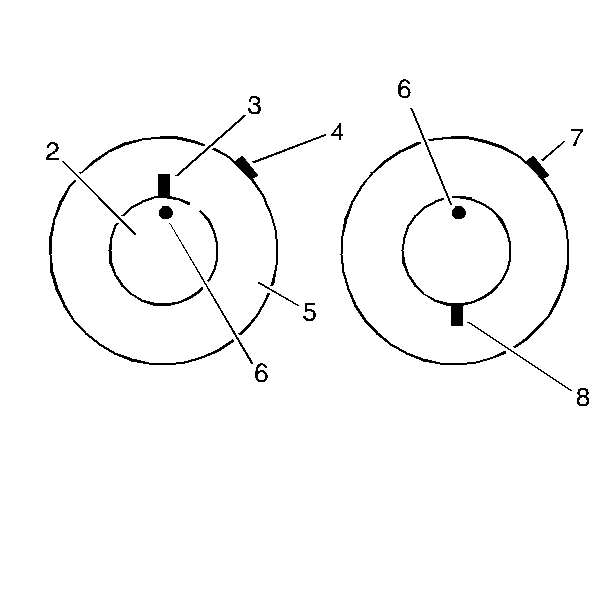
- Mark the tire sidewall at the valve location (3).
| • | This is the 12 o'clock position (6). |
| • | The location of the high spot is always with respect to the clock
location on the wheel. |
- Break the tire and wheel assembly down on a tire mounting machine
and rotate the tire 6 hours (180 degrees) on the rim (8).
| • | Reinflate the tire and measure the runout in question. |
| • | Record the magnitude and location of the high spot (valve stem
is 12 o'clock) (7). |
- If the clock location of the high spot remained at or near the
clock location of the original high spot, the rim is the major contributor
to the runout problem (4, 7).
| • | Confirm by removing the tire from the wheel and check the wheel
rim runout. |
| • | If the wheel rim runout exceeds specification, replace the wheel. |
Tire To Wheel Vectoring (Excessive Tire Runout)
Do the following to reduce radial/lateral runout (tire is major contributor):
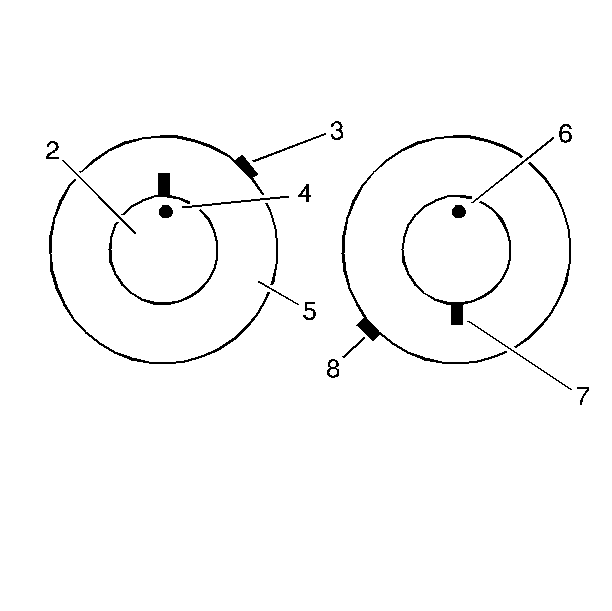
Important: Always rebalance the tire and wheel assembly after vectoring.
- Determine visually which runout needs to be minimized.
- If the radial runout is the problem, take a measurement on the
center tread rib.
- If the tread is uneven, wrap tape tightly around the tire, record
the runout magnitude, and mark the high spot location (3).
- If the lateral runout is the problem, take a measurement on the
sidewall just below the edge of the tread shoulder.
- Record the runout magnitude and mark the high spot location (3).
- Mark the tire sidewall at the valve location.
| • | This is the 12 o'clock position (4, 6). |
| • | The location of the high spot is always with respect to the clock
location on the wheel. |
- Break the tire and wheel assembly down on a tire mounting machine
and rotate the tire 6 hours (180 degrees) on the rim (7).
| • | Reinflate the tire and measure the runout in question. |
| • | Record the magnitude and location of the high spot (valve stem
is 12 o'clock) (7). |
- If the clock position of the high spot is 6 hours from the original
high spot, the tire is the major contributor of the runout problem. Replace
the tire (3, 8).
- After correcting the tire to wheel vectoring, rebalance the tire
and wheel assembly.
Tire And Wheel Assembly To Hub/Rotor Vectoring
This compensates for any imbalance in the brake rotor, drum, or wheel
cover. Do the following to reduce radial/lateral runout:
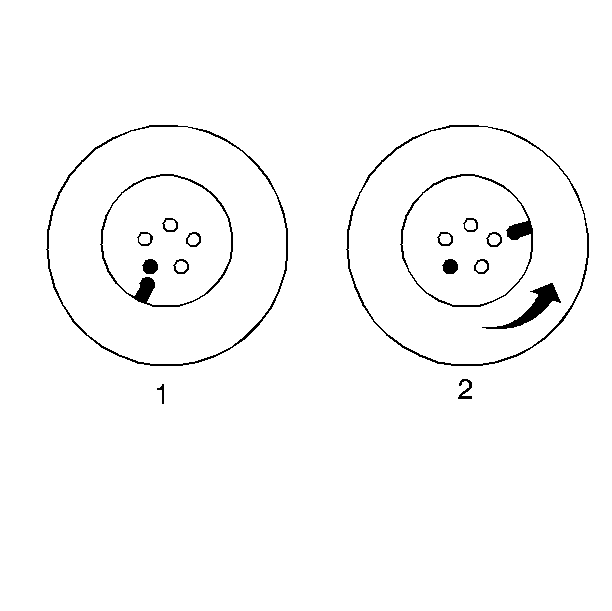
- Mark the wheel hub bolt
nearest to the valve stem for reference (1).
- Rotate the assembly two wheel hub bolts and recheck the runout
(2).
| • | Several positions may have to be tried to locate the optimum position. |
| • | This can be effective for both radial and lateral runout. |
- If there is some looseness in the wheel hub bolt holes, radial
runout can be reduced by loosening the hub bolt nuts slightly, moving the
wheel position on the bolts and then retightening the nuts.
- Balance the tire and wheel to the hub/rotor assembly.










